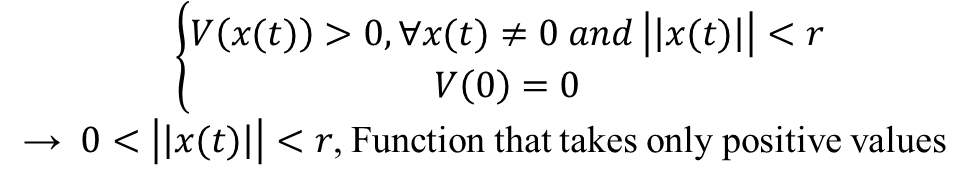
2024.01.24
Positive Definite Matrix
: a symmetric matrix M with real entries is positive-definite if the real number (z^T)Mz is positive for every nonzero real column vector z, where (z^T) is the transpose of z.
→ (z^T)Mz (Quadratic form)이 양수의 scalar값이 되어야 positive definite matrix라고 할 수 있다.
❓ 왜 scalar값이 될까?
: z는 column vector이기에 nx1 matrix 이다. 따라서 연산을 하면 (1xn)x(nxn)x(nx1) = 1x1 scalar 값만 추출된다. 이때의 scalar 값이 definiteness를 판단하는 지표가 될 수 있다. 이 scalar값이 양수이면 이 matrix는 positive definite matrix가 된다.
✔ Conditions for the positive definite matrix
1. All eigen values are positive.
2. All subdeterminants are also positive. (1x1,2x2, ..., nxn matrix)
3. All pivots are positive.
4. Quadratic form is positive.
→ the four conditions are equivalent.
∴ if one holds, the remaining three also hold.
∴ A matrix가 대칭행렬이고, 모든 eigen values가 양수일 때, 이는 positive definite하다고 이야기 할 수 있음.
Lyapunov Stability Thoery
: determination of stability without explicitly computing the solutions of the system
→ Lyapunov direct method (Applicable to time-variant & time-invariant)
❓ Based on what?
Positive definite function → 𝑽(𝒙(𝒕))
Positive definite function is defined as a scalar function that satisfies the following two conditions
Lyapunov Stability
𝑥 ̇=𝑓(𝑥), there exist 𝑽(𝒙) and 𝒓>𝟎 satisfying the following equation, the equilibrium state 0 of this system is stable
-
𝑽 ̇(𝒙)≤𝟎, |(|𝒙|)|<𝒓 (𝑉(𝑥) : Lyapunov Function) – Lyapunov stable
: time derivative of the Lyapunov function should be negative semi-definite. -
𝑽 ̇(𝒙)<𝟎, 𝒙≠𝟎 𝒂𝒏𝒅 |(|𝒙|)|<𝒓
→ If the time derivative is negative definite, we call “asymptotically stable”
Lyapunov Stability Theory Detail
Let’s define V(x(t)) = 𝑥(𝑡)^𝑇 𝑃𝑥(𝑡) (Quadratic form)
Due to the conditions for Lyapunov function,
V(x(t)) = 𝑥(𝑡)^𝑇 𝑃𝑥(𝑡) > 0
→ P must be positive definite (means symmetric and all eigen values are positive.)
Also due to the condition for Lyapunov stability,
𝑉 ̇(𝑥(𝑡))=𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑡 𝑉(𝑥(𝑡))=𝑥^𝑇 (𝑃𝐴+𝐴^𝑇 𝑃)𝑥< 0
→ (𝑃𝐴+𝐴^𝑇 𝑃) should be negative definite.
✔ So, we need to find P which is positive definite and 𝑃𝐴+𝐴^𝑇 𝑃 is negative definite. Lyapunov Equation 𝑃𝐴+𝐴^𝑇 𝑃 = -Q and Q is positive definite
MATLAB SIMULATION (LMI SYS)
Lyapunov function simulation
Setlmis([]);
X = lmivar(type, struct);
Lmiterm([termID, A,B,flag];
[tmin, xfeas] = feasp(lmisys, options, target);
(1) A= [0 1; -2 -3] 일때 2x2 matrix P 찾기
%Lypunov stability and LMI Slover
close all
clear
clc
A=[0 1; -2 -3];
setlmis([]);
% define size and structure of P
% type1 -> square and symmetrical structure
P = lmivar(1,[size(A,1) 1]);
% Conditions for Stability: P > 0, PA + A'P <0
% [PA + A'P 0; 0 -p] < 0
% flag 's' means add transpose form
lmiterm([1 1 1 P],1, A, 's'); % PA+A'P
lmiterm([1 1 1 0],1); % 0
lmiterm([1 2 2 P],-1,1); % -P
LMISYS = getlmis;
[tmin,Psol] = feasp(LMISYS); % Solution that maches best for LMI : Psol
P=dec2mat(LMISYS,Psol,P) % derive corresponding values of matrix variable이때 결과는 아래와 같다.
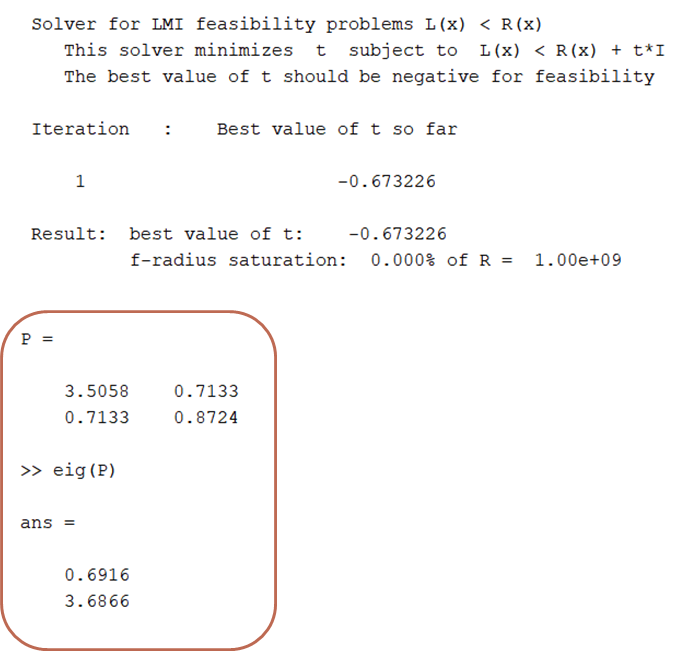
› all eigen values are positive.
∴ We found a positive definite matrix !
(2) A= [0 1 0; 0 0 1; -1 -5 -6] 일때 3x3 matrix P 찾기
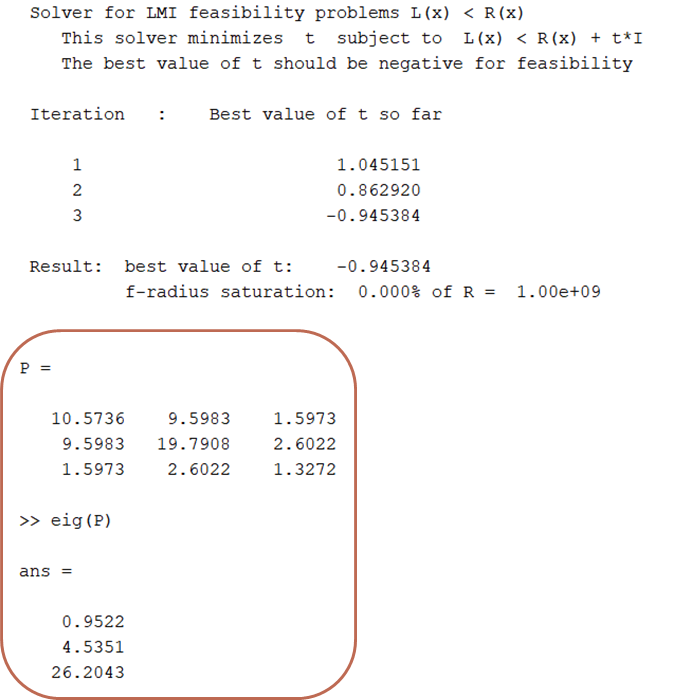
› all eigen values are positive.
∴ We found a positive definite matrix !
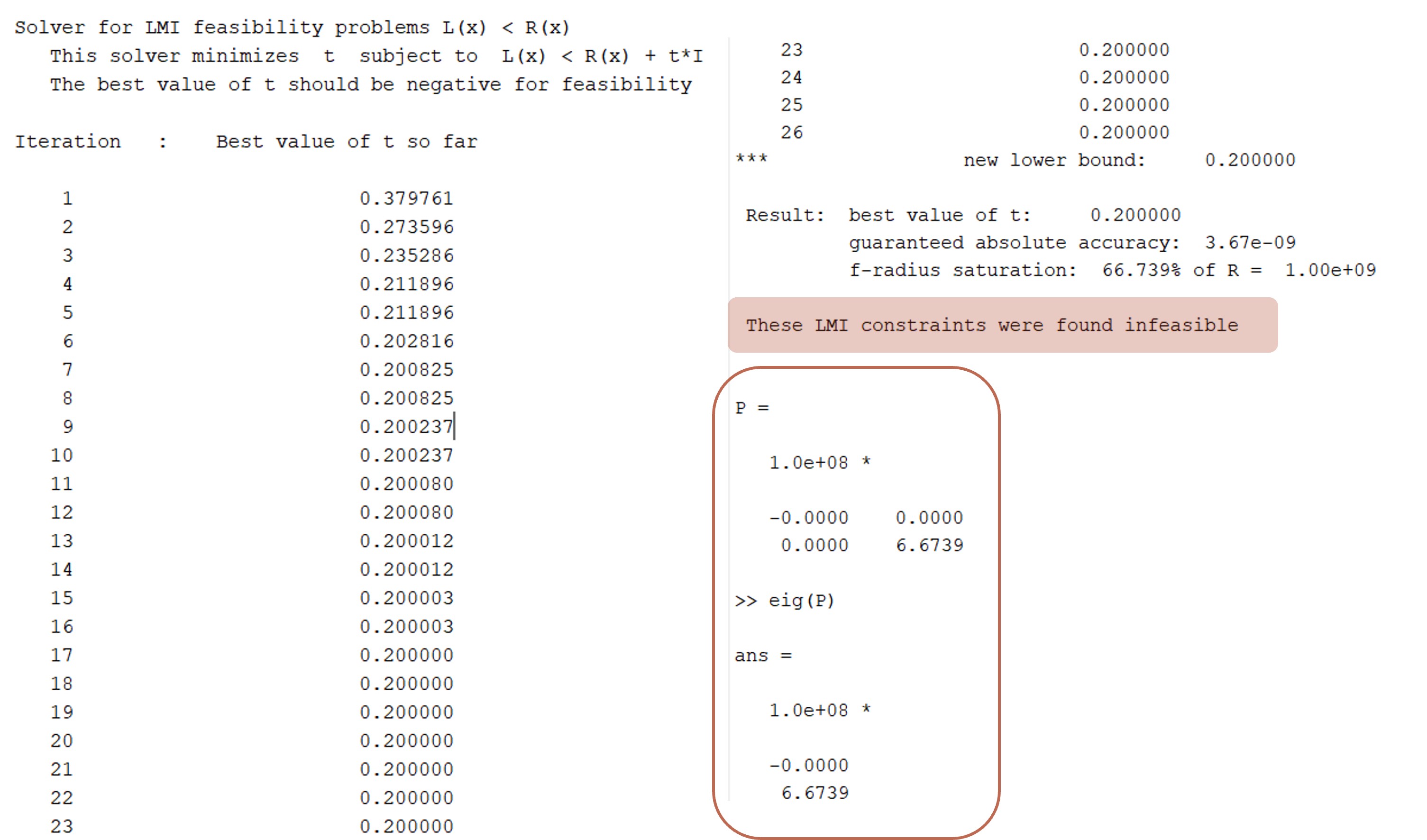
(3) When A = [2 1; 0 -1] (unstable sys)
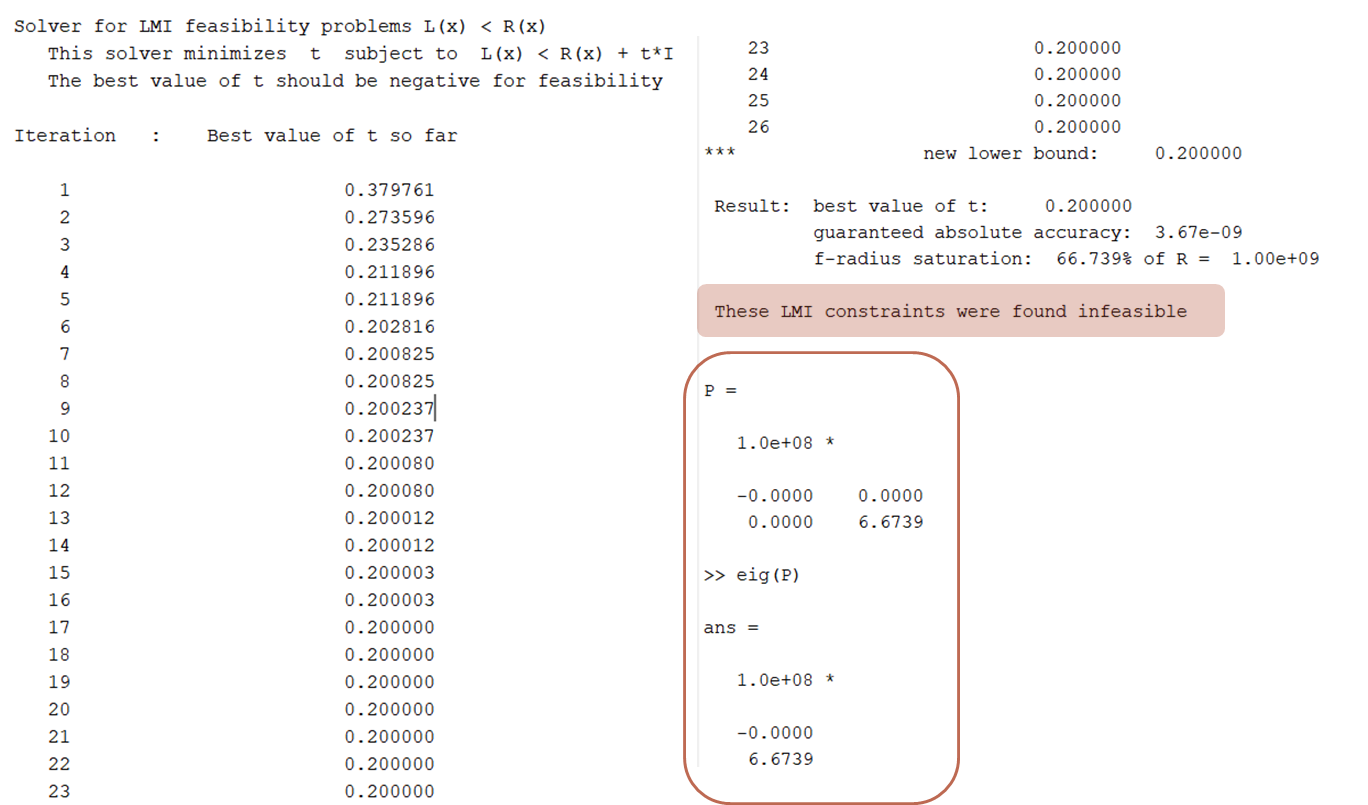
› there's one negative eigen value.
∴ We cannot find a positive definite matrix ✖ !