Sound-Guided Semantic Image Manipulation
0. Abstract
최근 generative model관련 연구의 성공은 multi-modal embedding space를 사용하여 text 정보를 바탕으로 image를 manipulate할 수 있음을 보여주었지만, 다른 Source를 사용한 manipulation은 쉽지 않은 작업이다. 특히 Sound의 경우 text로 전달하지 못하는 생생한 표현을 전달할 수 있다.
본 논문에서는 Sound를 multimodal(image-text) embedding space로 encoding하여 image를 manipulate하는 framework를 제시한다.
1. Introduction
Sementic image manipulation의 목적은 source image의 identity를 포함하고 동시에 user의 의도에 부합하는 sementic 정보를 포함하는 새로운 이미지를 생성하는 것이다. 기존의 manipulation방식은 sketch나 text를 원본 Image와 mix하는 방식으로 진행되었다. 특히 Text-based manipulation의 경우 image를 조건에 맞게 변경할 수 있는 장점을 가지고 있지만, sound와는 달리 연속적이고 dynamic한 특성을 표현하지 못하는 text가 가지고 있는 태생적인 표현의 한계를 가지고 있다.
몇개의 연구들이 sound의 의미를 시각화하는 시도를 하였지만 두가지 이유로 sound를 높은 해상도의 image로 반영하는 것을 실패했다.
- High-resolution audio-vidual pair dataset의 부재.
- Auditory modality와 Visual modality간 상관관계를 분석하는 것이 어려움.
Sound semantic으로 image를 조작하는 것의 어려움을 극복하기 위해 본 논문에서 제시하는 모델은 두 개의 stage를 제시한다.
- CLIP기반 Multi-Modal Representation Learning.
Pre-trained CLIP model의 representation power를 사용하여 text와 visual적으로 일치하는 latent representation을 생성하는 Audio encoder를 훈련시킨다. - Sound-Guided Image Manipulation.
User로부터 받아온 sound를 반영하는 의미있는 image를 생산하기 위해 direct latent code optimization을 사용한다.
본 논문에서 제시하는 sound-based 접근은 Scene과 관련된 더 다양하고 세부적인 정보를 image에 투영할 수 있도록 한다.
2. Related Work
Text-guided Image Manipulation
StyleCLIP과 TediGAN은 pre-trained된 StyleGAN과 CLIP을 사용하여 latent space를 사용, text기반 image manipulation을 수행한다. StyleCLIP의 경우 user가 제공하는 text prompt를 바탕으로 manipulation을 수행하고, TediGAN의 경우 multi-modal mapping을 통한 GAN inversion기술을 사용하여 image 생성과 조작을 수행한다.
Sound-guided Image Manipulation
Sound는 image manipulation에 사용될 수 있는 scene의 일시적이고 역동적인 정보를 담고있다. 기존의 sound-guided image manipulation은 sound의 semantic에 집중하기 보다는 음악에 치중하였고, 이는 생성모델로 사용된 StyleGAN에서 latent space의 direction에 영향을 미쳤다 (TräumerAI).
본 논문에서 제시되는 method는 source image의 수정되는 부분을 독립시킬 수 있다.
Interpreting Latent Space in StyleGAN
Pre-trained된 StyleGAN의 확장된 latent space 를 사용하여 image manipulation을 가능하게 한다.
Audio-reactive StyleGAN의 경우 audio 신호의 시간별 magnitude를 계산하여 StyleGAN의 latent space에 이동시킨다. 하지만 StyleGAM의 latent space에서의 motion이 오직 sound의 magnitude끼리만 mapping되고, latent space에서 sound의 의미론적 조작이 불가능 하다는 단점이 있다. 본 논문에서는 sound의 특성을 사용하여 image를 조작한다.
Audio-visual Representation Learning
Audio-visual representation learning 연구의 목적은 두 modality를 같은 embedding space에 mapping 시키는 것이다. modality간 상관도는 audio-visual pair를 통한 contrastive learning을 통해 학습된다.
하지만 Audio-visual representation learning은 CLIP과 같은 대용량의 text-visual pair dataset의 부재로 여전히 힘든 task이다. 본 논문에서의 audio encoder는 CLIP의 고성능의 representation ability를 사용하는 것 뿐만 아니라, self-supervised 방식으로 audio data 자체를 학습한다. 그 결과 image manipulation을 위한 audio-specific representation을 얻을 수 있었다.
3. Method
StyleCLIP과 비슷하게 본 논문에서도 StyleGAN의 latent code를 조작하여 image manipulation을 수행하지만, CLIP의 embedding space에 audio embedding을 추가했다는 점이 차별점이다.
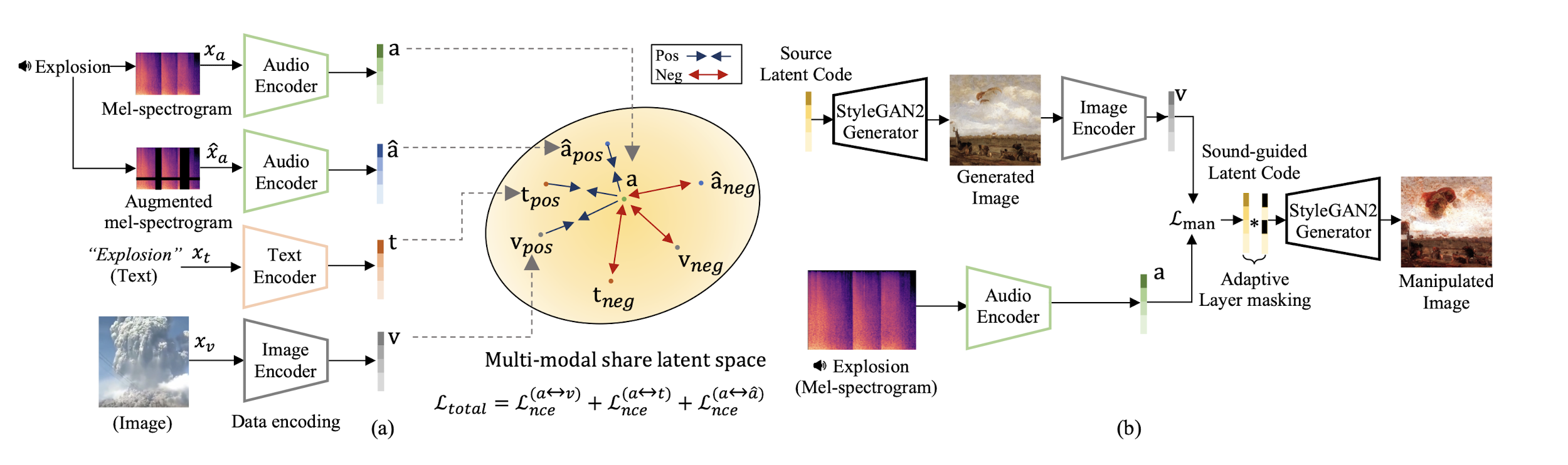
위 그림은 model이 수행하는 두 가지 step을 보여준다.
(a): 먼저 audio, text, image encoder가 새로운 latent representation을 생성하도록 훈련한다. 그렇게 하기 위해서 audio encoder를 InfoNCE loss를 사용하여 pre-trained된 CLIP의 text, image encoder에서 생성하는 representation과 정렬된 latent representation을 생성하도록 한다.
Multi-modal latent space에서 positive triplet pair는 가깝게 mapping되고, negative pair는 멀게 mapping된다.
(b): Source latent code가 user가 제공하는 audio에 따라 수정될 수 있도록 direct code optimization approach를 사용하여 sound-guided image manipulation image를 생성한다.
Multi-modal Latent Representation Learning
먼저 encoder set을 embedding space에서 matched representation을 생성할 수 있도록 세개의 서로 다른 modality {audio, text, image}로 학습시킨다. 주어진 audio, text, image input에 대해 {} 서로 다른 encoder를 사용하여 d dimensional latent representation들을 만들어 낸다 {}.
각각의 a, t, v를 contrastive learning 개념을 사용하여 positive triplet pair는 embedding space에서 가깝게 mapping되고, negative pair는 멀게 mapping된다.
하지만 positive와negative pair set을 제공하는 multi-modal dataset의 부족으로 이러한 joint representation을 학습하는 것은 매우 어려운 task이기 때문에, pre-trained CLIP을 사용하여 optimized된 visual-texual joint representation에 align된 representation을 생성할 수 있도록 audio encoder를 훈련시킨다.
latent represenation 중 는 augmented audio input인 에서 얻어진 것으로, latent representation의 질을 올리는데 유용하다.
Matching Multi-modal Representations via Contrastive Loss
CLIP-based joint embedding space에서 positive audio-text pair를 mapping하고 negative한 pair는 멀리 보내기 위해, InfoNCE loss를 사용한다.
N개의 {}가 있을 때 (for ) i번째 pair에 대해 audio-to-text loss function은 아래와 같다.
<>는 representation의 cosine유사도이고, 는 temperature parameter이다. 위 loss func는
{}를 true representation pair로 예측하고 싶은 N-way classifier이다.
loss function이 asymmetric하기 때문에 text-to-audio loss도 유사하게 정의했다.
최종적으로 , 를 와 의 합으로 정의하여 이를 최소화 하고, N개의 모든 positive audio-text representation pair를 mapping한다.
Applying Self-supervised Representation Learning for Audio Inputs
Self-supervised learning은 같은 class에 있는 다른 modality의 representation을 embedding space에서 가깝게 위치하도록, 다른 class에 대해서는 멀게 위치하도록 contrastive loss를 사용한다.
audio representations의 품질을 올리기 위해 contrastive loss approach를 차용하였다.
과 는 위에서 구했던 audio-to-text ↔ text-to-audio pair간 loss를 구하는 방식과 같은 방식으로 구할 수 있다. 위 loss function은 같은 input ()에 대한 상호 연관성은 높이고, 다른 input ()에 대한 상호 연관성은 줄여서 embedding 공간에 diffusive한 영향을 준다.
Data Augmentation
audio-text multimodal dataset의 부재와 representations의 질을 높이기 위해 data augmentation을 수행한다. Audio input에는 SpecAugment (frequency mask ratio=0.15, time masking ratio=0.3) **기법을 적용하고, text input에는 동의어 대체, 랜덤한 단어 순서 변경, 랜덤한 단어 삽입** 을 적용했다.
Loss Function
요약하자면 optimization을 수행할 loss function은 아래와 같이 정의된다.
결국 embedding space에서 audio와 visual, audio와 text, audio와 augmented audio 각각의 positive pair는 mapping하고, negative pair는 멀리 보내는 방식으로 optimization이 수행된다.
Sound-guided Image Manipulation
Multi-modal joint embedding space를 위에서 정의한 을 줄이는 방식으로 학습한 후, direc latent code optimization method를 사용하여 image를 최종적으로 manipulate한다. 추가로 Adaptive Layer Masking 기법을 사용하여 adaptively하게 latent code를 조정할 수 있도록 한다.
Direct Latent Code Optimization
아래 수식을 optimize하는 방식으로 direct latent code optmization을 구현하였다.
- source latent code:
- audio-driven latent code:
위 두 vector는 style layer의 특정 layer를 mask할 수 있는 훈련 가능한 vector이다.
StyleCLIP에서의 latent optimization과 유사하게 과 를 조절하여 source와의 유사도를 조정한다. 위 두 값이 높을 수록 Generator 는 source와의 유사도를 높게 유지한다.
그리고 latent code인 로부터 생성된 이미지 와 audio representative a 간의 cosine 유사도를 최소화 하여 optimization을 진행한다.
input image와의 유사도는 indentity loss function인 로 조절될 수 있다.
위 identity function 역시 StyleCLIP에서의 latent optimization에서의 identity function과 구조가 동일하다. source latent로 부터 생성된 이미지와 audio latent로 부터 생성된 이미지를 각각 ArcFace network에 입력한 값 간의 cosine 유사도를 최소화 함으로서 personal identity를 변경하지 않고 facial expression을 변경할 수 있도록 한다. 인 경우 위 identity loss를 비활성화 할 수 있다.
Adaptive Layer Masking
Adaptive layer masking을 통해 style change를 조절한다. StyleGAN의 latent code는 각 layer마다 다른 특성을 가지고 있기 때문에, layerwise masking을 사용하여 style latent code에 대한 특성을 유지한다.
Sound and Text Multi-modal Style Mixing
Audio와 text가 같은 multi-modal embedding space를 공유하기 때문에, audio와 text의 각 latent code의 특정 layer를 고름으로서 audio와 text의 특성을 사용한 image manipulation을 수행할 수 있다.
4. Experiments
Image와 text encoder로 pre-trained CLIP을 사용하였고, audio encode의 backbone으로 ResNet50을 사용하였다. ouput dim은 모두 512로 통일하였다. cosine cyclic learning rate scheduler를 SGD(lr=, momentum=0.9, weight decay=)에 적용하여 50 epoch으로 모델을 훈련하였다.
Qualitative Analysis
- Sound-guided Image Manipulation 측면에서 TräumerAI와 Crossing you in Style 모델과 비교를 진행하였고, 제안된 모델이 더 퀄리티 좋은 manipulated image를 생성하는 것을 확인하였다.
- Text-guided Image Manipulation 측면에서 TediGAN과 StyleCLIP 모델과 제안된 모델 간의 비교를 진행하였고, 제안된 모델이 text-guided 모델들 보다 더 많은 label들을 manipulated image에 반영하는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
- Multi-modal Image Manipulation 측면에서 논문에서 제안된 모델은 audio, text, image가 같은 embedding space를 공유하기 때문에, user로부터 제공되는 text와 audio input을 바탕으로 같은 embedding space에서 image를 manipulate 할 수 있다.
- Effect of Adaptive Layer Masking: StyleGAN의 특성 상 각 layer의 latent code가 다른 style attribute를 가지고 있기 때문에, 각각 style layer를 regularize해주는 것은 필수적이다. Adaptive masking은 semantic cue에 기반하여 latent code를 변경하고 그 결과로 direction을 변경해준다.
Quantitative Evaluation
- Zero-shot Transfer: 제안된 모델과 다른 zero-shot audio classification method를 비교하였다. ResNet50, Wav2clip, AudioCLIP과 비교했을 때 AudioCLIP은 zero-shot task에서 더 좋은 성능을 보였지만 다른 audio encoder를 사용하였고, 대용량의 데이터셋에 training되었다는 점에서 절대적인 비교가 힘들다. 또한 제안된 모델은 CLIP embedding 공간에서 3개의 modality를 배우고 더 풍부한 audio representation을 획득한다.
- Semantic Accuracy of Manipulation: FFGQ로 부터 학습된 StyleGAN weight와 LSUN로부터 학습된 weight를 사용하여 semantic classification을 수행했을 때 기존 text-driven manipulation method들 보다 더 좋은 성능을 보였다.
- Distribution of Manipulation Direction: StyleGAN2의 latent space에서 sound-guided latent code가 text-guided latent code보다 source latent code에서 더 많이 이동하는 것을 확인할 수 있었고 이것은 더 다양하고 dramatic한 manipulation을 이끈다는 것을 알 수 있다.
5. Applications
Sound-Guided Artistic Painting Manipulation
WikiArt로 pre-trained된 StyleGAN2 Generator를 사용하여 artistic painting에 manipulation을 적용할 수 있다.
Music Style Transfer: 제안된 모델은 음악의 분위기 또한 image style에 반영할 수 있다.
6. Limitation
주된 limitation은 pre-trained StyleGAN domain에 포함되어 있지 않은 sound로 manipulation을 진행할 때 색과 명암이 변한다는 문제점이다. 또한 더 많은 sound type이 필요하다.
