📦 Lab: CNN on CIFAR 100 data
# Read the CIFAR100 data, which is available in the torchvision package
(cifar_train, cifar_test) = [
CIFAR100(root="data", train=train, download=True)
for train in [True, False]
]
transform = ToTensor()
cifar_train_X = torch.stack([transform(x) for x in cifar_train.data])
cifar_test_X = torch.stack([transform(x) for x in cifar_test.data])
cifar_train = TensorDataset(cifar_train_X, torch.tensor(cifar_train.targets))
cifar_test = TensorDataset(cifar_test_X, torch.tensor(cifar_test.targets))
print(cifar_train_X.shape) # torch.Size([50000, 3, 32, 32])
The CIFAR100 dataset consists of:
- 50,000 training images and 10,000 test images
- Each image is represented as a 3D tensor of shape
(3, 32, 32), where:3is the number of color channels (RGB)32 x 32is the height and width in pixels
즉, 각 이미지는 RGB 컬러 이미지이며, 총 100개 클래스로 분류되는 구조입니다.
# Create the data module
max_num_workers = rec_num_workers()
print(max_num_workers) # 2
cifar_dm = SimpleDataModule(
cifar_train,
cifar_test,
validation=0.2,
num_workers=max_num_workers,
batch_size=128
)
for idx, (X_, Y_) in enumerate(cifar_dm.train_dataloader()):
print('X: ', X_.shape)
print('Y: ', Y_.shape)
if idx >= 1:
break

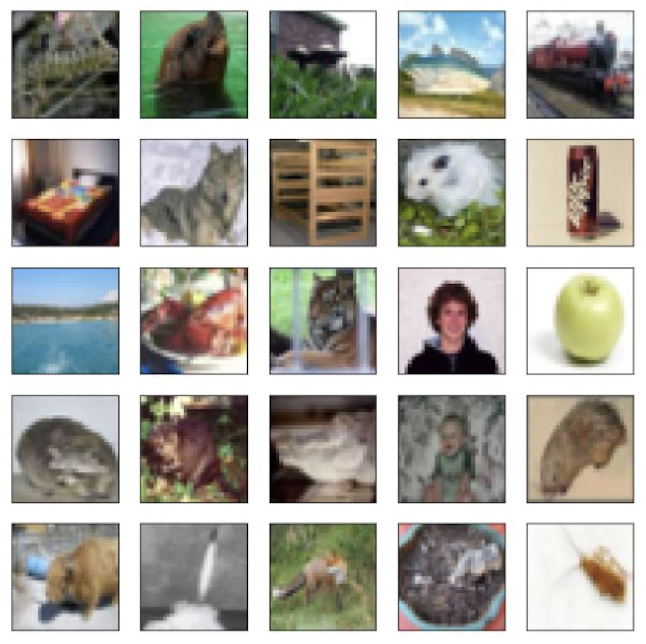
# Choose random images from the training data
fig, axes = subplots(5, 5, figsize=(10, 10))
rng = np.random.default_rng(4)
indices = rng.choice(np.arange(len(cifar_train)), 25, replace=False).reshape((5, 5))
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
idx = indices[i, j]
axes[i, j].imshow(
np.transpose(cifar_train[idx][0], [1, 2, 0]),
interpolation=None
)
axes[i, j].set_xticks([])
axes[i, j].set_yticks([])

# Specify a moderately-sized CNN
class BuildingBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(BuildingBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding='same'
)
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2))
def forward(self, x):
return self.pool(self.activation(self.conv(x)))
padding='same' 인자는 nn.Conv2d() 에서 입력과 출력의 공간 차원(Height, Width)을 동일하게 유지해 주는 역할을 합니다.
즉, 커널이 이미지의 가장자리를 벗어나지 않도록 필요한 만큼의 제로 패딩(zero-padding) 을 자동으로 적용합니다.
✅ 이렇게 하면 convolution 연산 후에도 feature map의 크기가 줄어들지 않아, 네트워크 설계가 단순해지고 feature dimension 추적이 쉬워집니다.
# Form the deep learning model for CIFAR100 data
# We use several BuildingBlock() modules sequentially
class CIFARModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CIFARModel, self).__init__()
sizes = [(3, 32), (32, 64), (64, 128), (128, 256)]
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
*[BuildingBlock(in_, out_) for in_, out_ in sizes]
)
self.output = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(2 * 2 * 256, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 100)
)
def forward(self, x):
val = self.conv(x)
val = torch.flatten(val, start_dim=1)
return self.output(val)
# Build the model and look at the summary
cifar_model = CIFARModel()
summary(
cifar_model,
input_data=X_,
col_names=['input_size', 'output_size', 'num_params']
)
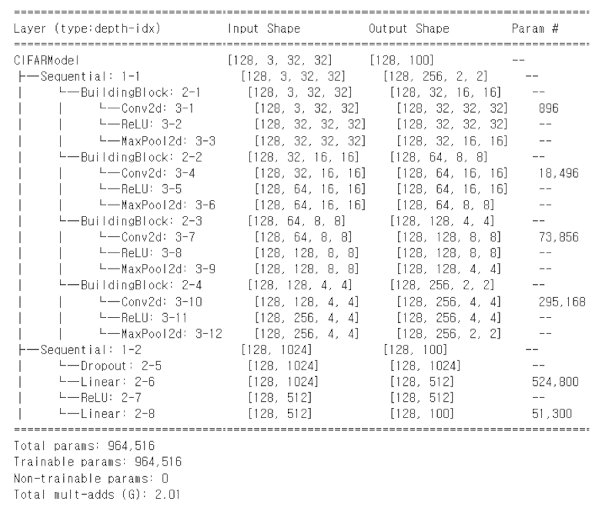 해당 모델에서 학습 가능한 파라미터 수는 총 964,516개
해당 모델에서 학습 가능한 파라미터 수는 총 964,516개
# Create the data module
cifar_optimizer = RMSprop(cifar_model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
cifar_module = SimpleModule.classification(
cifar_model,
num_classes=100,
optimizer=cifar_optimizer
)
cifar_logger = CSVLogger('logs', name='CIFAR100')
cifar_trainer = Trainer(
deterministic=True,
max_epochs=30,
logger=cifar_logger,
callbacks=[ErrorTracker()]
)
cifar_trainer.fit(cifar_module, datamodule=cifar_dm)

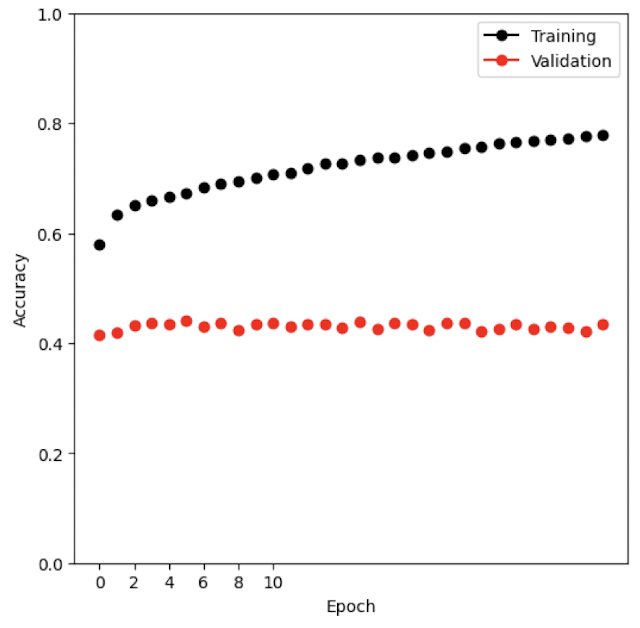
# Check validation and training accuracy
log_path = cifar_logger.experiment.metrics_file_path
cifar_results = pd.read_csv(log_path)
fig, ax = subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 6))
summary_plot(cifar_results,
ax,
col='accuracy',
ylabel='Accuracy')
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(0, 10, 6).astype(int))
ax.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
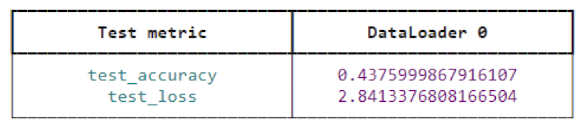
# Evaluate our model on our test data
cifar_trainer.test(cifar_module, datamodule=cifar_dm)
📦 Lab: Using Pretrained CNN Models
# Hardware Acceleration
try:
for name, metric in cifar_module.metrics.items():
cifar_module.metrics[name] = metric.to('mps')
cifar_trainer_mps = Trainer(
accelerator='mps',
deterministic=True,
max_epochs=30
)
cifar_trainer_mps.fit(cifar_module, datamodule=cifar_dm)
cifar_trainer_mps.test(cifar_module, datamodule=cifar_dm)
except:
pass
Trainer 호출 방식과 평가할 metric 설정을 변경함으로써, 학습 속도가 2~3배 빨라지는 효과를 얻을 수 있다.
→ 즉, 에폭당 연산 효율이 크게 향상되며, 동일한 모델이라도 더 빠르게 학습 가능해진다는 뜻이다.
# Use Pretrained CNN Models
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
import os
print(os.listdir('/content/drive/MyDrive'))
resize = Resize((232, 232), antialias=True)
crop = CenterCrop(224)
normalize = Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
imgfiles = sorted([
f for f in glob('/content/drive/MyDrive/book_images/*')
])
imgs = torch.stack([
torch.div(crop(resize(read_image(f))), 255)
for f in imgfiles
])
imgs = normalize(imgs)
imgs.size()
torch.Size([6, 3, 224, 224])
# Set up the trained network with the weights
resnet_model = resnet50(weights=ResNet50_Weights.DEFAULT)
summary(resnet_model,
input_data=imgs,
col_names=['input_size', 'output_size', 'num_params'])
# Set the mode to eval() to ensure that the model is ready to predict on new data.
resnet_model.eval()
# Feed our six images through the fitted network
img_preds = resnet_model(imgs)
img_probs = np.exp(np.asarray(img_preds.detach()))
img_probs /= img_probs.sum(1)[:, None]
# Download the index file associated with ImageNet
labs = json.load(open('/content/drive/MyDrive/book_images/imagenet_class_index.json'))
class_labels = pd.DataFrame([(int(k), v[1]) for k, v in labs.items()],
columns=['idx', 'label'])
class_labels = class_labels.set_index('idx')
class_labels = class_labels.sort_index()
# Construct a data frame for each image file with the
labels with the three highest probabilities as estimated
by the model above.
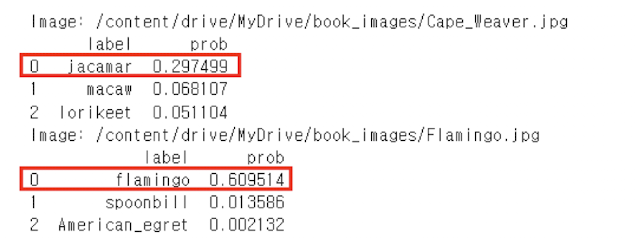
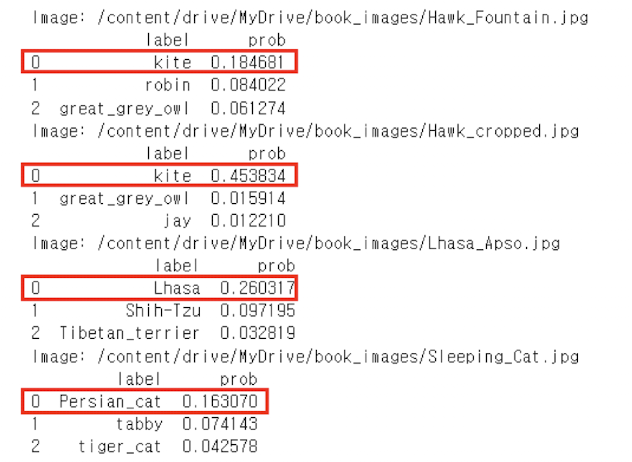
for i, imgfile in enumerate(imgfiles):
img_df = class_labels.copy()
img_df['prob'] = img_probs[i]
img_df = img_df.sort_values(by='prob',
ascending=False)[:3]
print(f'Image: {imgfile}')
print(img_df.reset_index().drop(columns=['idx']))