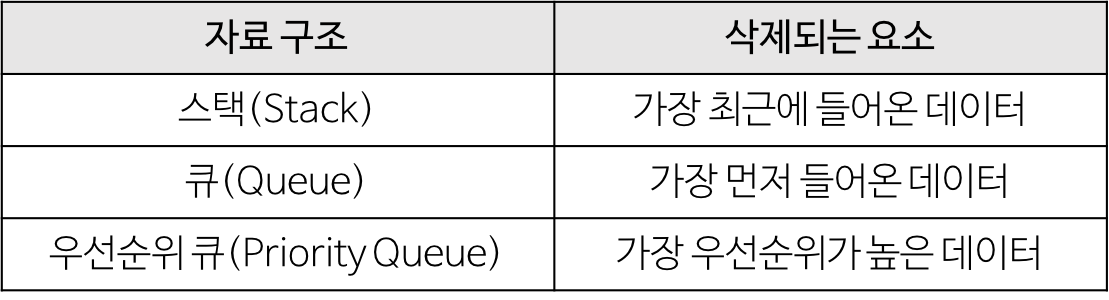
트리
정의
- 데이터의 각 요소들을 계층적으로 연관되도록 구조화 시키고자 할 때 사용하는 비선형 자료구조.
- 데이터의 각 요소들의 단순한 나열이 아닌 부모-자식 관계의 계층적 구조로 표현한다.
- 트리는 노드와 간선으로 이루어진 자료구조이다.
- 트리는 하나의 루트 노드를 갖는다.
- 루트 노드는 0개 이상의 자식 노드를 갖고 있는다.
- 자식 노드 또한 0개 이상의 자식 노드를 가지며, 반복적으로 트리가 구성된다.
- 각 노드들은 서로를 연결하는 간선으로 이어져있다.
- 노드가 N개인 트리는 항상 N-1개의 간선을 가진다.
- 트리에는 사이클이 존재할 수 없다(임의의 두 노드간의 경로가 유일).
- 트리는 그래프의 한 종류로 최소 연결 트리라고도 불린다.
- 사이클이 없는 하나의 연결 그래프
-> 즉, 루트노드에서 시작하여 같은 방향으로 다시 루트노드에 도착할 수 없다. - DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph, 방향성이 있는 비순환 그래프)의 한 종류.
- 사이클이 없는 하나의 연결 그래프
용어
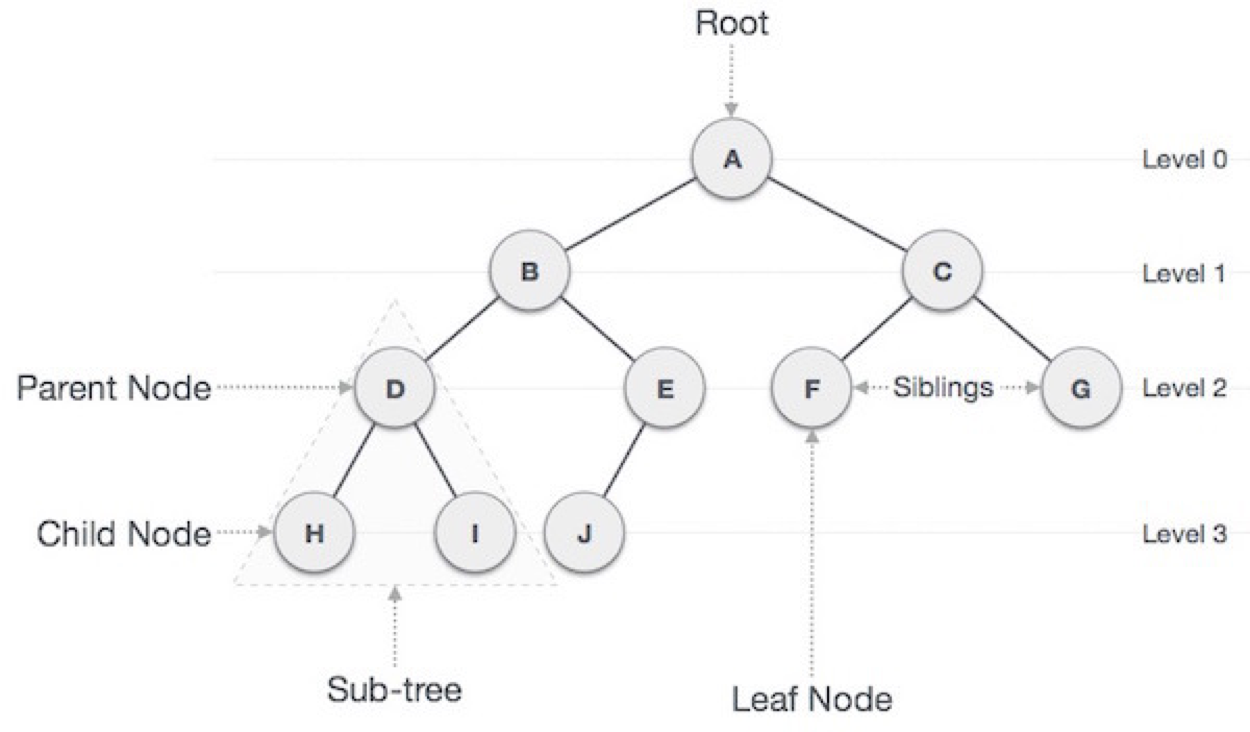
- 루트 노드(root node): 부모가 없는 노드, 트리는 하나의 루트 노드만을 가진다.
- 단말 노드(leaf node): 자식이 없는 노드, ‘말단 노드’ 또는 ‘잎 노드’라고도 부른다.
- 내부(internal) 노드: 단말 노드가 아닌 노드
- 간선(edge): 노드를 연결하는 선 (link, branch 라고도 부름)
- 형제(sibling): 같은 부모를 가지는 노드
- 노드의 크기(size): 자신을 포함한 모든 자손 노드의 개수
- 노드의 깊이(depth): 루트에서 어떤 노드에 도달하기 위해 거쳐야 하는 간선의 수
- 노드의 레벨(level): 트리의 특정 깊이를 가지는 노드의 집합
- 노드의 차수(degree): 하위 트리 개수 / 간선 수 (degree) = 각 노드가 지닌 다음 레벨의 하위 가지의 수
- 트리의 차수(degree of tree): 트리의 최대 차수(각 노드의 차수 중 가장 높은 차수)
- 트리의 높이(height): 루트 노드에서 가장 깊숙히 있는 노드의 깊이
순회
- 트리를 탐색하는 순회 방법에는 크게 두 가지가 존재한다.
너비우선탐색 : BFS(Breadth First Search)
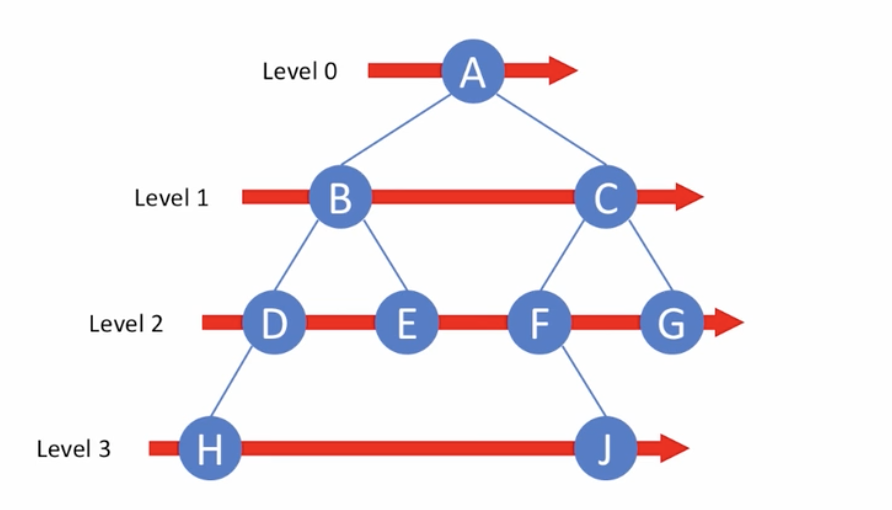
- 레벨 순회 방식
- 트리 전체를 탐색하되, 인접한 노드들을 차례대로 방문하도록 구현한다.
- 즉, 트리의 레벨이 가장 낮고 왼쪽의 노드 부터 순서대로 방문한다고 이해하면 된다.
- 큐 자료구조를 활용하면 구현이 편리하다.
- 구현 - JavaScript
// 전체 코드인 아래 이진 탐색 트리의 구현을 참고하여 코드를 이해하길 바란다.
// 위 이미지의 트리의 순회 결과는 : A -> B -> C -> D -> E -> F -> G -> H -> J
bfs() {
let curNode = this.root;
const queue = [curNode];
let printTree = '';
while(queue.length) {
curNode = queue.shift();
printTree += curNode.value + ' ';
if(curNode.left) {
queue.push(curNode.left);
}
if(curNode.right) {
queue.push(curNode.right);
}
}
console.log(printTree);
return;
}깊이우선탐색 : DFS(Depth First Search)
- 트리에서의 깊이우선탐색은 순회 방식에 따라 3가지로 나뉘어진다.
1. 전위 순회(Preorder Traversal)
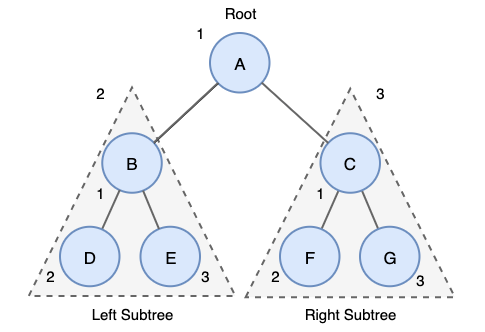
-
전위 순회의 탐색 방법은 다음과 같다.
- 루트노드 방문한다.
- 왼쪽 서브트리를 전위 순회한다.
- 오른쪽 서브트리를 전위 순회한다.
-
위 트리의 전위 순회 결과는 A->B->C->D->E->F->G 이다.
-
구현 - JavaScript
// 전체 코드인 아래 이진 탐색 트리의 구현을 참고하여 코드를 이해하길 바란다.
// 1. 전위 순회(Prerder Traversal)
preOrder(root = this.root) {
// 데이터가 없는 경우
if (!root) return;
console.log(root.value);
this.preOrder(root.left);
this.preOrder(root.right);
}2. 중위 순회(Inorder Traversal)
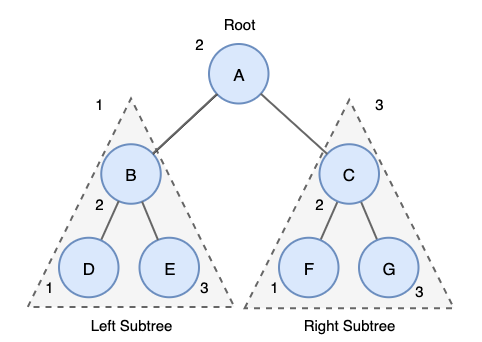
-
중위 순회의 탐색 방법은 다음과 같다.
- 왼쪽 서브트리를 중위 순회한다.
- 루트노드 방문한다.
- 오른쪽 서브트리를 중위 순회한다.
-
위 트리의 중위 순회 결과는 D->B->E->A->F->C->G 이다.
-
구현 - JavaScript
// 전체 코드인 아래 이진 탐색 트리의 구현을 참고하여 코드를 이해하길 바란다.
// 2. 중위 순회(Inorder Traversal)
inOrder(root = this.root) {
// 데이터가 없는 경우
if (!root) return;
this.inOrder(root.left);
console.log(root.value);
this.inOrder(root.right);
}3. 후위 순회(Postorder Traversal)
-
후위 순회의 탐색 방법은 다음과 같다.
- 왼쪽 서브트리를 후위 순회한다.
- 오른쪽 서브트리를 후위 순회한다.
- 루트노드 방문한다.
-
위 트리의 후위 순회 결과는 D->E->B->F->G->C->A 이다.
-
구현 - JavaScript
// 전체 코드인 아래 이진 탐색 트리의 구현을 참고하여 코드를 이해하길 바란다.
// 3. 후위 순회(Postorder Traversal)
postOrder(root = this.root) {
// 데이터가 없는 경우
if (!root) return;
this.postOrder(root.left);
this.postOrder(root.right);
console.log(root.value);
}1. 이진 트리
- 이진 트리(Binary Tree)는 각 노드가 자식 노드를 최대 2개까지 가지는 트리를 말한다.
- 각각의 자식 노드는 자신이 부모의 왼쪽 자식인지 오른쪽 자식인지 지정된다.
- 이진 트리의 종류에는 완전 이진 트리, 포화 이진 트리, 정 이진 트리, 편향 이진 트리 등이 있다.
완전 이진 트리
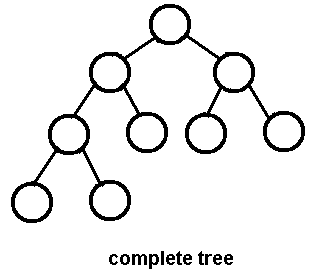
- 완전 이진 트리(complete binary tree)는 왼쪽 자식 노드부터 순서대로 노드가 채워지며 마지막 레벨을 제외하고는 모든 자식 노드가 채워져있는 트리를 말한다.
- 마지막 레벨 역시 노드가 왼쪽에서 부터 순서로 채워져야 한다.
포화 이진 트리
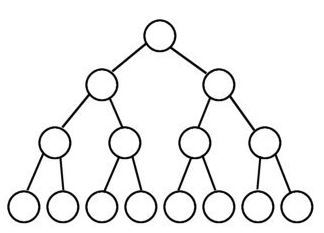
- 포화 이진 트리(perfect binary tree)는 모든 노드가 0개 혹은 2개의 자식 노드를 가지며 모든 리프노드가 똑같은 레벨에 있는 경우의 트리를 말한다.
정 이진 트리
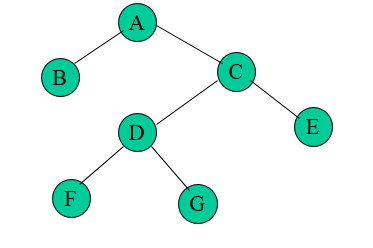
- 정 이진 트리(full binary tree)는 모든 노드가 0개 혹은 2개의 자식 노드를 가지는 트리를 말한다.
편향 이진 트리
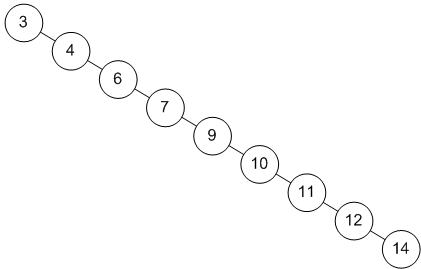
- 편향 이진 트리(skewed binary tree)는 말 그대로 노드들이 전부 한 방향으로 편향된 트리를 말한다.
2. 이진탐색트리
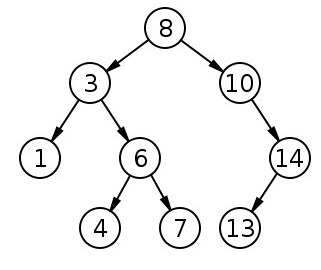
- 이진 탐색 트리(binary search tree)는 이진 트리의 한 종류이다.
- 이진 트리이지만 왼쪽 자식 노드가 루트 노드보다 값이 작고, 오른쪽 자식 노드가 루트 노드보다 값이 큰 트리를 말한다.
구현 - JavaScript
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// 노드 탐색
search(value) {
let curNode = this.root;
while (curNode) {
if (curNode.value === value) {
console.log('찾으시는 노드는 존재합니다.');
return;
}
if (curNode.value > value) {
curNode = curNode.left;
} else {
curNode = curNode.right;
}
}
console.log('찾으시는 노드는 존재하지 않습니다.');
return;
}
// 노드 삽입
insert(value) {
let newNode = new Node(value);
let curNode = this.root;
if (!this.root) {
this.root = newNode;
this.length++;
return;
}
while (curNode) {
// 이진탐색트리는 중복값을 허용하지 않는다.
if (value === curNode.value) return;
// 추가되는 값이 루트노드의 값보다 작은 경우 왼쪽 서브트리
if (value < curNode.value) {
if (!curNode.left) {
curNode.left = newNode;
break;
}
curNode = curNode.left;
} else {
// 추가되는 값이 루트노드의 값보다 큰 경우 오른쪽 서브트리
if (!curNode.right) {
curNode.right = newNode;
break;
}
curNode = curNode.right;
}
}
this.length++;
}
// 노드 삭제
remove(value) {
const removeNode = (node, value) => {
// 트리가 존재하지 않은 경우
if (!node) return null;
if (value === node.value) {
// 삭제할 노드가 자식 노드가 없는 경우
if (!node.left && !node.right) {
return null;
} else if (!node.right) {
// 삭제할 노드가 왼쪽 자식 노드만 존재하는 경우
return node.left;
} else if (!node.left) {
// 삭제할 노드가 오른쪽 자식 노드만 존재하는 경우
return node.right;
} else {
// 왼쪽, 오른쪽 모두 자식노드가 있는 경우
// 삭제할 노드의 오른쪽 자식 중에서 가장 왼쪽 아래의 자식을 선택하여 삭제할 노드의 위치로 변경하는 방법 사용
let curNode = node.right;
while (curNode.left) {
curNode = curNode.left;
}
node.value = curNode.value;
node.right = removeNode(node.right, curNode.value);
return node;
}
} else if (value < node.value) {
node.left = removeNode(node.left, value);
return node;
} else {
node.right = removeNode(node.right, value);
return node;
}
};
this.root = removeNode(this.root, value);
this.length--;
}
// Bfs : 너비우선탐색
bfs() {
let curNode = this.root;
const queue = [curNode];
let printTree = '';
while (queue.length) {
curNode = queue.shift();
printTree += curNode.value + ' ';
if (curNode.left) {
queue.push(curNode.left);
}
if (curNode.right) {
queue.push(curNode.right);
}
}
console.log(printTree);
return;
}
// Dfs : 깊이우선탐색
// 1. 전위 순회(Prerder Traversal)
preOrder(root = this.root) {
// 데이터가 없는 경우
if (!root) return;
console.log(root.value);
this.preOrder(root.left);
this.preOrder(root.right);
}
// 2. 중위 순회(Inorder Traversal)
inOrder(root = this.root) {
// 데이터가 없는 경우
if (!root) return;
this.inOrder(root.left);
console.log(root.value);
this.inOrder(root.right);
}
// 3. 후위 순회(Postorder Traversal)
postOrder(root = this.root) {
// 데이터가 없는 경우
if (!root) return;
this.postOrder(root.left);
this.postOrder(root.right);
console.log(root.value);
}
}
const bst = new BinarySearchTree();
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(1);
bst.insert(6);
bst.insert(14);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(4);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(13);
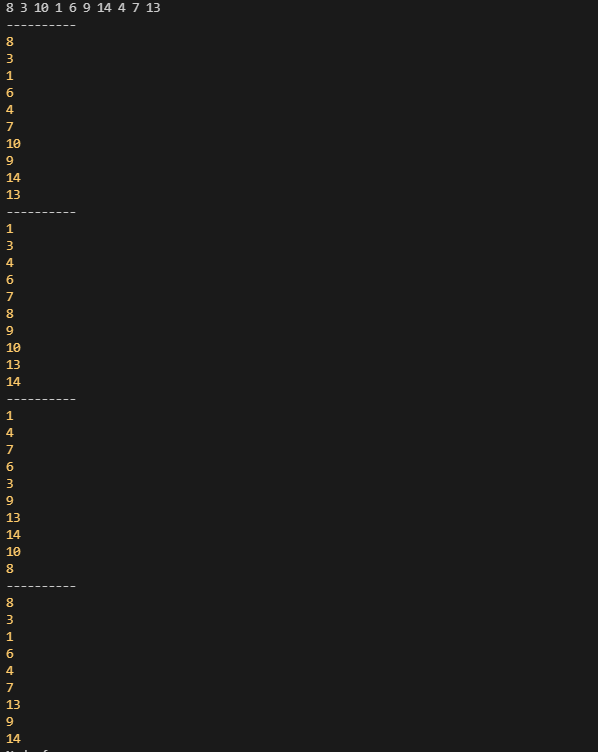
bst.bfs();
console.log('----------');
bst.preOrder();
console.log('----------');
bst.inOrder();
console.log('----------');
bst.postOrder();
console.log('----------');
bst.remove(10);
bst.preOrder();
console.log(bst.root);
결과
3. 힙
- 완전 이진 트리의 일종으로 우선순위 큐 개념을 구현하기에 적합한 자료구조이다.
- 데이터의 값들 중에서 최댓값이나 최솟값을 빠르게 찾아내기에 최적화된 자료구조이다.
- 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값 보다 항상 크거나 작은 이진 트리를 말한다.
- 이진 탐색 트리와 다르게 중복된 값을 허용한다.
- 최대힙(Max Heap)과 최소힙(Min Heap)으로 종류가 나뉘어진다.
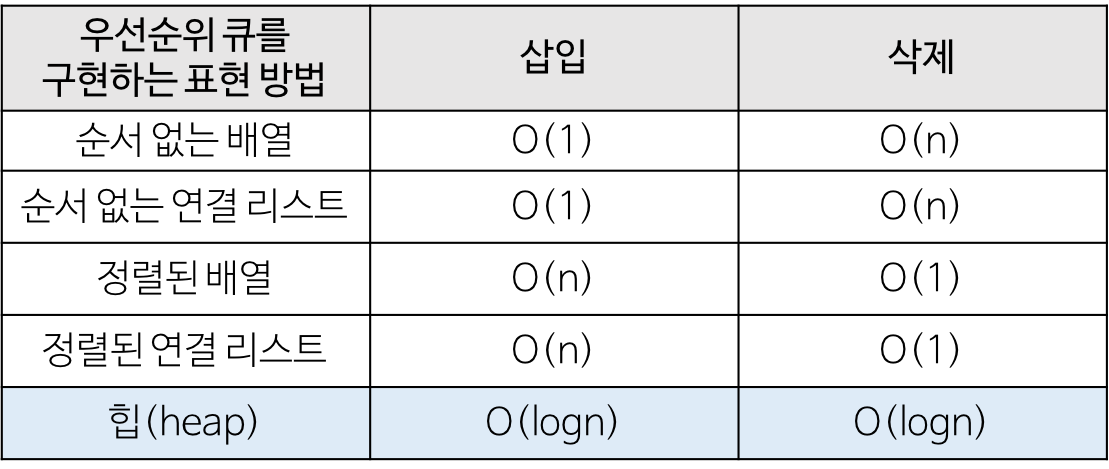
우선순위 큐 ?
- 우선순위의 개념을 큐에 도입한 자료구조이다.
- 데이터들이 우선순위를 가지고 있고 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나가는 자료구조.
- 우선순위 큐는 배열, 연결리스트, 힙으로 구현이 가능하며 이 중 힙이 가장 효율적이다.
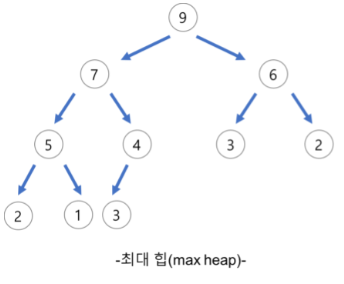
최대 힙(Max Heap)
- 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 크거나 같은 완전 이진 트리이다.
- 최대 힙의 루트 노드는 가장 큰 값이 된다.
구현 - JavaScript
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
// 삽입연산 : 힙을 구성
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this.moveUp();
}
// 삭제연산 : 최댓값을 뽑아내는 연산
pop() {
// 최대값을 저장
const max = this.heap[0];
// 힙의 가장 마지막 요소를 루트에 저장
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
// 루트노드 부터 아래로 대소 비교 시작하여 위치 조정
this.moveDown(0);
return max;
}
// 힙의 하단에서 부터 상단으로 값을 변경한다.
moveUp() {
// 힙의 맨 마지막 요소에 값이 추가 되었으므로
let curIdx = this.heap.length - 1;
// 최댓값을 가장 최상단으로 올리는 작업을 반복
while (curIdx > 0) {
const parentIdx = Math.floor((curIdx - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[parentIdx] >= this.heap[curIdx]) break;
[this.heap[parentIdx], this.heap[curIdx]] = [
this.heap[curIdx],
this.heap[parentIdx],
];
curIdx = parentIdx;
}
}
// 힙의 상단에서 부터 하단으로 값을 변경한다.
moveDown(idx) {
const leftIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
const rightIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
const length = this.heap.length;
let maxIdx = idx;
// 힙의 왼쪽 자식과 변경 여부
if (leftIdx < length && this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[maxIdx]) {
maxIdx = leftIdx;
}
// 힙의 왼쪽 자식으로 인덱스 바뀌어 있어도 오른쪽이 더 큰 요소였다면 오른쪽 인덱스 요소로 변경된다.
if (rightIdx < length && this.heap[rightIdx] > this.heap[maxIdx]) {
maxIdx = rightIdx;
}
// swap 후 재귀 호출울 통해 계속 값 변경
if (maxIdx !== idx) {
[this.heap[idx], this.heap[maxIdx]] = [this.heap[maxIdx], this.heap[idx]];
this.moveDown(maxIdx);
}
}
}
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
maxHeap.insert(4);
maxHeap.insert(7);
maxHeap.insert(6);
maxHeap.insert(5);
maxHeap.insert(2);
maxHeap.insert(9);
maxHeap.insert(1);
maxHeap.insert(3);
maxHeap.insert(2);
maxHeap.insert(3);
console.log(maxHeap.heap);
maxHeap.pop();
console.log(maxHeap.heap);결과

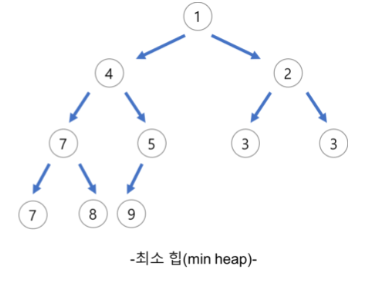
최소 힙(Min Heap)
- 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 작거나 같은 완전 이진 트리이다.
- 최소 힙의 루트 노드는 가장 작은 값이 된다.
구현 - JavaScript
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
// 삽입연산 : 힙을 구성
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this.moveUp();
}
// 삭제연산 : 최솟값을 뽑아내는 연산
pop() {
// 최솟값을 저장
const min = this.heap[0];
// 힙의 가장 마지막 요소를 루트에 저장
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
// 루트노드 부터 아래로 대소 비교 시작하여 위치 조정
this.moveDown(0);
return min;
}
// 힙의 하단에서 부터 상단으로 값을 변경한다.
moveUp() {
// 힙의 맨 마지막 요소에 값이 추가 되었으므로
let curIdx = this.heap.length - 1;
// 최솟값을 가장 최상단으로 올리는 작업을 반복
while (curIdx > 0) {
const parentIdx = Math.floor((curIdx - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[parentIdx] <= this.heap[curIdx]) break;
[this.heap[parentIdx], this.heap[curIdx]] = [
this.heap[curIdx],
this.heap[parentIdx],
];
curIdx = parentIdx;
}
}
// 힙의 상단에서 부터 하단으로 값을 변경한다.
moveDown(idx) {
const leftIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
const rightIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
const length = this.heap.length;
let minIdx = idx;
// 힙의 왼쪽 자식과 변경 여부
if (leftIdx < length && this.heap[leftIdx] < this.heap[minIdx]) {
minIdx = leftIdx;
}
// 힙의 왼쪽 자식으로 인덱스 바뀌어 있어도 오른쪽이 더 작은 요소였다면 오른쪽 인덱스 요소로 변경된다.
if (rightIdx < length && this.heap[rightIdx] < this.heap[minIdx]) {
minIdx = rightIdx;
}
// swap 후 재귀 호출울 통해 계속 값 변경
if (minIdx !== idx) {
[this.heap[idx], this.heap[minIdx]] = [this.heap[minIdx], this.heap[idx]];
this.moveDown(minIdx);
}
}
}
const minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.insert(4);
minHeap.insert(7);
minHeap.insert(6);
minHeap.insert(5);
minHeap.insert(2);
minHeap.insert(9);
minHeap.insert(1);
minHeap.insert(3);
minHeap.insert(2);
minHeap.insert(3);
console.log(minHeap.heap);
minHeap.pop();
console.log(minHeap.heap);
결과

4. 트라이
-
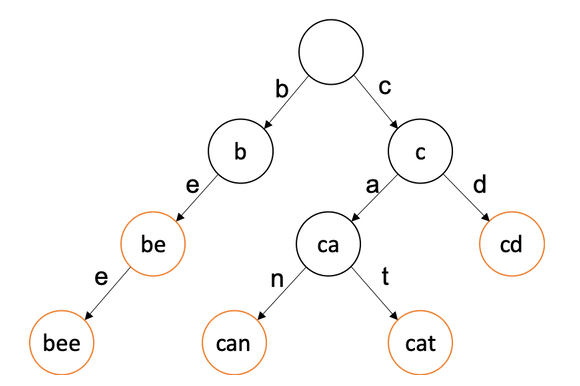
트라이(Trie)란 문자열을 저장하고 효율적으로 탐색하기 위한 트리 형태의 자료구조입니다.
-
저장된 단어는 끝을 표시하는 변수를 추가해서 저장된 단어의 끝을 구분할 수 있습니다.
-
문자열의 탐색을 하고자할 때 단순하게 하나씩 비교하면서 탐색을 하는것보다 훨씬 효율적입니다. (시간복잡도가 가장 긴 문자열의 길이만큼 걸린다. 즉, O(N))
-
빠르게 탐색이 가능하다는 장점이 있지만 각 노드에서 자식들에 대한 포인터들을 배열로 모두 저장하고 있다는 점에서 저장 공간의 크기가 크다는 단점도 있습니다.
-
아래 사진은 be, bee, can, cat, cd가 들어가 있습니다.
구현 - JavaScript
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
enqueue(node) {
if (this.size() === 0) {
this.head = this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
return;
}
dequeue() {
if (this.size() === 0) {
console.log('큐가 이미 비었습니다.');
return;
}
const deleteNode = this.head;
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head = deleteNode.next;
}
this.length--;
return deleteNode;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
}
class Node {
constructor(value = '') {
this.value = value; //현재 경로까지의 누적값
this.end = false; //해당 노드에서 끝나는 문자열이 있는지 여부
this.child = {}; //자식
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new Node();
}
insert(string) {
let curNode = this.root; //루트노드를 시작으로 탐색하면서 삽입한다
for (let i = 0; i < string.length; i++) {
const char = string[i];
//만일, 해당 키를 가진 자식이 없다면 새 노드를 만들어준다.
if (!curNode.child[char]) {
curNode.child[char] = new Node(curNode.value + char);
}
curNode = curNode.child[char]; // 자식 노드로 이동한다.
}
curNode.end = true; //해당 노드에서 끝나는 단어가 있음을 알린다.
}
search(string) {
let curNode = this.root;
for (let i = 0; i < string.length; i++) {
const char = string[i];
if (curNode.child[char]) {
curNode = curNode.child[char];
} else {
return false;
}
}
return curNode;
}
// 자동완성기능
autoComplete(string) {
const findNode = this.search(string); // 자동검색을 위한 입력 단어의 노드
if (!findNode) return; // 입력단어가 존재 하지 않는 경우
const queue = new Queue();
const result = []; // 자동완성단어의 리스트
queue.enqueue(findNode);
while (queue.size()) {
const curNode = queue.dequeue();
if (curNode.end) result.push(curNode.value);
Object.values(curNode.child).forEach((node) => {
if (node) queue.enqueue(node);
});
}
return result.sort(); // 자동완성된 단어들을 사전 순으로 정렬하여 반환하였다.
}
}
const trie = new Trie();
trie.insert('be');
trie.insert('bee');
trie.insert('can');
trie.insert('cat');
trie.insert('cd');
console.log(trie.autoComplete('ca')); // ['can', 'cat']
console.log(trie.search('can')); // 찾아야함
console.log(trie.search('cbn'));
console.log(trie.search('bee')); // 찾아야함
console.log(trie.search('bt'));
결과

참고자료
- https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/08/12/data-structure-tree.html
- https://velog.io/@adam2/TREE#tree
- https://sexycoder.tistory.com/81
- https://yoongrammer.tistory.com/70?category=956616
- https://velog.io/@teihong93/%EC%9E%90%EB%B0%94%EC%8A%A4%ED%81%AC%EB%A6%BD%ED%8A%B8%EB%A5%BC-%EC%9D%B4%EC%9A%A9%ED%95%9C-Trie-%EA%B5%AC%ED%98%84
- https://twpower.github.io/187-trie-concept-and-basic-problem
- https://velog.io/@inyong_pang/19%EA%B0%95-%EC%9D%B4%EC%A7%84-%ED%8A%B8%EB%A6%AC%EC%9D%98-%EB%84%93%EC%9D%B4-%EC%9A%B0%EC%84%A0-%EC%88%9C%ED%9A%8C-BFS-Breadth-First-Traversal