Oriented R-CNN for Object Detection Paper Review - Advancing Rotated Object Detection
Computer Vision

Summary
The Oriented R-CNN model aims to detect not only the location of objects but also ther orientations. It improves existing two-stage object detectors through:
- Lightweight Oriented Region Proposal Network (RPN):
Reduces computation by minimizing anchor complexity.
- Lightweight Oriented Region Proposal Network (RPN):
- Midpoint Offset Representation:
Enhances accuracy by learning vertex offsets rather than directly predicting angles.
- Midpoint Offset Representation:
- Rotated RoI Align:
Improves feature extraction for rotated objects.
- Rotated RoI Align:
Introduction
Traditional two-stage object detectors are computationally expensive, often introducing bottlenecks. Oriented R-CNN address these issues with:
- Oriented RPN
- Oriented R-CNN Head (Feature Extraction & alignment for oriented RoIs)
Limitations of Existing Models
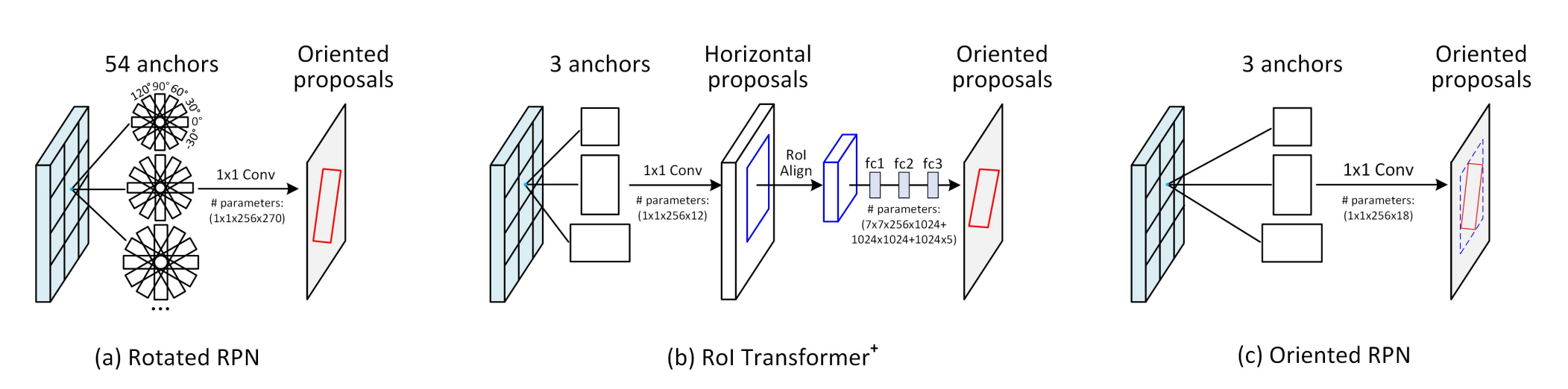
- Rotated RPN
- Uses 54 anchors (3 scales x 3 ratios x 6 angles)
- Performs well when distributed sparsely, ensuring good coverage
- However, massive computation and high memory footprint due to the large number of anchors.
- RoI Transformer
- Converts horizontal RoIs to oriented RoIs through multiple transformations.
- Still computationally expensive due to redundant operations.
Proposed Solution
Instead of excessive anchors or complex transformations, the authors suppsose:
- Light-weight CNN: Oriented RPN designed with fewer parameters, reduces computational cost and prevents overfitting
- Midpoint Offset Representation: Predicts offsets from the box center to vertices, avoiding angle regression instability.
Oriented R-CNN
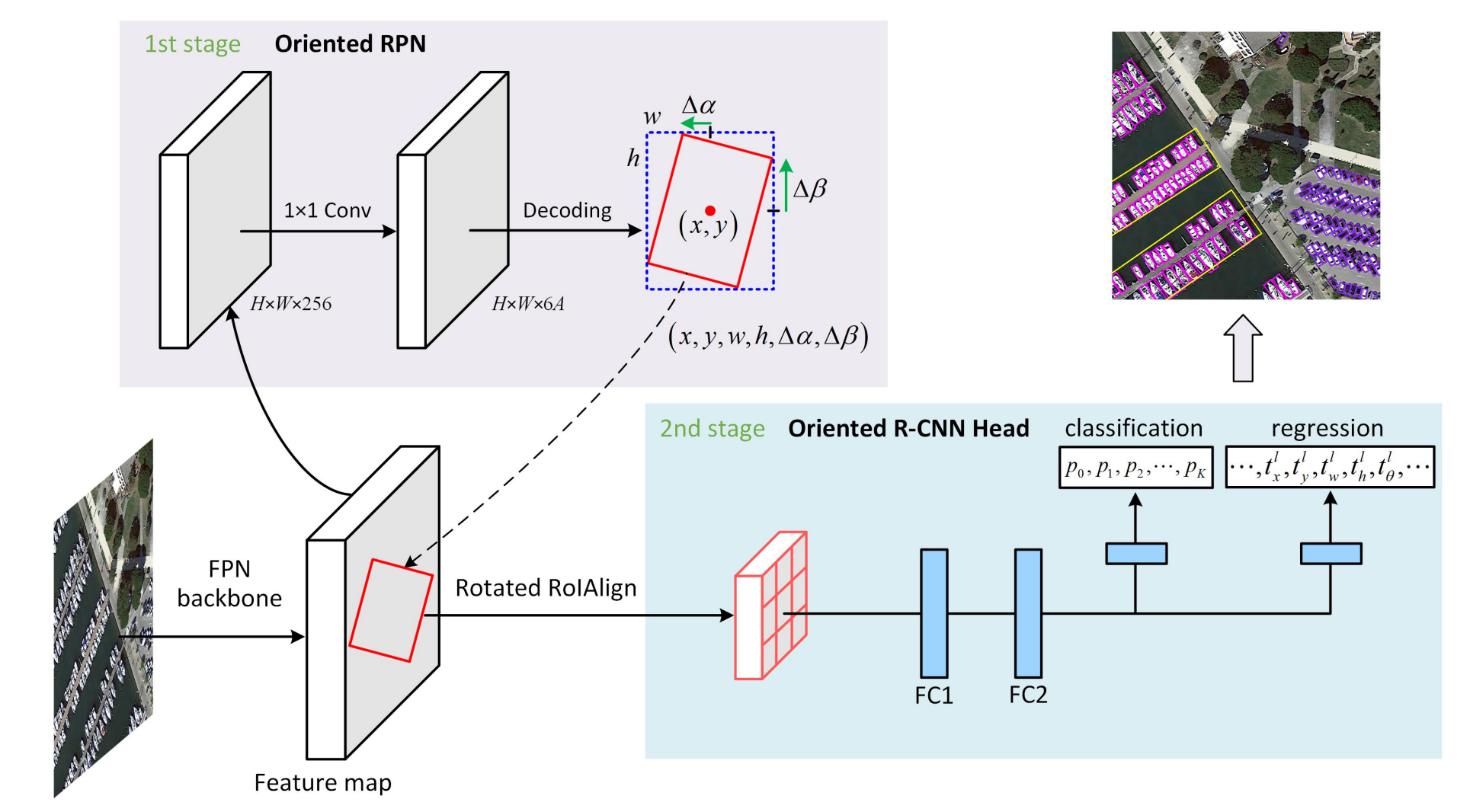
Oriented RPN
- Model Architecture
- 5-level Feature Pyramid Network (FPN)
- Each level consists of:
- 3x3 convolution layer
- Two sibling 1x1 convolution layers:
- Regression branch: Outputs bounding-box offsets δ=(δx,δy,δw,δh,δα,δβ)
- Classification branch: Determines object presence
- Three horizontal anchors assigned per spatial location (1:1, 1:2, 2:1)
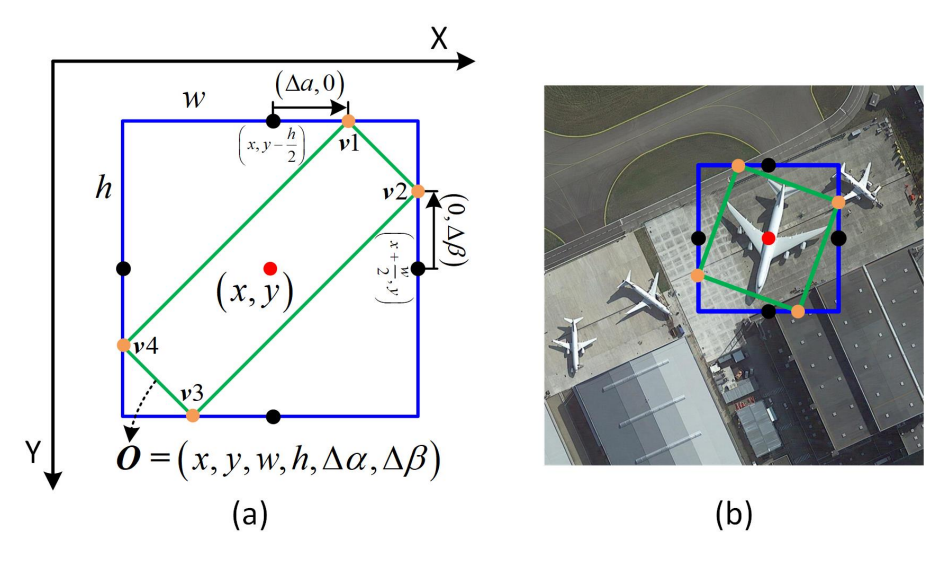
- Bounding-boxes represented as (x, y, w, h) where:
- x, y: Center coordinates
- w, h: Width and height
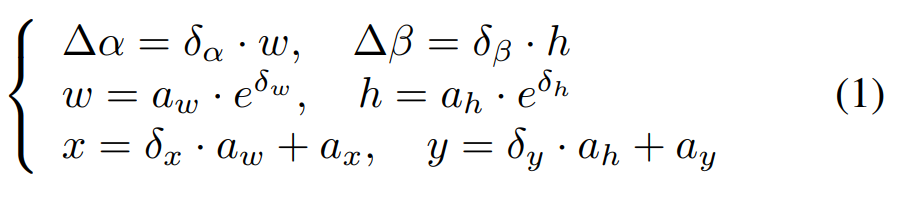
Midpoint Offset Representation
Instead of directly predicting the rotation angle θ, Oriented RPN learns offsets (Δα, Δβ) from the bounding-box center to its rotated vertices.
- Why Midpoint Offset?
- Eliminates angle ambiguity
- Reduces gradient discontinuity
- Simplifies regression
Loss Function
Anchor Classification
- Positive Anchor:
- IoU ≥ 0.7 with any ground-truth box.
- Highest IoU (≥ 0.3) with a specific ground-truth box.
- Negative Anchor
- IoU ≤ 0.3 (considered background)
- All other anchors are ignored during training.
Bounding-box Regression
- Uses Affine Transform (similar to Faster R-CNN)
- Loss function:
- Classification Loss: Cross-Entropy Loss
- Regression Loss: Smooth L1 Loss
By integrating affine transformation, the model enhances bounding-box refinement while maintaing stability.
Oriented R-CNN Head
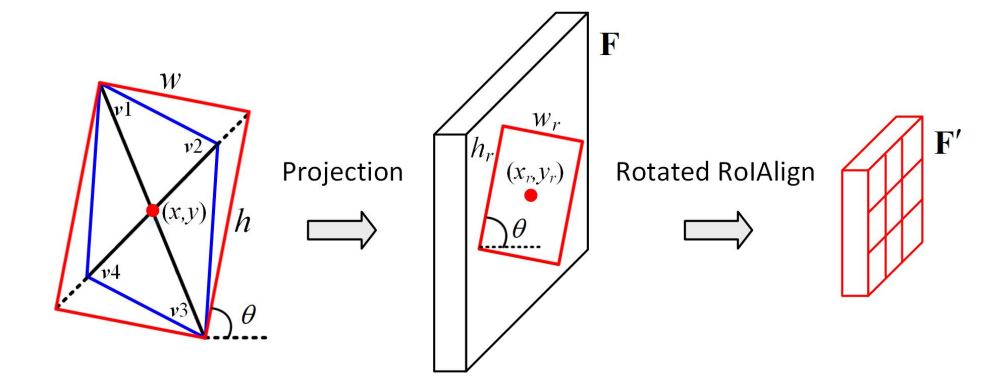
Feature Extraction & Alignment
- Oriented Proposals are extracted and refined
- Rotated RoI Align is applied to capture accurate object features.
Process:
- Projection:
- Since oriented proposals are generally parallelograms, they are first converted into a rectangular shape.
- The shorter diagonal is extended to match the length of the longer diagonal to ensure proper alignment.
- Grid-based Feature Extraction
- The oriented proposal is divided into fixed-size grids (e.g., 7x7)
- Each grid region undergoes feature sampling to extract relevant details.
Head Structure
-
Classification Branch -> Object classification
-
Regression Branch -> Final bounding-box refinement
By refining object proposals through Oriented R-CNN Head, the model ensures higher accuracy in both classification and localization.
Performance
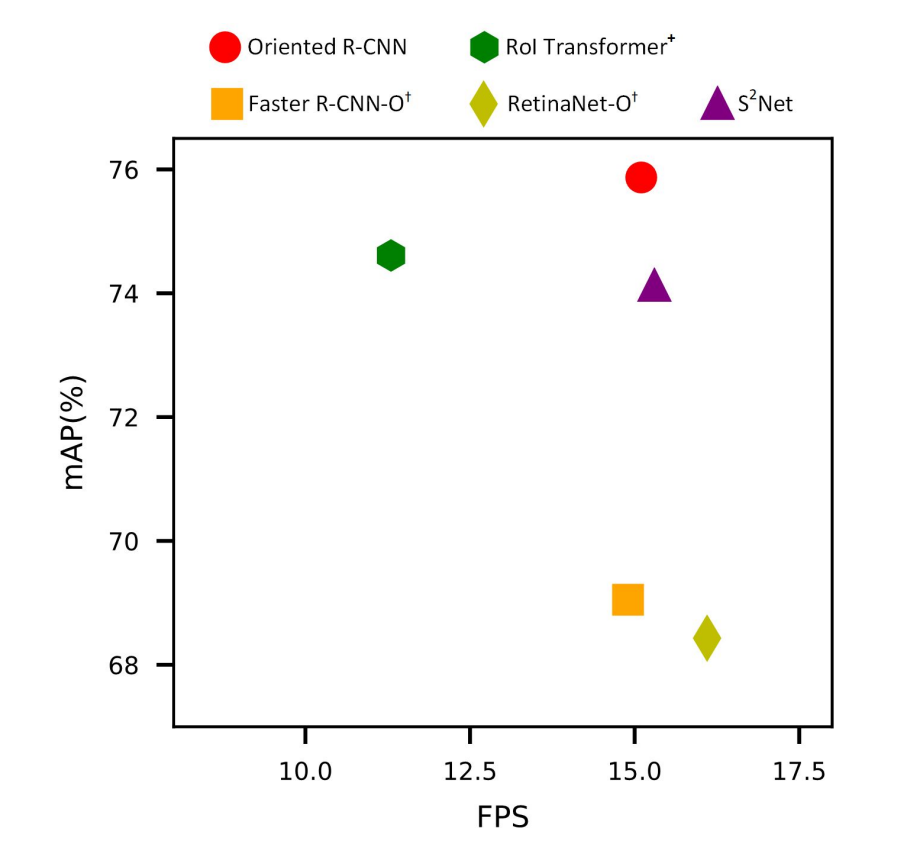
- Midpoint Offset Representation improves precision while reducing complexity.
- Rotated RoI Align significantly enhances feature extraction accuracy.
- Oriented R-CNN outperforms prior models with lower computational costs.
Conclusion
Instead of simply aiming for higher accuracy, this study highlights the importance of designing efficient resource utilization strategies. It made me realize that designing detection models should not be only focused on accuracy hundered percent but also about making practical efficiency This research serves as a strong reference for future works seeking to balance detection precision with computational feasibility.
References
Xie X, et al. (2021). Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv48922.2021.00350
