Kaggle을 보다보면 Cross-Validation의 함수인 train_test_split를 자주 사용하는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이러한 취지의 기본적인 목적은 Overfitting(과적합) 을 피하는 것이다.
- train_set == test_set인 경우 : 과적합이 생겨 새로운 test에 대하여 오류 발생 가능성이 높아짐
- train_set != test_set인 경우 : 과적합을 피할 수 있는 장점이 존재한다.
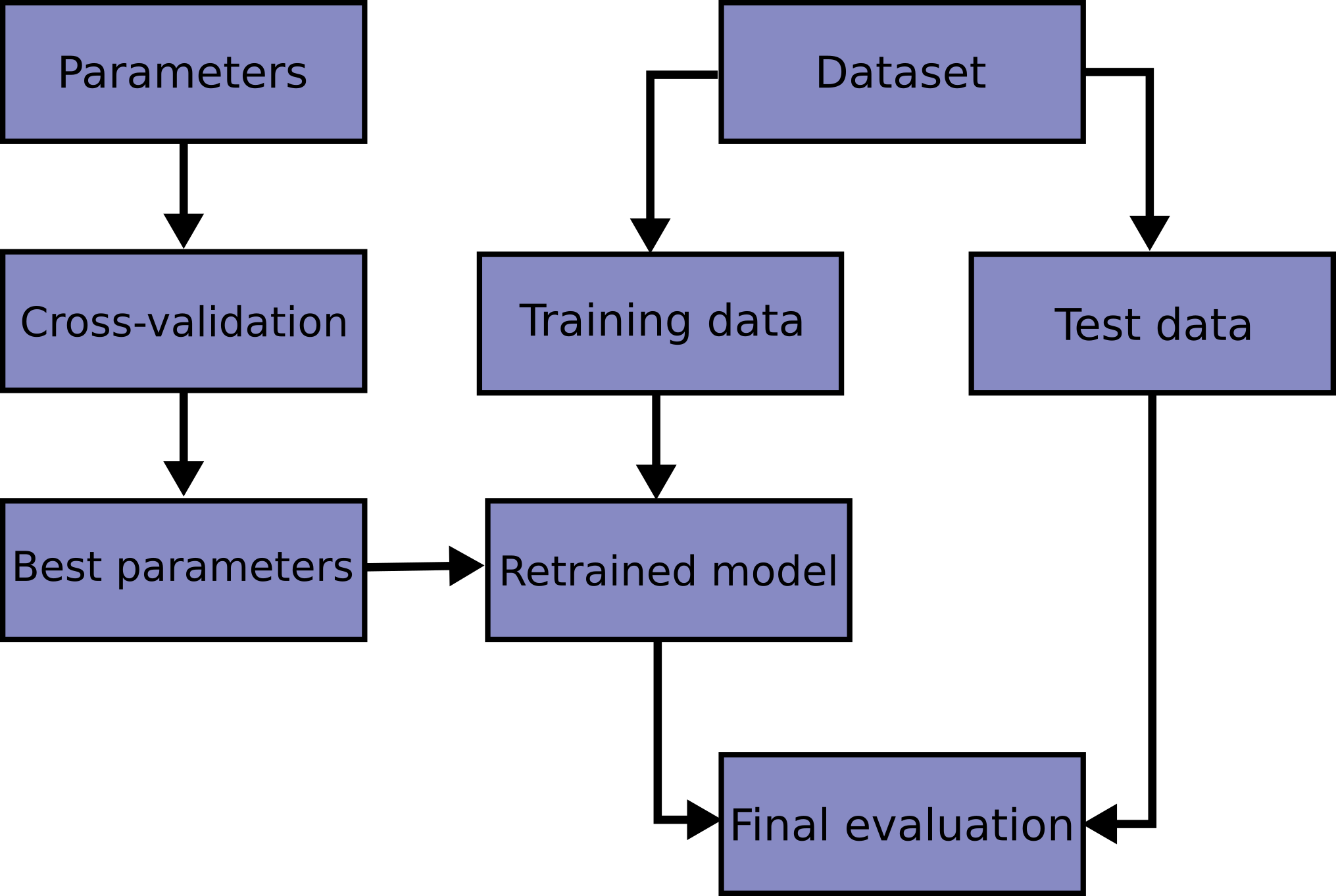
- Hyper Parameter(매개변수)를 최적화하는 흐름을 보면 교차 검증을 통해서 적합한 Parameter를 찾는 것을 알 수 있다.
과적합을 피하는 것은 최적의 매개변수를 구하는 것이라고 할 수 있다.
1. 교차 검증에 대하여
X, y = datasets.load_iris(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4, random_state=0)
clf = smv.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1).fit(X_train, y_train)
clf.score(X_test, y_test)- 데이터 셋에서 train : test = 6 : 4의 형태로 나누고 svm 모델에서 학습할 수 있다.
- 그러나, 우리가 데이터셋을 아무리 잘 섞고 테스트 해도 모델을 학습하는 과정에서 Parameter를 찾는 과정이 부족하다면 학습 모델에서 파라미터를 지정하기가 어렵다.
- 이러한 배경에서 교차검증이 등장하게 되었고 cross-validation의 방법 중 하나인 k-fold가 대표적인 예이다.
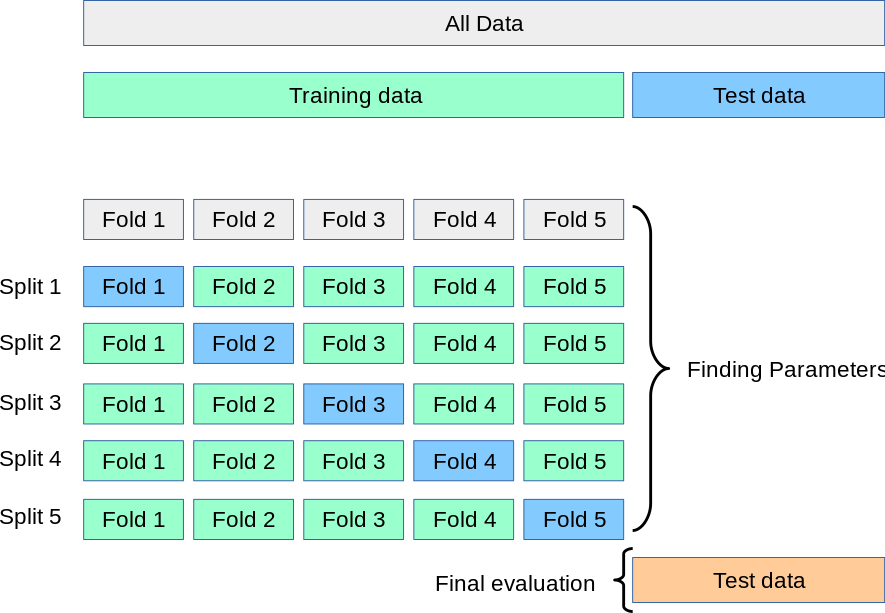
k=5 일 때
1. train_set을 5개로 나눠 5번을 순환해 test_set을 늘려주는 방식이다.
2. k-fold 교차검증이라고 부르면 반복과정에 평균 값을 사용하게 된다.
3. 비용이 크지만 데이터가 크지 않을 때 사용하면 좋다.
2. 교차 검증이 잘되었는지 확인하기(점수 계산 방법)
- 교차 검증이 잘 진행되었는지 알 수 있는 방법은 cross_val_score를 사용하는 방법이 있다.
기본 cross_val_score 형태
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1, random_state=42)
scores = cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=5)
scores- cv 값을 지정해서 k-fold를 횟수를 명시할 수 있다.
성능 나타내기
1. scores.mean()과 scores.std()를 출력하며 성능을 나타낼 수 있다.
2. metrics 지정을 통한 성능 도출
scores = cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=5, scoring='f1_macro')
scores- 이외 Scoring Parameter를 상세하게 나타나 있으니 틈틈히 공부하면 좋을 것 같다.
ShuffleSplit 사용하기
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
cv = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=5, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=cv)나만의 교차 검증 함수 만들기
def custom_cv_2folds(X):
n = X.shape[0]
while i <= 2:
idx = np.arange(n * (i-1)/2, n*i/2, dtype=int)
yield idx, idx
i += 1
custom_cv = custom_cv_2folds(X)
cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=custom_cv)3. 교차 검증 반복자(Cross Validation Iterators)
K-fold
K-fold는 앞서 설명한 것처럼 샘플을 K개의 그룹으로 나눠 K-1개를 훈련할 때 사용하고 나머지 하나는 테스트를 위해 사용한다.
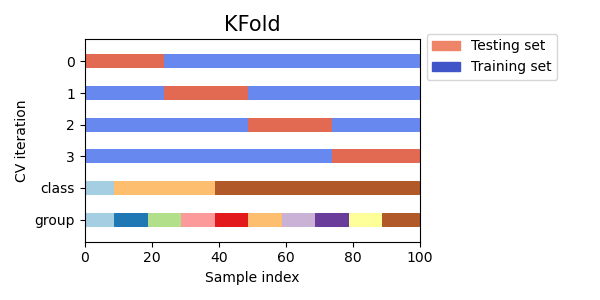
기본 K-Fold
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
kf = KFold(n_splits=2)
for train, test in kf.split(X):
print("%s %s" % (train, test))반복되는 K-Fold
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedKFold
X = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [1, 2], [3, 4]])
random_state = 12883823
rkf = RepeatedKFold(n_splits=2, n_repeats=2, random_state=random_state)
for train, test in rkf.split(X):
print("%s %s" % (train, test))Leave One Out (LOO)
LOO는 하나를 제외한 모든 샘플을 생성하는 방식으로 가장 간단한 교차검증 방식이다.
from sklearn.model_selection import LeaveOneOut
X = [1, 2, 3, 4]
loo = LeaveOneOut()
for train, test in loo.split(X):
print(train, test)기존 K-Fold 방식과 거의 비슷하지만
- k가 엄청 클 경우 : (k-1)n/k 보다 더 심플하다
- k가 작을 경우 : K-Fold보다 비용이 크다.
Leave P Out (LPO)
LPO는 One -> P가 된 것으로 P=2이면 2개를 아웃시킨다는 의미이다. (p > 1)
from sklearn.model_selection import LeavePOut
X = np.ones(4)
lpo = LeavePOut(p=2)
for train, test in lpo.split(X):
print(train, test)Shuffle & Split으로 랜덤 교차검증하기
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
X = np.arange(10)
ss = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=5, test_size=0.25, random_state=0)
for train_index, test_index in ss.split(X):
print(train_index, test_index)상기 내용은 기존 Scikit-Learn을 참고하여 정리하였습니다.
