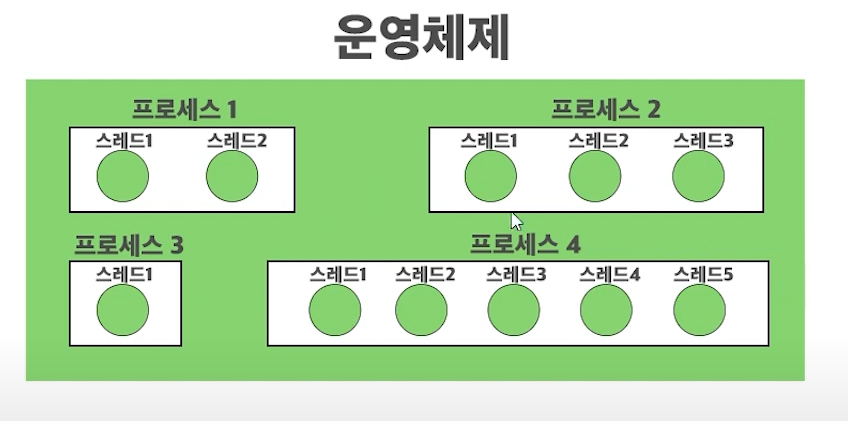
프로세스
운영체제안에서실행되는 프로그램실행 파일담긴데이터 및 코드가메모리에적재되어동작하는 것프로세스는 반드시하나 이상의쓰레드로 구성
쓰레드
- 운영체제가
CPU에 시간을 할당(일을 시키는)하는기본 단위- 운영체제가 명령어를 실행하기 위한
스케줄링 단위- 과거까지의 프로그래밍은
main 쓰레드를 사용한단일 쓰레드 프로그래밍- 쓰레드를 배우면
멀티 쓰레드 프로그래밍을 할 수 있게 된다.
멀티 쓰레드 프로그래밍
장점
- 장점1:
동시에여러 작업가능
- 복사에 5분이 소요되는 작업을 수행할 때, 싱글 쓰레드의 경우 아무것도 못함
- 취소도 못함
- 멀티 쓰레드의 경우 복사 하며 취소 or 다른 작업 수행 가능
- 장점2:
데이터 공유가 쉽다.
프로세스간 데이터 공유 난이도 >> (넘사벽) >>쓰레드간 데이터 공유 난이도프로그램간 데이터 공유를 위해서는소켓등 번거로운 구조 필요- 장점3:
메모리 절약
- 새 프로세스를 만드는 것 보다 메모리 소모가 적다.
단점
- 단점1: 구현이 빡쌤
- 코드의 순서가 순차적으로 진행되지 않음
쓰레드 간 우선순위에 따라자원(CPU)를선점하고,반납하며 프로세스가 돌아가기 때문- 단점2: 소프트웨어 안정성이 낮아짐
- 프로세스 종료 시, 자기 것만 꺼짐(독립적)
- 쓰레드는 여러 쓰레드와
유기적으로 연결되어 있어서, 문제가 생기면프로그램이 중단- 단점3: 성능 저하
- 스케줄러: 스케줄링에 따라 쓰레드가 일을 함
- Context Switching(문맥 교환)
- CPU는 실행중인 쓰레드의 정보(중단 쓰레드, 실행 쓰레드, 중단(재개) 지점 등)를 담음
- 이런 정보를 받는 것 자체도 비용을 소모하고 메모리를 쓰기 때문에 성능 저하가 발생
- context switching이 잦을수록 비용이 발생해 성능이 저하됨


-
유니티에선메인 로직이 하나이고,코루틴이Thread의 개념을 수행한다. -
하나의 쓰레드로 만들어 놓은 이유
- 장점: 멀티 쓰레드 시, 문제에서 벗어날 수 있음
- Race Condition: 두 개 이상의 스레드가 공유된 자원이 동시에 접근하려 할 때 발생하는 문제
접근 순서에 따라코드 실행 순서가 달라짐코드 실행 순서가 달라짐에 따라결과가 달라질 수 있음
- 동기화 이슈(Synchronization Issues): 레이스 컨디션을 방지하기 위해 Lock을 사용해서 공유 자원을 동기화하는 방식
- 교착상태(Dead Lock): 두 스레드 모두 다른 스레드가 원하는 자원(CPU)를 선점한 채로, 다른 스레드의 자원을 대기하는 현상
- Race Condition: 두 개 이상의 스레드가 공유된 자원이 동시에 접근하려 할 때 발생하는 문제
- 장점: 멀티 쓰레드 시, 문제에서 벗어날 수 있음
-
thread.cs
- PositionCheck는 main thread에서만 불릴 수 있음
Unity는하나의 Thread(Unity Main Thread)로만 접근 가능유니티 메인 쓰레드에선 UnityEngine에서 제공하는 기능을 다 쓸 수 있음- 이런 식으로 Thread를 따로 만들어서 쓰면, 유니티 내부 기능을 사용 불가
- 그래서
Unity에선Coroutine을 사용한다. - 단,
꼼수가 존재 -> 다음시간에...
- 그래서
using UnityEngine; using System.Threading; public class Thread: MonoBehaviour { Thread thread = new Thread(PositionCheck); thread.Start(): } void PositionCheck() { Debug.Log(transform.position); }
멀티 쓰레드
전처리 구문using System.Threading;
Thread.CurrentThread;
- 현재 Thread 반환
Thread thread1 = Thread.CurrentThread;
thread.ThreadState
- 해당 스레드의 상태 반환
Unstarted//Thread.Start호출 전Running//Thread.Start호출 후(스레드 실행 상태)Suspended//Thread.Suspend호출 후
Thread.Resume호출 시 RunningWaitSleepJoin//Thread.interrupt호출 후Aborted//Thread.Abort호출 후Stopped// 스레드가중지될 때Background// 스레드가백그라운드로 동작 중일 때Debug.Log(thread1.ThreadState);
Thread 선언법1Thread thread2; thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Temp)); thread2.Start(); void Temp() { Debug.Log("쓰레드 시작"); Debug.Log(thread2.ThreadState); Thread.Sleep(2000);//2초동안 쓰레드 중지 Debug.Log("쓰레드 종료"); }
Thread 선언법2//선언법3 Thread thread3; thread3 = new Thread(Temp); thread3.Start(); void Temp() { Debug.Log("쓰레드 시작"); Debug.Log(thread2.ThreadState); Thread.Sleep(2000);//2초동안 쓰레드 중지 Debug.Log("쓰레드 종료"); } //매개변수도 전달하는 방법 void Temp2(object num) { Debug.Log("쓰레드 시작"); Debug.Log(thread2.ThreadState); Thread.Sleep(2000);//2초동안 쓰레드 중지 Debug.Log(num); Debug.Log("쓰레드 종료"); }
Thread 선언법3Thread thread4; thread4 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(Temp2)); thread4.Start(10);
Thread 선언법4//매개변수 쓰레드 선언법 Thread thread5; Data data = new Data(1, 2f, "Test"); thread5 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(Temp3)); thread5.Start(data); void Temp3(object datas) { Data data = (Data)datas; Debug.Log("쓰레드 시작"); Debug.Log(thread2.ThreadState); Thread.Sleep(2000);//2초동안 쓰레드 중지 Debug.Log(data.a + data.b + data.c); Debug.Log("쓰레드 종료"); } public class Data { public int a; public float b; public string c; public Data() { a = 0; b = 0f; c = ""; } public Data(int a, float b, string c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }
Thread 실행 순서
Join()
Join(): 현재 쓰레드가 Join()을 호출한 다른 쓰레드의 작업이 완료될 때까지대기하도록 함
프로그램 실행 순서
Thread1 시작 -> Thread2 시작 -> Thread2 끝 -> Join 완료public class MultiThread2 : MonoBehaviour { private Thread thread1, thread2; void Start() { thread1 = new Thread(Thread1Function); thread1.Start(); } private void Thread1Function() { Debug.Log("Thread1 시작"); thread2 = new Thread(Thread2Function); thread2.Start(); thread2.Join(); Debug.Log("Join 완료."); } private void Thread2Function() { Debug.Log("Threa2 시작"); Thread.Sleep(2000); //2초동안 쓰레드 대기 Debug.Log("Thread2 끝"); } }
Abork & Interrupt
void ThreadFunction() { try { Debug.Log("스레드 시작"); Thread.Sleep(5000); Debug.Log("스레드 종료"); } catch (ThreadAbortException)//예외 발생 시, 실행 구문1 { Debug.Log("스레드 강제 종료"); } catch (ThreadInterruptedException)//예외 발생 시, 실행 구문2 { Debug.Log("스레드 WaitSleepJoin"); } }
Abort
Abort(): 코드 실행 즉시바로 강제 종료ThreadAbortException 예외를 발생시키고 쓰레드 강제 종료- 위험성이 크기 때문에, interrupt를 사용하는 것이 좋음
Interrupt
Interrupt(): 현재 스레드가Wait/Sleep/Join상태가 되면 종료ThreadInterruptedException 예외를 발생시키고 쓰레드 종료
private void Update() { if(Time.timeSinceLevelLoad > 2f)//2초 후 { thread1.Abort(); thread1.Interrupt(); } }
Background & Forward Thread
Background Thread
- 스레드 실행, 종료에 영향을 미치지 않는 스레드
thread.IsBackground = true를 통해백그라운드 화
Forward Thread
- 기본 스레드도
Forward Thread- 프로그램 실행, 종료에 영향을 미침
thread.IsBackground = false를 통해포그라운드 화
class Program { static void MainThread() { while (true) Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!"); } static void Main(string[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(MainThread); thread.IsBackground = true; thread.Start(); Console.WriteLine("대기중"); Console.WriteLine("스레드 종료"); } }
스레드 상태
- 스레드는 아래의 상태를 지닌다.
Running = 0, StopRequested = 1, SuspendRequested = 2, Background = 4, Unstarted = 8, Stopped = 16, WaitSleepJoin = 32, Suspended = 64, AbortRequested = 128, Aborted = 256상태 별 스레드 실행 순서
* #1. UnStarted * Unstarted * -Thread.Start(); * Running* #2. Suspended * Running * -Thread.Suspend(); * Suspended * -Thread.Resume(); * Running* #3.WaitSleepJoin * Sleep: 스레드가 특정 ms만큼 대기 * Join: 다른 스레드가 실행이 끝날 때까지 대기 * Running * -Monitor.Wait();/Thread.Sleep();/Thread.Join(); * WaitSleepJoin * -Monitor.Pulse();/Monitor.PulseAll();/Thread.Sleep(); Return/Thread.Join(); Return * Running* #4. Aborted * -스레드 취소 상태 * Running * -Thread.Abort(); * Aborted(ThreadAbortException) * Stopped* #5. Foreground Thread * -프로세스 수명에 영향을 줌* #6. Background Thread * -프로세스 수명에 영향을 주지 않음* #7. Interrupt * -스레드가 작동되다 호출되면, 계속 돌아가고, WaitSleepJoin 상태가 되면 중단 * Running * -Thread.Interrupt(); * Running * -Thread.Sleep(); * WaitSleepJoin; * Stopped()
스레드풀
스레드풀: 스레드 오브젝트 풀풀: 사용할 수 있는 자원의 집합스레드 동작 방식
상시 실행 스레드
- 스레드가 생성되면 비교적 오랜 시간동안 생성되는 방식
- 무한 루프 스레드
void AllTimeThread() { while (true) { ... } }
일회성 임시 실행 스레드
- 특정 연산만을 수행하고 바로 종료되는 스레드
- 무한 루프가 존재하지 않음
new를 통해 스레드를 만들어성능에 좋지 않음ThreadPool을 사용하는 이유void OnceTempExcuteThread() { //계산... //끝 }
- 사용법
- 운영체제가 알아서 스레드를
생성,시작,관리,재사용
- thread를 생성할 필요가 없다.
- thread.Start()를 호출할 필요가 없다.
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(delegate function);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(delegate function, Params param);private void Start() { //새로운 스레드 생성이 없다. ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(TestThreadPool); //상시실행 스레드: Thread.Start()가 없다. Thread threadAllTime = new Thread(AllTimeThread); //일회성 임시 실행 스레드: Thread threadOnceTempExecute = new Thread(OnceTempExcuteThread); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(TestParamThreadPool, 1); } //매개변수가 없는 스레드풀 private void TestThreadPool(object value) { Debug.Log("스레드를 시작"); } //매개변수가 있는 스레드풀 private void TestParamThreadPool(object value) { Debug.Log($"{value}번 째 스레드풀"); }