Text Processing and training with machine learning models or LSTM or BERT
MachineDeepLearning
You might find this link useful for tabular task Tabular Task Machine Learning and Deep Learning
This Blog was mainly helped from the 무료특강 AICE Professional google colab code
Text Processing
Using Machine Learning for sentiment classification
Downloading file from github directory
# AI-HUB 감성 대화 말뭉치 활용하여 만든 데이터 읽어오기
data = pd.read_csv('[github website]' )
# for example
data = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/ohgzone/file1/raw/main/aihub_coupus.csv' )Downloading font for matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rc('font', family='NanumBarunGothic')Read csv file
data = pd.read_csv('./directory/file.csv')checking dataframe
data.head()
# .info() can obtain:
"""
The df.info() function in Pandas provides a concise summary of a DataFrame. It includes:
Index Range – The number of entries (rows).
Column Names – The names of all columns.
Non-null Counts – The number of non-missing (non-null) values in each column.
Data Types – The data type (int64, float64, object, etc.) of each column.
Memory Usage – The estimated memory usage of the DataFrame.
"""
data.info()
data.tail()data.info() output
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {
"Name": ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", None],
"Age": [25, 30, 35, 40],
"Salary": [50000.0, 60000.0, None, 80000.0]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Display DataFrame info
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 4 entries, 0 to 3
Data columns (total 3 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Name 3 non-null object
1 Age 4 non-null int64
2 Salary 3 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 228.0 bytes
finding the null values/duplicated values in certain column
data.isnull().sum()
data['column_name'].isnull().sum()
# Erase row
data_cleaned = data.dropna(how='all') # if all values are null
data_cleaned = data.dropna(subset=['column_name']) # certain column has null value
data.dropna(inplace=True, subset=['column_name']) # modify the original dataframe in place
# Erase duplicated rows in certain column
data['column_name'].duplicated().sum()
# data.drop_duplicates(subset=['column_name'], inplace=True)
# the default of .drop_duplicates() has keep='first'
# If only column_name is considered for duplication and other columns have different values, only the first occurrence of each unique value in column_name is kept, while the others are dropped.Distribution of certain column in table/barplot
data['column_name'].value_counts()
data['column_name'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar')Ploting histogram of the label value_counts
data['감정'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar')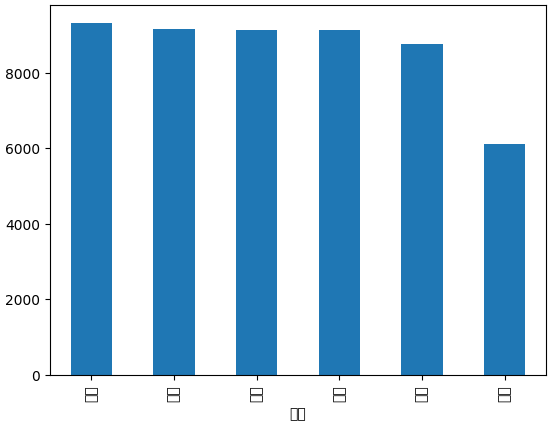
Preprocessing sentences
Preprocessing sentences (deleting spaces at both ends)
data['문장'] = data['문장'].str.strip()Preprocessing sentences (merging large space into one ' ')
data['문장'] = data['문장'].apply(lambda x: " ".join(x.split()))(Optional - Korean) Preprocessing sentences (Deleting special keys)
# find if there are any special keys or letters other than korean
data[data['문장'].str.contains('[^가-힣 ]')].values[:10]
# delete any words or letters that are not korean
data['문장'] = data['문장'].str.replace('[^가-힣 ]','', regex=True)
# Search if there are any sentences that contains letters other than korean
data['문장'][data['문장'].str.contains('[^가-힣 ]')].sum()(Optional - English) Preprocessing sentences (Deleting special keys)
# Find if there are any special keys or letters other than English
data[data['문장'].str.contains('[^A-Za-z ]')].values[:10]
# Delete any characters that are not English letters or spaces
data['문장'] = data['문장'].str.replace('[^A-Za-z ]', '', regex=True)
# Search if there are any sentences that contain letters other than English
data['문장'][data['문장'].str.contains('[^A-Za-z ]')].sum()(Optional - English and Korean) Preprocessing sentences (Deleting special keys)
# Find if there are any special keys or letters other than English & Korean
data[data['문장'].str.contains('[^A-Za-z가-힣 ]')].values[:10]
# Delete any characters that are not English or Korean letters or spaces
data['문장'] = data['문장'].str.replace('[^A-Za-z가-힣 ]', '', regex=True)
# Search if there are any sentences that contain letters other than English & Korean
data['문장'][data['문장'].str.contains('[^A-Za-z가-힣 ]')].sum()(Optional - English) Preprocessing sentences (Lowercasing)
data['문장'] = data['문장'].str.lower()LabelEncoder - encoding labels into numbers
# 라벨와 클래스을 매핑 작업
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
encoder = LabelEncoder()
data['감정'] = encoder.fit_transform(data['감정'])
encoder.classes_
final_data.tail()
감정 문장
51625 2 나이가 먹고 이제 돈도 못 벌어 오니까 어떻게 살아가야 할지 막막해 능력도 없고
51626 3 몸이 많이 약해졌나 봐 이제 전과 같이 일하지 못할 것 같아 너무 짜증 나
51627 4 이제 어떻게 해야 할지 모르겠어 남편도 그렇고 노후 준비도 안 되어서 미래가 걱정돼
51628 3 몇십 년을 함께 살았던 남편과 이혼했어 그동안의 세월에 배신감을 느끼고 너무 화가 나
51629 4 남편과 결혼한 지 사십 년이야 이제 사람 만나는 것도 버겁고 알던 사람도 점점 사라져
Obtaining values as array in dataframe
obtain features and labels
#Examples) Obtaining features and labels as array/s
features = data['문장'].values
labels = data['감정'].valuesobtain max/avg length of the sentence, histogram
print('Max number of characters in single sentence:{}'.format(max(len(l) for l in features)))
print('Avg number of characters in sentences :{}'.format(sum(map(len, features))/len(features)))
plt.hist([len(s) for s in features], bins=50)
plt.xlabel('length of samples')
plt.ylabel('number of samples')
plt.show()plotting histogram of the length of sentences
plt.hist([len(s) for s in features], bins=50)
plt.xlabel('length of samples')
plt.ylabel('number of samples')
plt.show()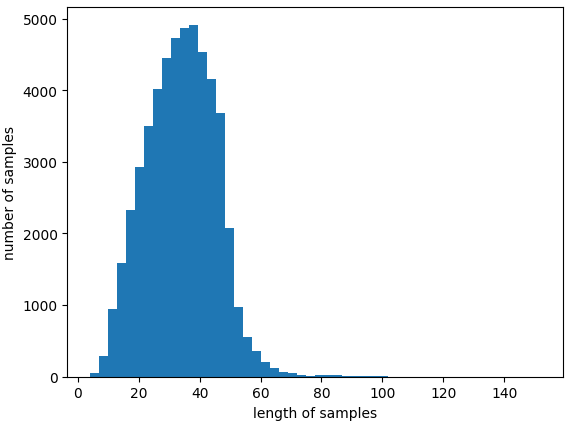
prune dataset to have same dataset number
# Count class distribution
class_counts = df['label'].value_counts()
min_count = class_counts.min()
# Undersample majority class
df_balanced = df.groupby('label').sample(n=min_count, random_state=42)delete items conditioned on certain label
keep only Male & Female
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
data = {'gender': ['Male', 'Female', 'Other', 'Unknown', 'Male', 'Female', 'Non-Binary'],
'age': [25, 30, 22, 40, 35, 29, 26]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Keep only rows where gender is "Male" or "Female"
df = df[df['gender'].isin(['Male', 'Female'])]
# Display cleaned DataFrame
print(df)seperating trainset and testset
train_test_split(features, labels, test_size = 0.2, stratify = labels, random_state = 42)
"stratify=labels" option enables the seperation to preserve the distribution of dataset in terms of labels
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, labels , test_size=0.2, stratify=labels, random_state=41)
x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shapeChanging sentence in to sparse matrix (TF-IDF)
Apply TF-IDF to the test using the one fitted to the train dataset
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
TF_IDF = TfidfVectorizer()
x_train_v = TF_IDF.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test_v = TF_IDF.transform(x_test)
# 각 라인의 각 단어에 대한 TF-IDF 값 표현
print(x_train_v)
(0, 7693) 0.111187811269913
(0, 13709) 0.18855847419928837
(0, 13176) 0.39919262490035207
(0, 42487) 0.34419359480238104
(1, 7358) 0.18117439292798176
(1, 10229) 0.37305687876063215
(1, 34322) 0.36171558646285557
(1, 23164) 0.3193145358690778
(1, 37279) 0.35397733348891164
(1, 37377) 0.3006716005267158
# 학습데이터셋의 TF-IDF 매트릭스 확인하기 : 41259 라인, 47366 단어
x_train_v.shape
(41259, 47366)Machine Learning model
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rf = RandomForestClassifier()
fr.fit(x_train_v, y_train)
rf.score(x_test_v, y_test)
0.4988851187590887
Try prediction
# 출력 결과 해석 : (0, 44327) 0.241660101642553
# 0 : 첫라인, 44327 : 단어에 맵핑된 번호, 0.241660101642553 : tf-idf 계산 값
print(f'검증데이터셋의 첫번째 TF-IDF : {x_test_v[0]}')
검증데이터셋의 첫번째 TF-IDF : (0, 10803) 0.26743393755207734
(0, 11829) 0.5118450810111637
(0, 12582) 0.20749688472303796
(0, 13416) 0.42025584693136303
(0, 21156) 0.36669996163564406
(0, 28457) 0.31179323030597017
(0, 33660) 0.2448445072222418
(0, 41703) 0.31111324348104824
(0, 44327) 0.241660101642553
print(f'검증데이터셋의 첫번째 TF-IDF 역변환 : {tfidf.inverse_transform(x_test_v[:1])}')
검증데이터셋의 첫번째 TF-IDF 역변환 : [array(['돈이', '든다는', '때문에', '만나기가', '사실', '어려워', '일을', '친구들은', '하는'],
dtype='<U22')]
# RandomForest 모델로 예측하기
predict = rfc.predict(x_test_v[:1])
predict, encoder.inverse_transform(predict)
(array([4]), array(['상처'], dtype=object))
(번외) Other machine learning models
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# Define different models
models = {
"RandomForest": RandomForestClassifier(),
"LogisticRegression": LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000), # Works well with sparse data
"SVM": SVC(),
"NaiveBayes": MultinomialNB(), # Designed for sparse text data (TF-IDF)
"KNN": KNeighborsClassifier(),
"DecisionTree": DecisionTreeClassifier()
}
# Train and evaluate each model
scores = {}
for name, model in models.items():
model.fit(x_train_v, y_train) # Train model
score = model.score(x_test_v, y_test) # Evaluate model
scores[name] = score
print(f"{name} Accuracy: {score:.4f}") # Print accuracy scoreGirdSearchCV for NaiveBayes model
Using GridSearchCV for Hyperparameter Tuning on Naive Bayes (MultinomialNB)
Since MultinomialNB is commonly used for text classification with TF-IDF sparse matrices, we can tune its main hyperparameter alpha (smoothing factor).
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# Define the Naive Bayes model
nb_model = MultinomialNB()
# Define hyperparameters to tune
param_grid = {
'alpha': [0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0] # Alpha controls Laplace smoothing
}
# Perform GridSearchCV
grid_search = GridSearchCV(nb_model, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=-1, verbose=1)
grid_search.fit(x_train_v, y_train) # Fit on sparse matrix (TF-IDF)
# Best hyperparameters
print("Best Parameters:", grid_search.best_params_)
# Best model score
print("Best Cross-Validation Score:", grid_search.best_score_)
# Test score on the best model
best_nb = grid_search.best_estimator_
test_score = best_nb.score(x_test_v, y_test)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_score)
Explanation
alpha: Controls Laplace smoothing (prevents zero probabilities for unseen words).
cv=5: Uses 5-fold cross-validation for robust evaluation.
scoring='accuracy': Optimizes for classification accuracy.
n_jobs=-1: Uses all CPU cores for faster computation.
verbose=1: Shows progress updates.
✅ Why use MultinomialNB?
It’s fast, especially on large text datasets.
Works well with TF-IDF sparse matrices.
The alpha hyperparameter affects classification performance.
Fitting 5 folds for each of 6 candidates, totalling 30 fits
Best Parameters: {'alpha': 1.0}
Best Cross-Validation Score: 0.4837005405945888
Test Accuracy: 0.4928744546776539
GridSearchCV Runtime: 2.78 seconds
RandomizedSearchCV for NaiveBayes model
Using RandomizedSearchCV for Hyperparameter Tuning on Naive Bayes (MultinomialNB)
RandomizedSearchCV is a faster alternative to GridSearchCV because it randomly samples a subset of hyperparameters instead of testing all possible combinations.
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
import numpy as np
# Define the Naive Bayes model
nb_model = MultinomialNB()
# Define the hyperparameter search space
param_dist = {
'alpha': np.linspace(0.1, 10, 50) # Randomly search from 50 values between 0.1 and 10
}
# Perform RandomizedSearchCV
random_search = RandomizedSearchCV(
nb_model, param_distributions=param_dist,
n_iter=10, cv=5, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=-1, verbose=1, random_state=42
)
# Fit on sparse matrix (TF-IDF)
random_search.fit(x_train_v, y_train)
# Best hyperparameters
print("Best Parameters:", random_search.best_params_)
# Best model score
print("Best Cross-Validation Score:", random_search.best_score_)
# Test score on the best model
best_nb = random_search.best_estimator_
test_score = best_nb.score(x_test_v, y_test)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_score)Key Differences from GridSearchCV
✅ Randomly samples hyperparameters, making it faster for large datasets.
✅ n_iter=10 → Tests only 10 random combinations (instead of all).
✅ Uses np.linspace(0.1, 10, 50) to randomly sample alpha values from a wider range.
✅ Best for quick tuning when searching over large parameter spaces.
Fitting 5 folds for each of 10 candidates, totalling 50 fits
Best Parameters: {'alpha': 2.7265306122448982}
Best Cross-Validation Score: 0.4753871458933311
Test Accuracy: 0.48841492971400874
RandomSearchCV Runtime: 1.33 seconds
GirdSearchCV for Logistic Regression model
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# Define the Logistic Regression model
log_reg = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
# Define hyperparameters to tune
param_grid = {
'C': [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100], # Regularization strength
'solver': ['liblinear', 'lbfgs'], # Optimization algorithm
}
# Perform GridSearchCV
grid_search = GridSearchCV(log_reg, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=-1, verbose=1)
grid_search.fit(x_train_v, y_train) # Fit on sparse matrix (TF-IDF)
# Best hyperparameters
print("Best Parameters:", grid_search.best_params_)
# Best model score
print("Best Cross-Validation Score:", grid_search.best_score_)
# Test score on the best model
best_log_reg = grid_search.best_estimator_
test_score = best_log_reg.score(x_test_v, y_test)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_score)Fitting 5 folds for each of 10 candidates, totalling 50 fits
Best Parameters: {'C': 1, 'solver': 'liblinear'}
Best Cross-Validation Score: 0.5130516355690197
Test Accuracy: 0.528065923412506
GridSearchCV Runtime: 209.11 seconds
RandomizedSearchCV for Logistic Regression model (worked best for TF-IDF data)
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
import numpy as np
# Define the Logistic Regression model
log_reg = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
# Define hyperparameter distributions
param_dist = {
'C': np.logspace(-3, 3, 10), # Randomly search from 10 values between 0.001 and 1000
'solver': ['liblinear', 'lbfgs']
}
# Perform RandomizedSearchCV
random_search = RandomizedSearchCV(
log_reg, param_distributions=param_dist,
n_iter=10, cv=5, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=-1, verbose=1, random_state=42
)
random_search.fit(x_train_v, y_train) # Fit on sparse matrix (TF-IDF)
# Best hyperparameters
print("Best Parameters:", random_search.best_params_)
# Best model score
print("Best Cross-Validation Score:", random_search.best_score_)
# Test score on the best model
best_log_reg = random_search.best_estimator_
test_score = best_log_reg.score(x_test_v, y_test)
print("Test Accuracy:", test_score)Fitting 5 folds for each of 10 candidates, totalling 50 fits
Best Parameters: {'solver': 'lbfgs', 'C': 2.154434690031882}
Best Cross-Validation Score: 0.5098280277194915
Test Accuracy: 0.5220552593310712
RandomSearchCV Runtime: 280.26 seconds
Fitting 2 folds for each of 10 candidates, totalling 20 fits
Best Parameters: {'solver': 'lbfgs', 'C': 0.6951927961775606}
Best Cross-Validation Score: 0.49480112812681026
Test Accuracy: 0.5251575375666505
RandomSearchCV Runtime: 95.86 seconds
If you want to eliminate cross validation change cv=5 to cv=2
Full pipeline example
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, RandomizedSearchCV
# Load dataset
final_data = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/ohgzone/file1/raw/main/aihub_coupus.csv')
# Remove non-Korean characters
final_data['문장'] = final_data['문장'].str.replace('[^가-힣 ]', '', regex=True)
final_data['문장'] = final_data['문장'].str.strip()
# Remove duplicates
final_data.drop_duplicates(subset=['문장'], inplace=True)
# Encode labels
encoder = LabelEncoder()
final_data['감정'] = encoder.fit_transform(final_data['감정'])
# Split dataset into features (X) and labels (y)
features = final_data['문장'].values
labels = final_data['감정'].values
# Train-test split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, labels, test_size=0.2, stratify=labels, random_state=41)
# Convert text data to TF-IDF sparse matrix
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer()
x_train_v = tfidf.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test_v = tfidf.transform(x_test)
# Train RandomForest model
rfc = RandomForestClassifier()
rfc.fit(x_train_v, y_train)
random_forest_score = rfc.score(x_test_v, y_test)
# Define Logistic Regression model
log_reg = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
param_dist = {
'C': np.logspace(-3, 3, 20), # Search for C values from 0.001 to 1000
'solver': ['liblinear', 'lbfgs']
}
# Perform RandomizedSearchCV
random_search = RandomizedSearchCV(
log_reg, param_distributions=param_dist,
n_iter=10, cv=2, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=-1, verbose=1, random_state=42
)
# Train and time RandomizedSearchCV
start_time = time.time()
random_search.fit(x_train_v, y_train)
end_time = time.time()
runtime = end_time - start_time
# Extract best model and evaluate on test data
best_log_reg = random_search.best_estimator_
test_score = best_log_reg.score(x_test_v, y_test)Preprocessing sentences for LSTM/BERT
Necessary libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pdReading dataset from csv file
# AI-HUB 감성 대화 말뭉치 활용하여 만든 데이터 읽어오기
final_data = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/ohgzone/file1/raw/main/aihub_coupus.csv' )
# 총 51,630건
final_data.info()delete unnecessary characters
# '문장' 컬럼의 내용중에 영문, 특수문자 있는지 확인 : 영문과 특수문자 존재 확인
final_data[final_data['문장'].str.contains('[^가-힣!? ]')].values[:10]
array([['분노', '일은 왜 해도 해도 끝이 없을까? 화가 난다.'],
['분노', '이번 달에 또 급여가 깎였어! 물가는 오르는데 월급만 자꾸 깎이니까 너무 화가 나.'],
['분노', '회사에 신입이 들어왔는데 말투가 거슬려. 그런 애를 매일 봐야 한다고 생각하니까 스트레스 받아. '],
['분노', '직장에서 막내라는 이유로 나에게만 온갖 심부름을 시켜. 일도 많은 데 정말 분하고 섭섭해.'],
['분노', '얼마 전 입사한 신입사원이 나를 무시하는 것 같아서 너무 화가 나.'],
['분노', '직장에 다니고 있지만 시간만 버리는 거 같아. 진지하게 진로에 대한 고민이 생겨.'],
['분노', '성인인데도 진로를 아직도 못 정했다고 부모님이 노여워하셔. 나도 섭섭해.'],
['기쁨', '퇴사한 지 얼마 안 됐지만 천천히 직장을 구해보려고.'],
['불안', '졸업반이라서 취업을 생각해야 하는데 지금 너무 느긋해서 이래도 되나 싶어.'],
['기쁨', '취업해야 할 나이인데 취업하고 싶지가 않아.']], dtype=object)
# '문장' 컬럼의 내용에서 숫자, 영문자, 특수문자등의 글자는 삭제처리
final_data['문장'] = final_data['문장'].str.replace('[^가-힣!? ]','', regex=True)
# '문장' 컬럼의 내용에서 영문, 특수문자 없음 확인
final_data['문장'][final_data['문장'].str.contains('[^가-힣!? ]')].sum()delete null values
# '문장' 컬럼의 내용을 양끝의 빈공간 삭제
final_data['문장'] = final_data['문장'].str.strip()
final_data = final_data.dropna()
# Null 있는지 확인 : 없음
final_data.isnull().sum()
# 중복 데이터 있는지 확인 : 56건 중복 존재 확인
final_data['문장'].duplicated().sum()
# 중복 데이터 제거
final_data.drop_duplicates(subset=['문장'], inplace=True)
# 기존 51,630건 --> 이후 51,574건 : 56건 중복 삭제 확인
final_data.info()Access for the distribution of labels
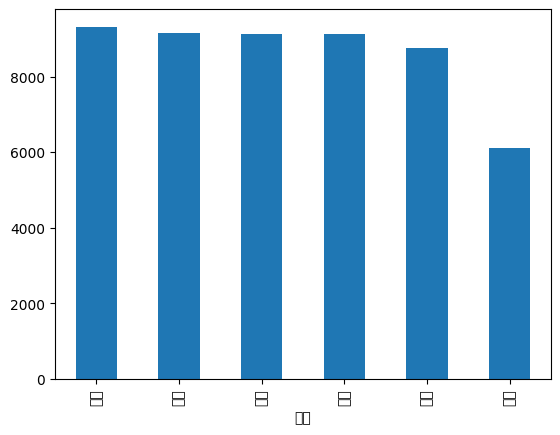
# label '감정' 분포 확인 : 총 6개이며, 고루게 분포 확인. 단 기쁨이 약간 부족해 보임
final_data['감정'].value_counts()
# plot Bar차트 그리기
final_data['감정'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar')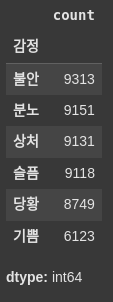
Encoding labels into numbers
# 감정 리스트 만듬
list1 = final_data['감정'].value_counts().index.values
list1
array(['불안', '분노', '상처', '슬픔', '당황', '기쁨'], dtype=object)
# 라벨와 클래스을 매핑 작업
label2class = {}
class2label = {}
for cl, la in enumerate(list1):
# print(i, j)
label2class[la] = cl
class2label[cl] = la
print(label2class)
print(class2label)
{'불안': 0, '분노': 1, '상처': 2, '슬픔': 3, '당황': 4, '기쁨': 5}
{0: '불안', 1: '분노', 2: '상처', 3: '슬픔', 4: '당황', 5: '기쁨'}
# '감정' 라벨링 수행
final_data['label'] = final_data['감정'].map(label2class)
final_data.tail()
감정 문장 label
51625 분노 나이가 먹고 이제 돈도 못 벌어 오니까 어떻게 살아가야 할지 막막해 능력도 없고 1
51626 불안 몸이 많이 약해졌나 봐 이제 전과 같이 일하지 못할 것 같아 너무 짜증 나 0
51627 상처 이제 어떻게 해야 할지 모르겠어 남편도 그렇고 노후 준비도 안 되어서 미래가 걱정돼 2
51628 불안 몇십 년을 함께 살았던 남편과 이혼했어 그동안의 세월에 배신감을 느끼고 너무 화가 나 0
51629 상처 남편과 결혼한 지 사십 년이야 이제 사람 만나는 것도 버겁고 알던 사람도 점점 사라져 2
train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
features = data['문장'].values
labels = data['label'].values
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, labels , test_size=0.2, stratify=labels, random_state=41)
x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape
((41268,), (10317,), (41268,), (10317,))
# 샘플확인 , 라벨 확인
# {0: '불안', 1: '분노', 2: '상처', 3: '슬픔', 4: '당황', 5: '기쁨'}
x_train[:2], y_train[:2]
(array(['전에는 몰랐는데 병에 걸리고 보니 지금 모아둔 돈으로는 얼마 가지 못한단 걸 깨달았어 좀 불안하네',
'요즘 여자친구 말투가 달라진 거 같아'], dtype=object),
array([0, 0]))Tokenization and Training
Using LSTM model for sentiment analysis (doesn't work better than the navie machine learning approach) (TensorFlow)
Tokenizing
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# Tokenizer 구현 : 단어 사전 만들기(fit_on_texts)
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(x_train)
# 단어에 대한 숫자 매핑
print(tokenizer.word_index)
# 반대로 숫자로 단어 매핑
print(tokenizer.index_word)
# 단어별 빈도수 확인
print(tokenizer.word_counts)
# 총 단어 갯수 : 47,646
max_words = len(tokenizer.index_word)
print(max_words)text to sequence(sequence of numbers)
# 문장을 숫자로 나열
x_train_seq = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(x_train)
x_test_seq = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(x_test)
# 문장을 숫자로 변경후 갯수 확인
# x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape : ((41259,), (10315,), (41259,), (10315,))
print(len(x_train_seq), len(x_test_seq))
print(x_train[1:3])
print(x_train_seq[1:3])
['혼자가 편하다고 한 게 후회돼' '나 부모님께 너무 죄송한 마음이 들어']
[[1664, 8292, 40, 15, 195], [5, 232, 1, 3601, 59, 24]]padding sequence
# 문장의 최대 길이 파악 : 제일 긴 문장 seq 길이는 38개로 구성됨.
max(len(line) for line in x_train_seq)
*********38*********
# 모든 문장을 최대 문장 Seq 길이 38에 맞춘다.
x_train_pad = pad_sequences(x_train_seq, maxlen=38)
x_test_pad = pad_sequences(x_test_seq, maxlen=38)
# 문장 Seq 내용을 보니 잘 패딩되어 있음 확인
x_train_pad[:1]
array([[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6210, 708, 20133,
20134, 24]], dtype=int32)
# 문장 Seq 패딩의 shape 확인
x_train_pad.shape, x_test_pad.shape
((41259, 38), (10315, 38))LSTM modeling
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv1D, MaxPool2D
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, Bidirectional, LSTM, SimpleRNN, GRU, GlobalMaxPooling1D
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Embedding, LSTM, GRU, Bidirectional, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
# Hyperparameters
max_words = 47646 + 1 # Vocabulary size
max_len = 38 # Max sentence length
embedding_dim = 32 # Embedding dimension
# Model declaration
model = Sequential()
# Explicitly defining input shape in the first layer
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=max_words, output_dim=embedding_dim, input_length=max_len))
# RNN Layers
model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(16, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(max_len, embedding_dim)))) # Define input_shape
model.add(Dropout(0.3)) # Regularization
model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(16, return_sequences=False)))
model.add(Dropout(0.3))
# Fully Connected Layers
model.add(Dense(64, activation='swish'))
model.add(Dense(32, activation='swish'))
model.add(Dense(6, activation='softmax'))
# **Force model to build before summary**
model.build(input_shape=(None, max_len))
# Compile model
model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Print model summary
model.summary()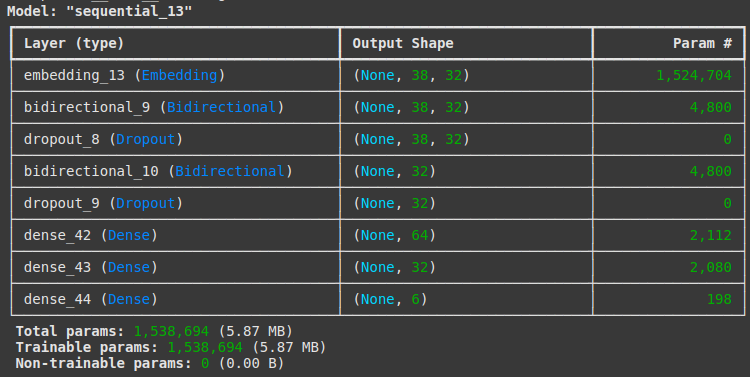
hybrid LSTM + Attention modeling
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Embedding, LSTM, Bidirectional, Dropout, Attention, Input
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
# Hyperparameters
max_words = 47646 + 1 # Vocabulary size
max_len = 38 # Max sentence length
embedding_dim = 32 # Embedding dimension
# Define input
inputs = Input(shape=(max_len,))
# Embedding Layer
x = Embedding(input_dim=max_words, output_dim=embedding_dim, input_length=max_len)(inputs)
# Bi-LSTM Layer (Output shape: (batch_size, max_len, 128))
x = Bidirectional(LSTM(64, return_sequences=True))(x)
# **Fix Attention Layer: Use LSTM output directly as query & value**
attention_output = Attention()([x, x]) # Both query and value = LSTM output
# Global Pooling (Instead of Flatten)
x = tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D()(attention_output)
# Fully Connected Layers
x = Dense(64, activation='swish')(x)
x = Dense(32, activation='swish')(x)
outputs = Dense(6, activation='softmax')(x)
# Build Model
model = Model(inputs, outputs)
model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()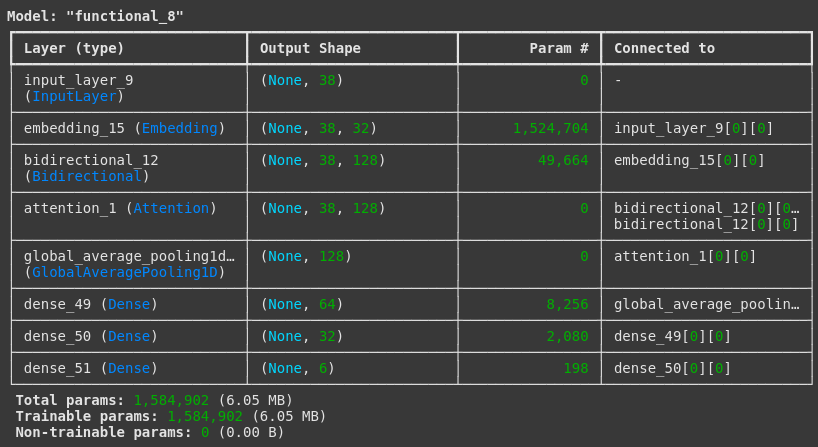
setting up EarlyStopping and ModelCheckpoint
# 조기종료 콜백함수 정의(EarlyStopping)
es = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=10, verbose=1)
# 체크포인트 저장(ModelCheckpoint)
checkpoint_path = 'tmp_checkpoint.keras'
cp = ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_path, monitor='val_loss', verbose=1, save_best_only=True)
# 모델 학습(fit)
history = model.fit(x_train_pad, y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=512,
validation_split=0.2, verbose =1, callbacks=[es, cp])
Epoch 1/20
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 16ms/step - accuracy: 0.1823 - loss: 1.7855
Epoch 1: val_loss improved from inf to 1.78048, saving model to tmp_checkpoint.keras
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 28ms/step - accuracy: 0.1823 - loss: 1.7854 - val_accuracy: 0.1677 - val_loss: 1.7805
Epoch 2/20
64/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 15ms/step - accuracy: 0.2413 - loss: 1.6808
Epoch 2: val_loss improved from 1.78048 to 1.56033, saving model to tmp_checkpoint.keras
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 20ms/step - accuracy: 0.2421 - loss: 1.6790 - val_accuracy: 0.3057 - val_loss: 1.5603
Epoch 3/20
63/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 15ms/step - accuracy: 0.3528 - loss: 1.4541
Epoch 3: val_loss improved from 1.56033 to 1.55394, saving model to tmp_checkpoint.keras
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 20ms/step - accuracy: 0.3533 - loss: 1.4532 - val_accuracy: 0.3568 - val_loss: 1.5539
Epoch 4/20
63/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 15ms/step - accuracy: 0.4472 - loss: 1.2674
Epoch 4: val_loss improved from 1.55394 to 1.55081, saving model to tmp_checkpoint.keras
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 20ms/step - accuracy: 0.4479 - loss: 1.2666 - val_accuracy: 0.3952 - val_loss: 1.5508
Epoch 5/20
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 17ms/step - accuracy: 0.5482 - loss: 1.0856
Epoch 5: val_loss did not improve from 1.55081
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 23ms/step - accuracy: 0.5483 - loss: 1.0855 - val_accuracy: 0.3912 - val_loss: 1.6691
Epoch 6/20
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 20ms/step - accuracy: 0.6376 - loss: 0.9203
Epoch 6: val_loss did not improve from 1.55081
65/65 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 26ms/step - accuracy: 0.6377 - loss: 0.9203 - val_accuracy: 0.4103 - val_loss: 1.7879
epoch and loss diagram
epochs = range(1, len(history.history['accuracy']) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, history.history['accuracy'])
plt.plot(epochs, history.history['val_accuracy'])
plt.title('model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend(['train', 'valid'], )
plt.show()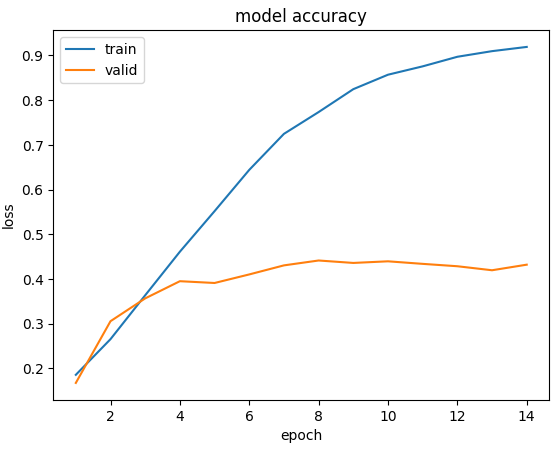
Evaluation and prediction
model.evaluate(x_test_pad, y_test)
323/323 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 2s 6ms/step - accuracy: 0.4215 - loss: 2.4267
[2.3810784816741943, 0.42898690700531006]
print(f'문자열 : {x_test[0]}')
print(f'Sequence : {x_test_pad[0]}')
문자열 : 눈 수술을 했더니 시력이 좋아졌어
Sequence : [ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1954 412 493 2450 961]
# 모델 예측하기(predict)
predict = model.predict(x_test_pad[:1])
print(f'True : {class2label[y_test[0]]}')
print(f'Predict : {class2label[np.argmax(predict)]}')
True : 기쁨
Predict : 상처The LSTM model and the attention model both showed poor prediction
Fine Tuning Pretrained DistillBERT model for sentiment analysis (Pytorch)
(Fully trainable) Fine tuning the pretrained DistillBERT model
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from transformers import DistilBertTokenizerFast, DistilBertForSequenceClassification, AdamW
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
#######################################
# 1. Automatically Determine Max Length
#######################################
def find_max_length(tokenizer, texts, max_cap=512):
"""
Tokenize each text, find the maximum token length,
and optionally cap it at `max_cap`.
"""
max_length = 0
for text in texts:
# Encode the text (add_special_tokens=True includes [CLS], [SEP], etc.)
tokens = tokenizer.encode(text, add_special_tokens=True)
if len(tokens) > max_length:
max_length = len(tokens)
# Cap at 512 by default to avoid excessive memory usage
max_length = min(max_length, max_cap)
return max_length
#########################################
# 2. Create Custom Dataset (Unchanged)
#########################################
class TextDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, texts, labels, tokenizer, max_len=38):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_len = max_len
def __len__(self):
return len(self.texts)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.texts[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
# Tokenize for PyTorch (batch dimension = 1)
encoded = self.tokenizer(
text,
truncation=True,
padding='max_length',
max_length=self.max_len,
return_tensors='pt'
)
# Squeeze out the batch dimension to get shape [seq_len]
input_ids = encoded['input_ids'].squeeze(0)
attention_mask = encoded['attention_mask'].squeeze(0)
return input_ids, attention_mask, torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
#########################################
# 3. Convert to Lists & Load Tokenizer
#########################################
train_texts = x_train.tolist()
train_labels = y_train.tolist()
test_texts = x_test.tolist()
test_labels = y_test.tolist()
model_name = "distilbert-base-multilingual-cased"
tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_name)
#########################################
# 4. Compute Auto Max Length
#########################################
all_texts = train_texts + test_texts
auto_max_len = find_max_length(tokenizer, all_texts, max_cap=512)
print(f"Detected max sequence length: {auto_max_len}")
#########################################
# 5. Create Datasets & Dataloaders
#########################################
batch_size = 64
train_dataset = TextDataset(train_texts, train_labels, tokenizer, max_len=auto_max_len)
test_dataset = TextDataset(test_texts, test_labels, tokenizer, max_len=auto_max_len)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
#########################################
# 6. Load Model & Move to Device
#########################################
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
model_name,
num_labels=6 # Adjust for your number of classes
)
model.to(device)
#########################################
# 7. Define Optimizer & Train
#########################################
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
epochs = 5
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
correct = 0
total = 0
# Training
for input_ids, attention_mask, labels in tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}", leave=False):
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
labels=labels
)
loss = outputs.loss
logits = outputs.logits
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1)
correct += (preds == labels).sum().item()
total += labels.size(0)
avg_train_loss = total_loss / len(train_loader)
train_acc = correct / total
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{epochs}] | Loss: {avg_train_loss:.4f} | Train Acc: {train_acc:.4f}")
# Validation
model.eval()
val_correct = 0
val_total = 0
val_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for input_ids, attention_mask, labels in test_loader:
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
labels=labels
)
loss = outputs.loss
logits = outputs.logits
val_loss += loss.item()
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1)
val_correct += (preds == labels).sum().item()
val_total += labels.size(0)
avg_val_loss = val_loss / len(test_loader)
val_acc = val_correct / val_total
print(f" Validation Loss: {avg_val_loss:.4f} | Validation Acc: {val_acc:.4f}")
#########################################
# 8. Save Model & Tokenizer (Optional)
#########################################
model.save_pretrained("my_distilbert_model")
tokenizer.save_pretrained("my_distilbert_tokenizer")Each epochs trains for 6 minutes on colab
Epoch [1/5] | Loss: 1.3647 | Train Acc: 0.4586
Validation Loss: 1.2314 | Validation Acc: 0.5276
Epoch [2/5] | Loss: 1.1862 | Train Acc: 0.5447
Validation Loss: 1.1993 | Validation Acc: 0.5441
Epoch [3/5] | Loss: 1.1052 | Train Acc: 0.5780
Validation Loss: 1.2166 | Validation Acc: 0.5482
Epoch 4/5: 36%
233/645 [02:13<03:53, 1.76it/s]
(Only re-training linear classifier) Fine tuning the pretrained DistillBERT model (Not good)
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from transformers import DistilBertTokenizerFast, DistilBertForSequenceClassification, AdamW
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
#######################################
# 1. Automatically Determine Max Length
#######################################
def find_max_length(tokenizer, texts, max_cap=512):
"""
Tokenize each text, find the maximum token length,
and optionally cap it at `max_cap`.
"""
max_length = 0
for text in texts:
# Encode the text (add_special_tokens=True includes [CLS], [SEP], etc.)
tokens = tokenizer.encode(text, add_special_tokens=True)
if len(tokens) > max_length:
max_length = len(tokens)
# Cap at 512 by default to avoid excessive memory usage
max_length = min(max_length, max_cap)
return max_length
#########################################
# 2. Create Custom Dataset (Unchanged)
#########################################
class TextDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, texts, labels, tokenizer, max_len=38):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_len = max_len
def __len__(self):
return len(self.texts)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.texts[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
# Tokenize for PyTorch (batch dimension = 1)
encoded = self.tokenizer(
text,
truncation=True,
padding='max_length',
max_length=self.max_len,
return_tensors='pt'
)
# Squeeze out the batch dimension to get shape [seq_len]
input_ids = encoded['input_ids'].squeeze(0)
attention_mask = encoded['attention_mask'].squeeze(0)
return input_ids, attention_mask, torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
#########################################
# 3. Convert to Lists & Load Tokenizer
#########################################
train_texts = x_train.tolist()
train_labels = y_train.tolist()
test_texts = x_test.tolist()
test_labels = y_test.tolist()
model_name = "distilbert-base-multilingual-cased"
tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_name)
#########################################
# 4. Compute Auto Max Length
#########################################
all_texts = train_texts + test_texts
auto_max_len = find_max_length(tokenizer, all_texts, max_cap=512)
print(f"Detected max sequence length: {auto_max_len}")
#########################################
# 5. Create Datasets & Dataloaders
#########################################
batch_size = 64
train_dataset = TextDataset(train_texts, train_labels, tokenizer, max_len=auto_max_len)
test_dataset = TextDataset(test_texts, test_labels, tokenizer, max_len=auto_max_len)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
#########################################
# 6. Load Model & Move to Device
#########################################
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
model_name,
num_labels=6 # Adjust for your number of classes
)
print('before changing require grad')
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
print(name, param.requires_grad)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if "distilbert" in name:
param.requires_grad = False
# Leaves `pre_classifier` and `classifier` trainable
print('after changing require grad')
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
print(name, param.requires_grad)
model.to(device)
#########################################
# 7. Define Optimizer & Train
#########################################
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
epochs = 5
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
correct = 0
total = 0
# Training
for input_ids, attention_mask, labels in tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}", leave=False):
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
labels=labels
)
loss = outputs.loss
logits = outputs.logits
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1)
correct += (preds == labels).sum().item()
total += labels.size(0)
avg_train_loss = total_loss / len(train_loader)
train_acc = correct / total
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{epochs}] | Loss: {avg_train_loss:.4f} | Train Acc: {train_acc:.4f}")
# Validation
model.eval()
val_correct = 0
val_total = 0
val_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for input_ids, attention_mask, labels in test_loader:
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
labels=labels
)
loss = outputs.loss
logits = outputs.logits
val_loss += loss.item()
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1)
val_correct += (preds == labels).sum().item()
val_total += labels.size(0)
avg_val_loss = val_loss / len(test_loader)
val_acc = val_correct / val_total
print(f" Validation Loss: {avg_val_loss:.4f} | Validation Acc: {val_acc:.4f}")
#########################################
# 8. Save Model & Tokenizer (Optional)
#########################################
model.save_pretrained("my_distilbert_model")
tokenizer.save_pretrained("my_distilbert_tokenizer")Detected max sequence length: 107
Epoch [1/5] | Loss: 1.7570 | Train Acc: 0.2372
Validation Loss: 1.7235 | Validation Acc: 0.2716
Epoch [2/5] | Loss: 1.7030 | Train Acc: 0.2910
Validation Loss: 1.6840 | Validation Acc: 0.3072
Epoch 3/5: 75/645 [00:14<01:50, 5.18it/s]
(Re-training linear classifier, and top part of embedding layers) Fine tuning the pretrained DistillBERT model (Not good)
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from transformers import DistilBertTokenizerFast, DistilBertForSequenceClassification, AdamW
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
#######################################
# 1. Automatically Determine Max Length
#######################################
def find_max_length(tokenizer, texts, max_cap=512):
"""
Tokenize each text, find the maximum token length,
and optionally cap it at `max_cap`.
"""
max_length = 0
for text in texts:
# Encode the text (add_special_tokens=True includes [CLS], [SEP], etc.)
tokens = tokenizer.encode(text, add_special_tokens=True)
if len(tokens) > max_length:
max_length = len(tokens)
# Cap at 512 by default to avoid excessive memory usage
max_length = min(max_length, max_cap)
return max_length
#########################################
# 2. Create Custom Dataset (Unchanged)
#########################################
class TextDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, texts, labels, tokenizer, max_len=38):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_len = max_len
def __len__(self):
return len(self.texts)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.texts[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
# Tokenize for PyTorch (batch dimension = 1)
encoded = self.tokenizer(
text,
truncation=True,
padding='max_length',
max_length=self.max_len,
return_tensors='pt'
)
# Squeeze out the batch dimension to get shape [seq_len]
input_ids = encoded['input_ids'].squeeze(0)
attention_mask = encoded['attention_mask'].squeeze(0)
return input_ids, attention_mask, torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
#########################################
# 3. Convert to Lists & Load Tokenizer
#########################################
train_texts = x_train.tolist()
train_labels = y_train.tolist()
test_texts = x_test.tolist()
test_labels = y_test.tolist()
model_name = "distilbert-base-multilingual-cased"
tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_name)
#########################################
# 4. Compute Auto Max Length
#########################################
all_texts = train_texts + test_texts
auto_max_len = find_max_length(tokenizer, all_texts, max_cap=512)
print(f"Detected max sequence length: {auto_max_len}")
#########################################
# 5. Create Datasets & Dataloaders
#########################################
batch_size = 64
train_dataset = TextDataset(train_texts, train_labels, tokenizer, max_len=auto_max_len)
test_dataset = TextDataset(test_texts, test_labels, tokenizer, max_len=auto_max_len)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
#########################################
# 6. Load Model & Move to Device
#########################################
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
model_name,
num_labels=6 # Adjust for your number of classes
)
# Example: Freeze the first 3 layers but keep layers 4, 5 (and the classifier) trainable
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
# Freeze embedding and layers 0..2
if ("embeddings" in name or "layer.0" in name or "layer.1" in name or "layer.2" in name):
param.requires_grad = False
else:
param.requires_grad = True
model.to(device)
#########################################
# 7. Define Optimizer & Train
#########################################
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
epochs = 5
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
correct = 0
total = 0
# Training
for input_ids, attention_mask, labels in tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}", leave=False):
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
labels=labels
)
loss = outputs.loss
logits = outputs.logits
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1)
correct += (preds == labels).sum().item()
total += labels.size(0)
avg_train_loss = total_loss / len(train_loader)
train_acc = correct / total
print(f"Epoch [{epoch+1}/{epochs}] | Loss: {avg_train_loss:.4f} | Train Acc: {train_acc:.4f}")
# Validation
model.eval()
val_correct = 0
val_total = 0
val_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for input_ids, attention_mask, labels in test_loader:
input_ids = input_ids.to(device)
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = model(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
labels=labels
)
loss = outputs.loss
logits = outputs.logits
val_loss += loss.item()
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1)
val_correct += (preds == labels).sum().item()
val_total += labels.size(0)
avg_val_loss = val_loss / len(test_loader)
val_acc = val_correct / val_total
print(f" Validation Loss: {avg_val_loss:.4f} | Validation Acc: {val_acc:.4f}")
#########################################
# 8. Save Model & Tokenizer (Optional)
#########################################
model.save_pretrained("my_distilbert_model")
tokenizer.save_pretrained("my_distilbert_tokenizer")Descent Accuracy and takes 4 minutes per epoch (on colab GPU)
Epoch [1/5] | Loss: 1.4337 | Train Acc: 0.4223
Validation Loss: 1.3029 | Validation Acc: 0.4954
Epoch [2/5] | Loss: 1.2462 | Train Acc: 0.5183
Validation Loss: 1.2298 | Validation Acc: 0.5193
Epoch [3/5] | Loss: 1.1825 | Train Acc: 0.5457
Validation Loss: 1.2256 | Validation Acc: 0.5297
Epoch [4/5] | Loss: 1.1312 | Train Acc: 0.5676
Validation Loss: 1.2234 | Validation Acc: 0.5362
Epoch 5/5: 3%
18/645 [00:06<03:47, 2.76it/s]
Epoch [5/5] | Loss: 1.0737 | Train Acc: 0.5930
Validation Loss: 1.2308 | Validation Acc: 0.5380
Evaluating and predicting
# Suppose you have a mapping from class indices to labels
# e.g., class2label = {0: '불안', 1: '분노', 2: '상처', 3: '슬픔', 4: '당황', 5: '기쁨'}
index = 4
# Pick the first test example
test_text_0 = test_texts[index]
true_label_0 = test_labels[index]
# Tokenize
encoded = tokenizer(
test_text_0,
truncation=True,
padding=True,
max_length=38,
return_tensors='pt' # Return PyTorch tensors
)
print(f"Raw Text: {test_text_0}")
print(f"True Label: {class2label[true_label_0]}")
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# Move input to GPU if available
for k, v in encoded.items():
encoded[k] = v.to(device)
outputs = model(**encoded)
logits = outputs.logits
predicted_label_id = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1).item()
print(f"Predicted: {class2label[predicted_label_id]}")
Raw Text: 결혼하기 싫은데 부모님이 결혼하라고 재촉해서 우울해
True Label: 슬픔
Predicted: 슬픔
Raw Text: 아빠가 재혼했는데 장애를 갖고 계신 새엄마께 화가 나서 막말을 한 것을 뉘우치고 있어
True Label: 당황
Predicted: 분노
Raw Text: 미래라는 단어를 들으면 사람들은 장밋빛이나 푸른색을 떠올린다지만 난 우중충한 잿빛이나 검은색이 떠오르니 왜일까? 나이 탓일까 아니면 노후준비가 안 돼 있는 탓일까?
True Label: 슬픔
Predicted: 불안
Raw Text: 이력서를 이백 통을 넣었는데 연락 오는 곳이 없어 실망이 커
True Label: 슬픔
Predicted: 슬픔
Raw Text: 맨날 이유 없이 나를 툭툭 치는 애들 때문에 학교 가는 게 짜증 나
True Label: 분노
Predicted: 분노
