해당 글은 FastCampus - '[skill-up] 처음부터 시작하는 딥러닝 유치원 강의를 듣고,
추가 학습한 내용을 덧붙여 작성하였습니다.
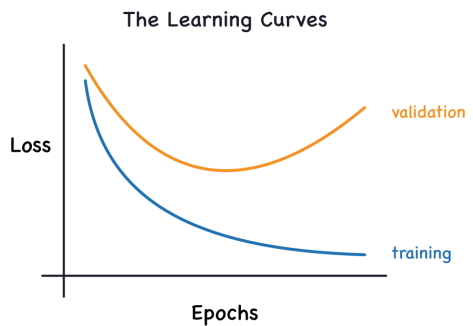
1. Overfitting이란?
- 우리의 목표: 학습 데이터뿐 아니라 새로운 데이터(unseen data)에 대해서도 잘 예측하는 모델
→ 즉, Training error를 최소화 하는 것이 최종 목표가 아님 Overfitting: Training Error (학습 데이터 오차)보다 Generalization Error (일반화 오차)가 현저히 높아지는 현상- 학습 데이터의 bias와 noise까지 과도하게 학습함
- Overfitting 현상이 꼭 나쁜 것은 아님
→ 모델의 capacity가 충분한지 확인하는 하나의 방법 (물론 확인 후에는 overfitting 해결 必)
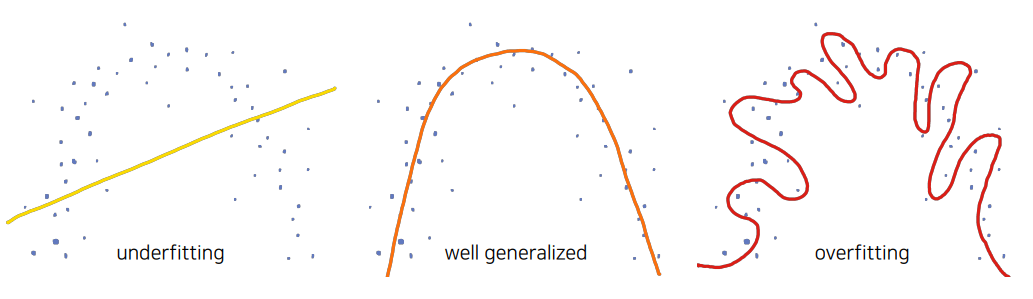
2. Underfitting이란?
- 모델의 capacity(depth, width)가 부족해 training error 가 충분히 낮지 않은 상태
3. Overfitting vs Underfitting
| 용어 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Overfitting | 불필요한 패턴까지 학습 |
| Underfitting | 데이터의 기본 패턴조차 학습하지 못함 |
| Well-generalized | 학습 데이터와 새로운 데이터 모두에서 좋은 성능 |
4. Overfitting을 막기 위한 Validation Set 활용
- train/validation/test 데이터를 random하게 분할 e.g. 6:2:2
- validaiton, test set은 절대 학습에 사용 X (Scaling fit 단계에서도 마찬가지임!)
- training set으로 학습, 매 epoch가 끝나면 validation set으로 generalization 성능 추정
- training error만 낮고 validation error가 높다면 overfitting 신호
Early Stopping: 일정 epoch 동안 validation loss 개선 없으면 학습 중단
| 데이터셋 | 목적 |
|---|---|
| Training Set | 파라미터 학습 |
| Validation Set | generalization 및 hyperparameter 검증 |
| Test Set | 최종 모델 및 알고리즘 검증 |
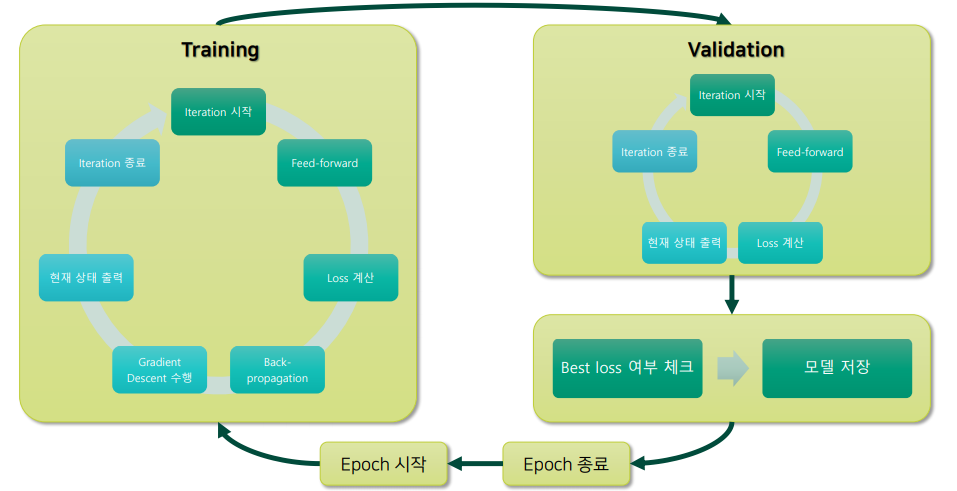
5. Typical Training Procedure
- 데이터 분할
- train set으로 feed-forward, loss 계산, SGD 수행
- training error 계산
- validation set으로 feed-forward, loss 계산 (학습은 X)
- validation error 계산
- best 모델 저장 (최저 validation loss 기준)
- test set으로 최종 평가
6. Pytorch 실습 코드
# Split into Train / Valid / Test set
## Load Dataset from sklearn
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
california = fetch_california_housing()
df = pd.DataFrame(california.data, columns=california.feature_names)
df["Target"] = california.target
df.tail()
## Convert to PyTorch Tensor
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
data = torch.from_numpy(df.values).float()
x = data[:, :-1]
y = data[:, -1:]
print(x.size(), y.size())
# Train / Valid / Test ratio
ratios = [.6, .2, .2]
train_cnt = int(data.size(0) * ratios[0])
valid_cnt = int(data.size(0) * ratios[1])
test_cnt = data.size(0) - train_cnt - valid_cnt
cnts = [train_cnt, valid_cnt, test_cnt]
print("Train %d / Valid %d / Test %d samples." % (train_cnt, valid_cnt, test_cnt))
# Shuffle before split.
indices = torch.randperm(data.size(0))
x = torch.index_select(x, dim=0, index=indices)
y = torch.index_select(y, dim=0, index=indices)
# Split train, valid and test set with each count.
x = list(x.split(cnts, dim=0))
y = y.split(cnts, dim=0)
for x_i, y_i in zip(x, y):
print(x_i.size(), y_i.size())
## Preprocessing
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(x[0].numpy()) # You must fit with train data only.
x[0] = torch.from_numpy(scaler.transform(x[0].numpy())).float()
x[1] = torch.from_numpy(scaler.transform(x[1].numpy())).float()
x[2] = torch.from_numpy(scaler.transform(x[2].numpy())).float()
df = pd.DataFrame(x[0].numpy(), columns=california.feature_names)
df.tail()
## Build Model & Optimizer
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(x[0].size(-1), 6),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(6, 5),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(5, 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(4, 3),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(3, y[0].size(-1)),
)
model
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
## Train
n_epochs = 4000
batch_size = 256
print_interval = 100
from copy import deepcopy
lowest_loss = np.inf
best_model = None
early_stop = 100
lowest_epoch = np.inf
train_history, valid_history = [], []
for i in range(n_epochs):
# Shuffle before mini-batch split.
indices = torch.randperm(x[0].size(0))
x_ = torch.index_select(x[0], dim=0, index=indices)
y_ = torch.index_select(y[0], dim=0, index=indices)
# |x_| = (total_size, input_dim)
# |y_| = (total_size, output_dim)
x_ = x_.split(batch_size, dim=0)
y_ = y_.split(batch_size, dim=0)
# |x_[i]| = (batch_size, input_dim)
# |y_[i]| = (batch_size, output_dim)
train_loss, valid_loss = 0, 0
y_hat = []
for x_i, y_i in zip(x_, y_):
# |x_i| = |x_[i]|
# |y_i| = |y_[i]|
y_hat_i = model(x_i)
loss = F.mse_loss(y_hat_i, y_i)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss += float(loss)
train_loss = train_loss / len(x_)
# You need to declare to PYTORCH to stop build the computation graph.
with torch.no_grad():
# You don't need to shuffle the validation set.
# Only split is needed.
x_ = x[1].split(batch_size, dim=0)
y_ = y[1].split(batch_size, dim=0)
valid_loss = 0
for x_i, y_i in zip(x_, y_):
y_hat_i = model(x_i)
loss = F.mse_loss(y_hat_i, y_i)
valid_loss += loss
y_hat += [y_hat_i]
valid_loss = valid_loss / len(x_)
# Log each loss to plot after training is done.
train_history += [train_loss]
valid_history += [valid_loss]
if (i + 1) % print_interval == 0:
print('Epoch %d: train loss=%.4e valid_loss=%.4e lowest_loss=%.4e' % (
i + 1,
train_loss,
valid_loss,
lowest_loss,
))
if valid_loss <= lowest_loss:
lowest_loss = valid_loss
lowest_epoch = i
# 'state_dict()' returns model weights as key-value.
# Take a deep copy, if the valid loss is lowest ever.
best_model = deepcopy(model.state_dict())
else:
if early_stop > 0 and lowest_epoch + early_stop < i + 1:
print("There is no improvement during last %d epochs." % early_stop)
break
print("The best validation loss from epoch %d: %.4e" % (lowest_epoch + 1, lowest_loss))
# Load best epoch's model.
model.load_state_dict(best_model)
## Loss History
plot_from = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.grid(True)
plt.title("Train / Valid Loss History")
plt.plot(
range(plot_from, len(train_history)), train_history[plot_from:],
range(plot_from, len(valid_history)), valid_history[plot_from:],
)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()
## Let's see the result!
test_loss = 0
y_hat = []
with torch.no_grad():
x_ = x[2].split(batch_size, dim=0)
y_ = y[2].split(batch_size, dim=0)
for x_i, y_i in zip(x_, y_):
y_hat_i = model(x_i)
loss = F.mse_loss(y_hat_i, y_i)
test_loss += loss # Gradient is already detached.
y_hat += [y_hat_i]
test_loss = test_loss / len(x_)
y_hat = torch.cat(y_hat, dim=0)
sorted_history = sorted(zip(train_history, valid_history),
key=lambda x: x[1])
print("Train loss: %.4e" % sorted_history[0][0])
print("Valid loss: %.4e" % sorted_history[0][1])
print("Test loss: %.4e" % test_loss)
df = pd.DataFrame(torch.cat([y[2], y_hat], dim=1).detach().numpy(),
columns=["y", "y_hat"])
sns.pairplot(df, height=5)
plt.show()