해시 Hash
코딩 시에 사용하는 변수들은 데이터 특성에 따라 다양한 자료형을 갖는다.
e.g.) 연속열(Sequence) 데이터는 배열을 활용
해시hash는 인덱스가 아닌 키key와 데이터를 매칭시켜 키를 통해 데이터에 접근할 수 있도록 만든 구조이다.
mapping, assiciative array 등으로 불리기도 하는데,
파이썬에는 딕셔너리dict가 해당 기능을 수행한다.
보통 numpy의 ndarray 객체를 사용하는 경우가 많다.
# 지역번호 dict
Country_PhoneNumber = {'Korea': 82, 'America': 1, 'Swiss': 41, 'Italy': 39, 'Japan': 81, 'China': 86, 'Rusia': 7}
Country_PhoneNumber['Korea']
>>> 82판타지 게임 로직 설계 (feat. dict)
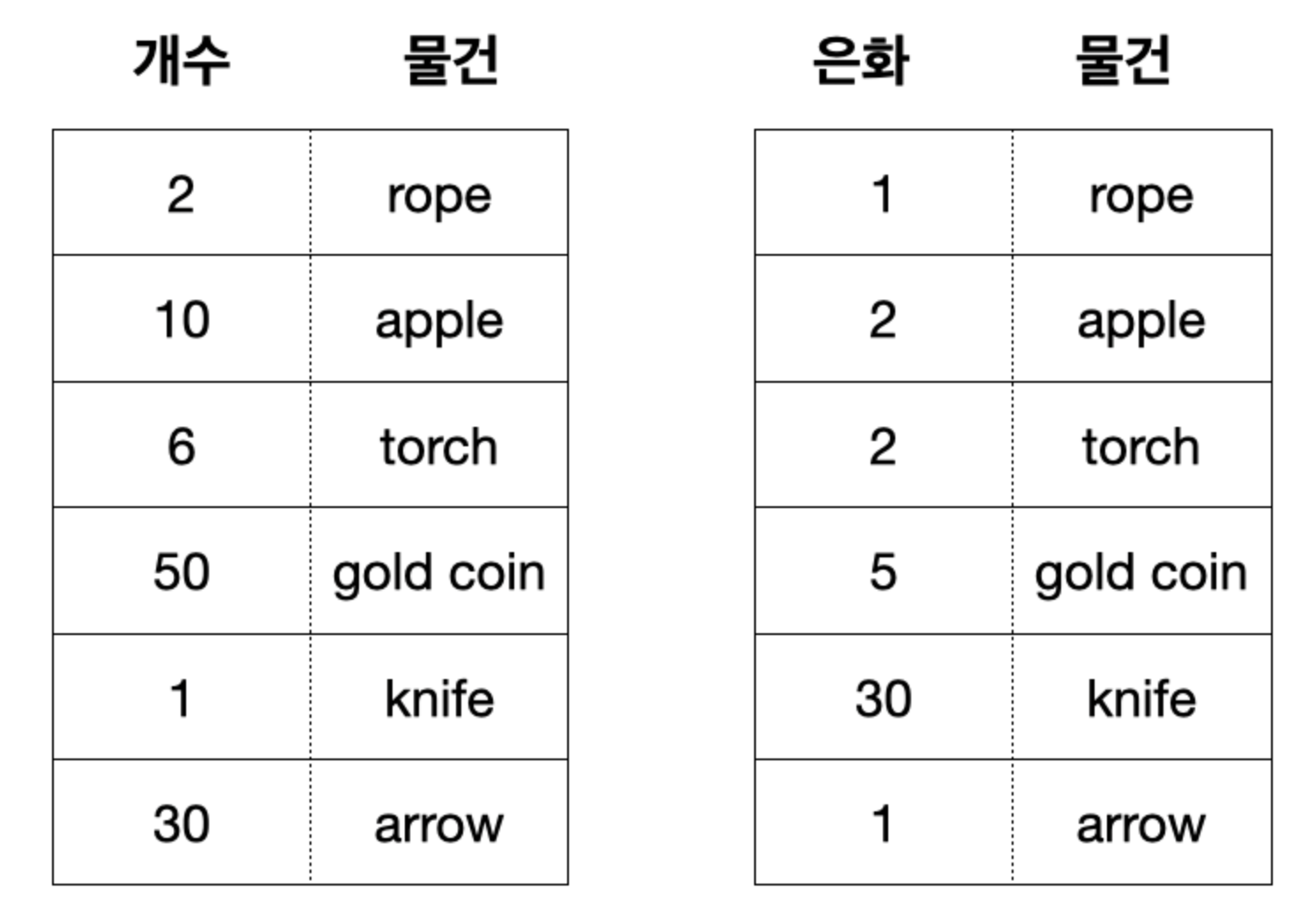
위 그림은 던전의 보물상자를 열어서 획득 가능한 아이템들을 딕셔너리로 구현한 것이다.
보물상자를 열었을 때 위의 아이템들 중 랜덤으로 한 가지를 주는 코드는 다음과 같다.
# 보물상자 내용물 dict
treasure_box = {'rope':2,
'apple':10,
'torch': 6,
'gold coin': 50,
'knife': 1,
'arrow': 30}
# 아이템을 띄워주는 함수
def display_stuff(treasure_box):
print("Congraturation!! you got a treasure box")
for k, v in treasure_box.items():
print("you have {} {}pcs".format(k, v))
display_stuff(treasure_box)마찬가지 방식으로 은화를 주는 코드도 작성할 수 있다.
coin_per_treasure = {'rope':1,
'apple':2,
'torch': 2,
'gold coin': 5,
'knife': 30,
'arrow': 1}
def total_silver(treasure_box, coin_per_treasure):
total_coin = 0
for treasure in treasure_box:
coin = coin_per_treasure[treasure] * treasure_box[treasure]
print("{} : {}coins/pcs * {}pcs = {} coins".format(
treasure, coin_per_treasure[treasure], treasure_box[treasure], coin))
total_coin += coin
print('total_coin : ', total_coin)
total_silver(treasure_box, coin_per_treasure)위처럼 두 개의 딕셔너리를 사용할 수도 있고, 하나로 묶어서 사용할 수도 있다.
treasure_box = {'rope': {'coin': 1, 'pcs': 2},
'apple': {'coin': 2, 'pcs': 10},
'torch': {'coin': 2, 'pcs': 6},
'gold coin': {'coin': 5, 'pcs': 50},
'knife': {'coin': 30, 'pcs': 1},
'arrow': {'coin': 1, 'pcs': 30}
}
treasure_box['rope']이 경우 아이템과 은화를 띄워주는 함수는 다음과 같다.
# 아이템 처리 함수
def display_stuff(treasure_box):
print("Congraturation!! you got a treasure box!!")
for treasure in treasure_box:
print("You have {} {}pcs".format(treasure, treasure_box[treasure]['pcs']))
display_stuff(treasure_box)
# 은화 처리 함수
def total_silver(treasure_box, coin_per_treasure):
total_coin = 0
for treasure in treasure_box:
coin = coin_per_treasure[treasure] * treasure_box[treasure]['pcs']
print("{} : {}coins/pcs * {}pcs = {} coins".format(
treasure, coin_per_treasure[treasure], treasure_box[treasure]['pcs'], coin))
total_coin += coin
print('total_coin : ', total_coin)
total_silver(treasure_box, coin_per_treasure)이처럼 내부에 자체적인 서브 데이터 구조를 가진 데이터를 구조화된 데이터라고 한다.
해당 데이터 구조는 앞서 언급했듯 언어와 상황에 따라 여러가지 단어로 지칭된다.
(구조체, 해시, 테이블, ...., etc)
