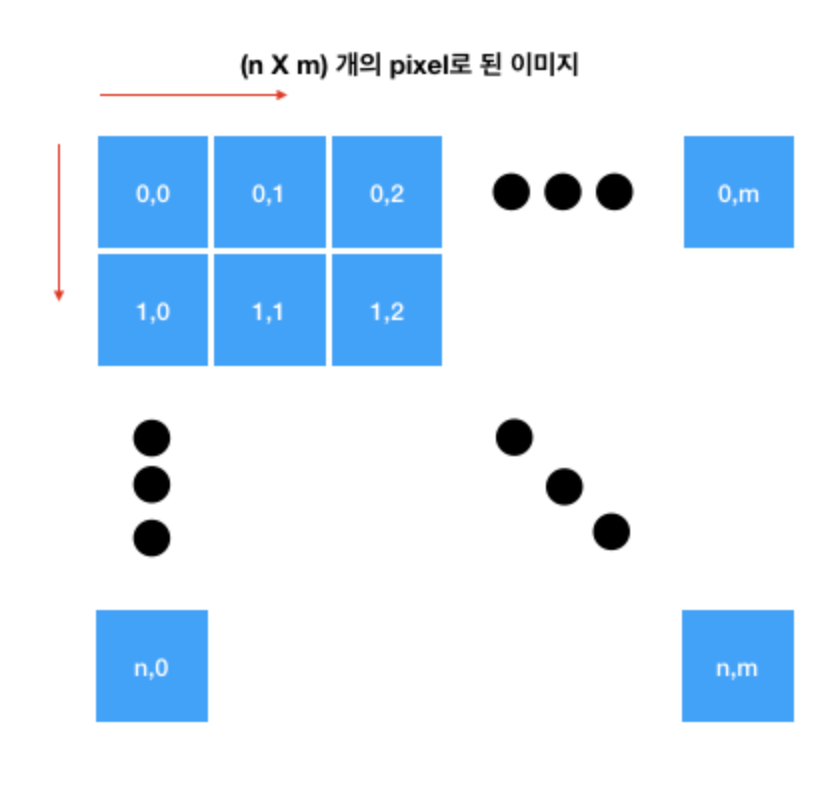
- 일반적인 이미지의 좌표 값은 위와 같다.
- 흑백이미지의 각 픽셀은 0~255 사이의 튜플 값을 갖는다.
- 컬러이미지는 보통 R, G, B 3개의 값을 갖지만 투명도(Alpha)까지 4개의 튜플 값을 갖는 경우도 있다.
PIL과 matplotlib
PIL과 matplotlib은 다양한 이미지 처리 기능을 지원하는 라이브러리이다.
Image.open(): open
Image.size: size
Image.filename: filename
Image.crop((x0, y0, xt, yt)): crop
Image.resize((w,h)): resize
Image.save(): save

위와 같은 예시 이미지를 가지고 진행해보자.
from PIL import Image, ImageColor
import os
img_path = 'mydrive/MyDrive/newyork.jpg' # 파일 경로
img = Image.open(img_path)
print(type(img))
>>> <class 'PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile'>
# 가로, 세로 사이즈 튜플로 리턴
print(img.size)
>>> (212, 300)
# 이렇게도 사용 가능
W, H = img.size
print((W, H))
>>> (212, 300)
# 다양한 파일 데이터 확인 가능
print(img.format)
>>> JPEG
print(img.size)
>>> (212, 300)
print(img.mode)
>>> RGB
# 시작점 = (30, 30) | 종료점 = (100, 100) 크기로 이미지 자르기
img.crop((30,30,100,100))
# 잘라낸 파일 저장
cropped_img_path = 'mydrive/MyDrive/newyork_cropped.jpg'
img.crop((30,30,100,100)).save(cropped_img_path)행렬로 변환하기
import numpy as np
img_arr = np.array(img)
print(type(img))
>>> <class 'PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile'>
print(type(img_arr))
>>> <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
# RGB 채널 수까지 포함해 3차원 배열
print(img_arr.shape)
>>> (300, 212, 3)
print(img_arr.ndim)
>>> 3위 코드에서 np.array(img) 부분을 보면 img 객체가 파이썬 리스트가 아님에도 불구하고 정상작동하고 있다.
img는 PIL.Image.Image 클래스를 상속받은 PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile 자료형을 쓰는데, 해당 클래스에는 __array_interface__ 속성이 정의돼 있어서 ndarray 변환이 가능하다.
Ref.
흑백 모드로 파일 열기
# grayscale
img_g = Image.open(img_path).convert('L')
# 행렬 변환은 위와 동일
img_g_arr = np.array(img_g)
print(type(img_g_arr))
>>> <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
# 흑백은 채널 수가 없으므로 2차원 배열
print(img_g_arr.shape)
>>> (300, 212)
print(img_g_arr.ndim)
>>> 2Ref.
색상값 추출
getcolor 메소드를 사용하면 색상값을 추출할 수 있다.
red = ImageColor.getcolor('RED','RGB')
reda = ImageColor.getcolor('red','RGBA')
yellow = ImageColor.getcolor('yellow','RGB')
print(red)
>>> (255, 0, 0)
print(reda)
>>> (255, 0, 0, 255)
print(yellow)
>>> (255, 255, 0)