Contents
- Random forest
- Extra trees
- Random forest vs Extra trees
1. Random forest
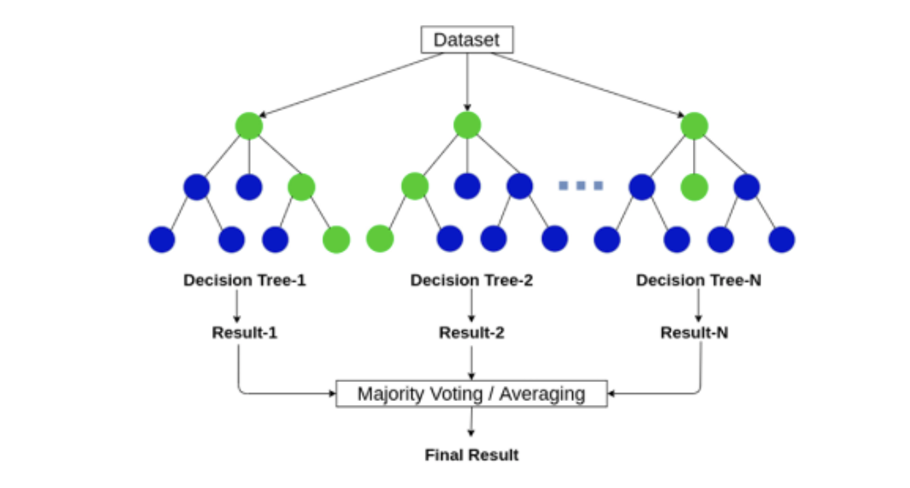
대표적 ensemble model 인 RandomForest 에 대해 알아보자. 이름 그대로 여러 개의 랜덤한 결정트리들을 모아놓은 숲을 만든 후 하나로 aggregate 하는 알고리즘이다. 기본적으로 100개의 트리 (n_estimator=100) 가 생성된다. 분류에서는 정확도 또는 확률이, 회귀에서는 예측값이 score 로 출력되며 이를 더해 트리의 개수로 나눈다면 앙상블 모델의 평균 확률 또는 평균 예측값을 얻을 수 있다.
bootstrap = True
Random forest algorithm 의 특징으로는 bootstrap sampling 을 들 수 있는데, 이는 전체 샘플의 개수는 유지하되 중복을 허용해 기존 훈련세트에서 random subsets 를 추출해 각각의 결정트리를 만든다. 따라서 기존의 과대적합을 방지하기 위해 sampling 단계에서 무작위성을 부여하는 것이다.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier()
rf = RandomForestClassifier()
scores = cross_validate(rf, train_input, train_target, n_jobs=-1, return_train_score=True)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.9974343316805905 0.8846473964092032Feature importances
또한 모든 특성을 사용했을 때 과대적합되므로 그 개수에도 무작위성을 적용하여 특성개수 만큼만 랜덤선택을 한다면 과대적합에 대처할 수 있다. 단, 회귀 모델에서는 언제나 전체 특성이 사용된다. 그렇다면 모델 훈련 후 feature importances 를 이용해 impurity-based 의 특성 중요도를 파악해보자.
rf.fit(train_input, train_target)
print(rf.feature_importances_) # [0.23647625 0.49298036 0.27054339]결과적으로 두번째 'sugar' 특성이 제일 중요도가 높았으나 나머지 두 특성에 대해서도 골고루 사용되었음을 알 수 있다.
Out-of-bag score
부트스트랩 샘플들을 사용하면 분명 사용되지 않은 데이터들이 존재한다. 이러한 남는 샘플들을 out-of-bag (oob) 이라고 하는데, Randomforest 에서는 따로 검증세트를 준비하거나 교차검증을 할 필요 없이 oob score 만을 이용해 성능 확인이 가능하다.
rf = RandomForestClassifier(oob_score=True, n_jobs=-1)
rf.fit(train_input, train_target)
print(rf.oob_score_) # 0.8899835796387521즉, 앞서 얻은 평균 교차검증 점수 ('test_score': 0.8846473964092032) 와 매우 비슷함을 알 수 있다.
2. Extra trees
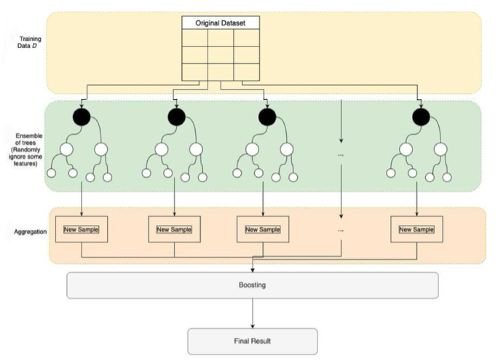
그 다음으로 sklearn 에서 제공하는 ensemble model 로는 extra tree (ET) algorithm 이 있다. 이 역시 100개의 트리가 디폴트로 생성되며 분류 시 특성개수 만큼 특성이 랜덤선택된다.
bootstrap = False
Random forest 와의 가장 큰 차이 중 하나로는 boostrap sampling 을 하지 않고 모든 class 가 일괄적으로 전체 샘플을 사용한다는 것이다. 그렇다면 과대적합을 방지하기 위해 bootstrap 대신 어떤 방법을 적용한 것일까?
Random node split
기존 결정트리 모델들은 Gini 또는 entropy 를 이용해 Locally optimal value 를 계산해 impurity 차이가 가장 크도록 노드를 분할해왔다. 하지만 extra trees algorithm 은 split value 를 마구잡이로 선택해 노드를 나누므로 성능이 낮아지지만 random forest 에 비해 속도가 빠르다. 또한 이러한 randomized split value selection 은 diversified 하며 uncorrelated 한 결정트리들을 만들기 때문에 과대적합에 대처할 수 있다.
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
et = ExtraTreesClassifier()
scores = cross_validate(et, train_input, train_target, n_jobs=1, return_train_score=True)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.9974343316805905 0.8809510872426684Feature importances
Random forest 와 같이 특성 중요도를 출력해보면 다음처럼 상당히 비슷한 결과를 얻게 된다.
et.fit(train_input, train_target)
print(et.feature_importances_) # 0.19357211 0.51967883 0.28674906]3. Random forest vs Extra trees
요약하자면, random forest 와 extra trees algorithms 는 굉장히 비슷하지만 성능을 억제하는 방법이 조금 다르다. Random forest 는 bootstrapping 을 이용하는 반면 extra trees 는 노드 분할을 무작위로 하는 것이 주요한 특징이다.
| Random forest | Extra trees | |
|---|---|---|
| Datasets | Samples subsets through bootstrapping | Samples the entire dataset |
| Nodes | Nodes are split based on the best split | Randomized node split |
| Variance | Medium variance | Low variance |
| Time | It takes time to find the best node to split on | Faster since node splits are random |