Contents
- Gradient boosting
- Histogram-based gradient boosting
- XGBoost vs LightGBM
1. Gradient boosting
Ensemble models 중에는 gradient boosting 이 가장 효과적이라고 알려져있으며, SGD (stochastic gradient descent) 와 비슷하게 손실함수의 값을 낮추기 위해 잔여 오차에 대해 학습하는 "회귀 트리" 를 추가한다. 따라서, Gradient boosting classifier 와 regressor 모두 Decision tree regressor 를 기반으로 한다.
Gradient boosting classifier
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
gb = GradientBoostingClassifier()
scores = cross_validate(gb, train_input, train_target, return_train_score=True, n_jobs=-1)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.8864942352809051 0.8655553098509976훈련 점수와 검증점수를 비교해보면, 이전에 비해 train_score 는 감소했지만 검증점수가 많이 낮아진 것도 아니기 때문에 트리의 개수를 늘리면 더 좋은 성능을 낼 것이라 기대할 수 있다.
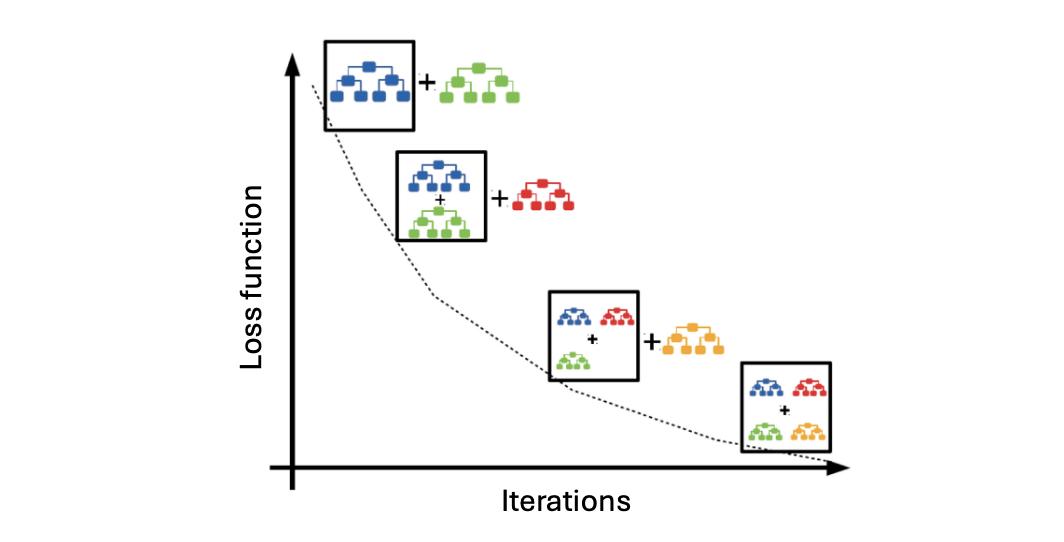
그렇다면 트리의 개수와 learning rate 을 달리 하여 다시 gradient boosting 을 해보자. 여기서 n_estimators 는 boosting stages 의 개수를 나타낸다.
gb = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=500, learning_rate=0.2)
scores = cross_validate(gb, train_input, train_target, return_train_score=True, n_jobs=-1)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.9426314041151755 0.8766410782920022이전에는 모델을 더 많이 훈련할수록 과대적합이 되어 검증점수가 더 급격히 낮아지곤 했다. 하지만 기존 n_estimators=100 의 5배로 훈련 횟수를 늘려도 검증점수에 큰 차이가 없는 것이 gradient boosting 의 장점이다.
Feature importances
특성 중요도를 알아보면 두번째 특성이 특히나 중요한 것을 알 수 있으며 random forest 와 extra trees 보다 더욱 특정 특성에 대해 directed towards 된 것을 알 수 있다.
gb.fit(train_input, train_target)
print(gb.feature_importances_) # [0.15529419 0.67198522 0.17272058]2. Histogram-based gradient boosting
Sci-kit learn 의 또 다른 gradient boosting algorithm 으로 histogram 을 이용한 class 가 있다. 이는 훈련데이터를 256개의 구간으로 나눠 각 구간들에 대한 특성을 학습하는 알고리즘이다.
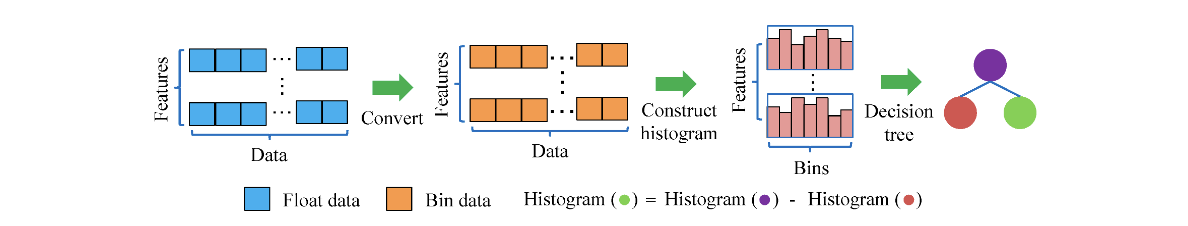
255 + 1
조금 더 정확히 말하면 256개의 구간이 255개의 bin data 와 1개의 누락값에 대한 구간으로 나뉜다. 따라서, null values 는 이 구간으로 할당되기 때문에 pandas 이용해 굳이 다른 값들의 평균 등으로 이 값을 채워주지 않아도 된다는 장점이 있다.
from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingClassifier
hgb = HistGradientBoostingClassifier()
scores = cross_validate(hgb, train_input, train_target, return_train_score=True, n_jobs=-1)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.9299052974272219 0.8764344758595272Permutation feature importance
A model inspection technique that measures the contribution of each feature to a fitted model’s statistical performance on a given tabular dataset.
- This technique is particularly useful for non-linear or opaque estimators, and involves randomly shuffling the values of a single feature and observing the resulting degradation of the model’s score.
특성 중요도를 파악하기 위해 지금까지 사용했던 feature importances 보다도 더 권장되는 permutation importance 에 대해 알아보자. 이는 decision tree 뿐만 아니라 다른 모델들에도 사용 가능하다.
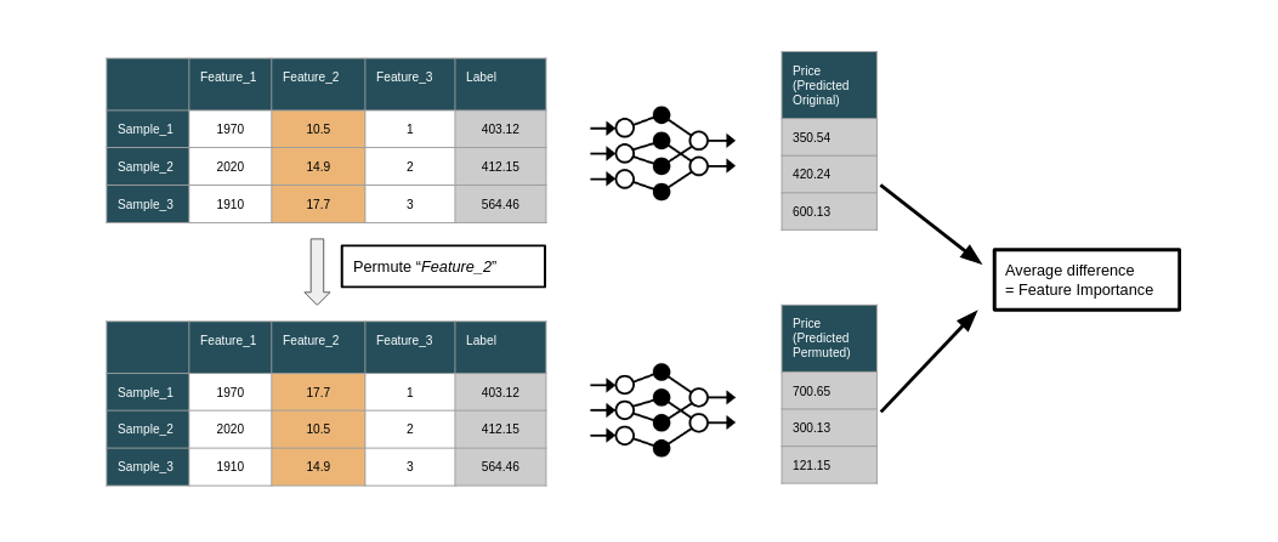
위에 보이는 것과 같이 하나의 특성 내에서 무작위로 순서를 바꿔가며 성능 저하를 유도하는데, 이때 원래 성능과의 차이를 바탕으로 특성 중요도를 계산한다. 예로 들어 Feature_1 을 permute 시킬 시 얻은 분류 정확도가 80% 이고 Feature_2 를 통해 얻은 정확도가 70% 라면, Feature_2 가 더 중요한 특성임을 알 수 있다.
from sklearn.inspection import permutation_importance
hgb.fit(train_input, train_target)
result = permutation_importance(hgb, train_input, train_target, n_repeats=10, n_jobs=-1)
print(result.importances_mean) # [0.08448276 0.24316502 0.07608785]따라서, 두번째 특성을 건들인다면 정확도가 약 0.24 만큼 감소하므로 다른 것보다 더 중요한 것이다.
Test set
Feature importances 는 트리 생성 시 fit() 을 기반으로 특성 중요도를 계산하므로 훈련세트에 대해서만 특성 중요도를 알 수 있었는데, permutation importance 는 테스트세트에 대해서도 적용 가능한 것이 또 다른 특성이다. 이를 통해 우리는 모델을 실전 투입 시 어떤 특성에 더 민감할 것인지 미리 예측가능하다.
result = permutation_importance(hgb, test_input, test_target, n_repeats=10, n_jobs=-1)
print(result.importances_mean) # [0.05138462 0.20553846 0.0472 ]Test set 에 대해서도 두번째 특성의 중요성을 염두하고 score 를 계산하면 약 87.9% 의 정확도를 얻는다.
hgb.score(test_input, test_target) # 0.87938461538461543. XGBoost vs LightGBM
지금까지는 sklearn 에서 제공하는 ensemble models 에 대해 알아보았다. 하지만 gradient boosting specific packages 또는 libraries 로 XGBoost 와 LightGBM 등도 존재한다.
XGBoost
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
xgb = XGBClassifier(tree_method='hist')
scores = cross_validate(xgb, train_input, train_target, return_train_score=True, n_jobs=-1)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.9538686203079738 0.8766389722529354LightGBM
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
lgb = LGBMClassifier()
scores = cross_validate(lgb, train_input, train_target, return_train_score=True, n_jobs=-1)
print(np.mean(scores['train_score']), np.mean(scores['test_score']))
# 0.9332921365489734 0.8760259042805245특히 histogram-based gradient boosting 에 대해 이 두 classes 모두 sklearn 의 HistGradientBoostingClassifier 와 비슷한 cross-validation score 를 보인다.