1. Regression(회귀)
- 학습데이터에 답이 있는 지도학습 중 연속된 값을 예측하는 경우
- 주택가격 예측 등을 예로 들 수 있다.
2. Linear Regression(선형 회귀)
- 학습데이터와 답이 선형관계에 있다고 가정하고 함수식을 구해서 예측
- OLS(Ordinary Linear Least Square): 선형관계에 해당하는 함수식을 구하는 방법. 학습데이터로 유추한 예측값과 정답의 차이가 최소가 되게하는 계수를 찾음.
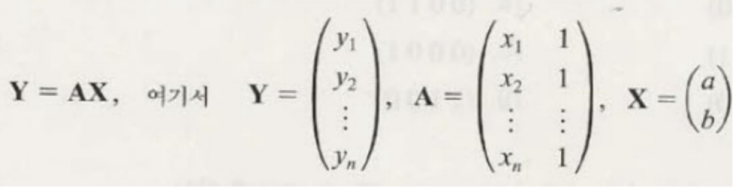

3. 선형회귀 실습
임의의 x,y 좌표값들에 대하여 선형 방정식 생성
# !pip install statsmodels
import pandas as pd
data = { 'x': [1,2,3,4,5], 'y': [1,3,4,6,5]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
lm_model = smf.ols(formula = 'y ~ x', data = df).fit()
lm_model.paramsIntercept 0.5
x 1.1
dtype: float64
그래프로 시각화
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.lmplot(x='x', y ='y', data = df );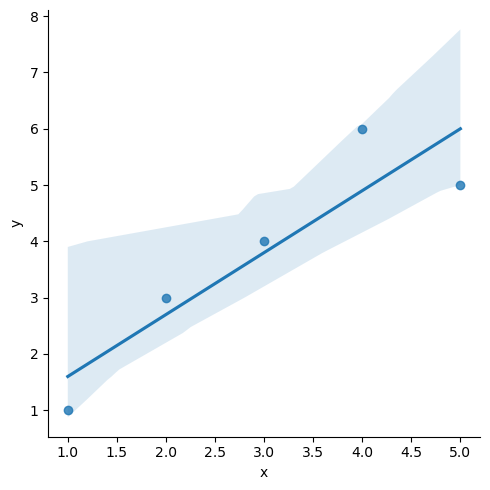
4. 잔차와
- 잔차: 실제 값과 예측값의 차이로 평균이 0인 정규분포를 따라야 이상적인 선형모델
- 결정계수 R-sqaured: 예측치가 실제 데이터를 얼만큼 대변해주는지를 측정한 지표
- R-squared는 설명력이 좋을수록 1에 가까워짐.
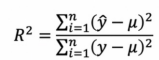
5. 잔차 실습
잔차 구하기
resid = lm_model.resid
resid0 -0.6
1 0.3
2 0.2
3 1.1
4 -1.0
dtype: float64
구하기
lm_model.rsquared0.8175675675675675
