❇️ 요약
- 역행렬이 존재하는 행렬 : Invertible Matrix
- 2 × 2 행렬에서의 결정자 (ad - bc) : Determinant
- 기본 행렬 : Elementary matrix
- A−1를 찾는 알고리즘 : Algorithm for Finding A−1
📖 역행렬
🔆 역행렬
- 역행렬이 존재하는 행렬 : Invertible Matrix
- 2 × 2 행렬에서의 결정자 (ad - bc) : Determinant
- 기본 행렬 : Elementary matrix
- A−1를 찾는 알고리즘 : Algorithm for Finding A−1
🔆 1. 숫자의 승수 역수 - Multiplicative Inverse of a Number
5−1⋅5=1and5⋅5−1=1
🔆 2. 역행렬이 존재하는 행렬 - Invertible Matrix
중요 핵심
CA=IandAC=I
Ann×nmatrixAis said to beinvertibleif there is ann×nmatrixCsuch thatCA=IandAC=I
- Invertible의 첫 번째 조건은 Row와 Column의 size가 동일해야함
- AC=I 인 C 행렬이 있어야 하며 C는 유일(unique) 해야 함
- C 대신 A−1로 표기함
- Matrix가
- not invertible이면 singular matrix(해가 존재하지 않는 행렬)임
- invertible이면 nonsingular matrix(해가 존재)함
A−1A=IandAA−1=I
🔆 3. 이론 4 - Theorem 4
중요 핵심
Ifad−bc=0,A−1=ad−bc1[d−c−ba]
Let A=[acbd]Ifad−bc=0, then A is invertible and If ad−bc=0, then A is not invertible.A−1=ad−bc1[d−c−ba]
- A가 2×2 행렬일 때
- ad−bc=0 이면 A는 invertrible 함
- ad−bc=0 이면 not invertible 함
- ad−bc는 pivot position이 2개 있을 조건을 의미하며 determinant(결정자)라고 부름
- 어떤 matrix가 invertible을 판단할 때 determinant가 0인지 아닌지 확인하면 됨
A=[3546]
A−1=−21[6−5−43]=[6/(−2)−5/(−2)−4/(−2)3/(−2)]=[−35/22−3/2]
🔆 4. 이론 5 - Theorem 5
중요 핵심
Au=b,A−1Au=A−1b,Iu=A−1b,u=A−1b
If A is an invertible n×n matrix, then for each b in Rn, the equation Ax=b has the unique solution x=A−1b
Au=b,A−1Au=A−1b,Iu=A−1b,u=A−1b
3x1+4x2=35x1+6x2=7
x=A−1b=[−35/22−3/2][37]=[5−3]
🔆 5. 이론 6 - Theorem 6
중요 핵심
(A−1)−1=A
(AB)−1=B−1A−1
(AT)−1=(A−1)T
- A가 invertible matrix이면 A−1도 invertible임
a. If A is an invertible matrix, then A−1 is invertible and (A−1)−1=A
- (AB)−1은 B−1A−1 와 동일
- ❗주의할 점 : 순서가 뒤바뀌어 B가 먼저 나온다는 것
b. If A and B are n×n invertible matrices, then so is AB,and the inverse of AB is the product of the inverses of A and B in the reverse order. That is, (AB)−1=B−1A−1
- A가 invertible matrix이면 AT도 invertible
- AT : 대각 행렬을 중심으로 돌린 행렬
c. If A is an invertible matrix, then so is AT, and the inverse of AT is the transpose of A−1.That is,(AT)−1=(A−1)T
🔆 6. 기본 행렬 - Elementary Matrices
[참고 - 선형대수 : 03 선형대수학 - 2 : 소거법(elimination) 중 소거법]
- 가우스 소거법에서 행할 수 있는 기본 행 연산(elementary row operations)
- 0이 아닌 상수를 행에 곱할 수 있다. (scaling)
- 두 행을 교환할 수 있다. (interchange)
- 한 행을 상수배 하여 다른 행에 더할 수 있다. (replacement)
- 기본 행렬(elementary matrix)는 항등 행렬(identity matrix)에 단일 기본 행 연산(row operation)을 적용해서 얻어짐
Repalcement 적용한 행렬E1=⎣⎢⎡10−4010001⎦⎥⎤,Interchange 적용한 행렬E2=⎣⎢⎡010100001⎦⎥⎤,Scaling 적용한 행렬E3=⎣⎢⎡100010005⎦⎥⎤
A=⎣⎢⎡adgbehcfi⎦⎥⎤
- E1은 Replacement를 적용한 행렬
- E1A는 A에 Replacement를 적용한 것과 동일한 값 나옴
E1A=⎣⎢⎡10−4010001⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎡adgbehcfi⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡adg−4abeh−4bcfi−4c⎦⎥⎤
- E2는 Interchange를 적용한 행렬
- E3는 Scaling을 적용한 행렬
- A와 곱하면 A에도 행 연산을 적용한 결과가 나옴
E2A=⎣⎢⎡010100001⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎡adgbehcfi⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡dagebhfci⎦⎥⎤
E3A=⎣⎢⎡100010005⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎡adgbehcfi⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡ad5gbe5hcf5i⎦⎥⎤
- 알 수 있는 특성
-
[m × n] matrix에 elementary row operation을 수행했다는 것은
어떤 [m × m] elementary matrix가 존재한다는 의미
-
A에 적용한 row operation을 [m × m] indentity matrix에 적용하면 E가 생성
If an elementary row operation is performed on an m×n matrix A, the resulting matrix can be written as EA, where the m×m metrix E is created by performing the same row operation on Im.
-
elementary matrix E가 invertible이면 E의 inverse(역행렬)는 E를 I로 변환하는 elementary matrix(기본 행렬) 임
Each elementary matrix E is invertible.The inverse of E is the elementary matrix of the same typethat transforms E back into I.
E1=⎣⎢⎡10−4010001⎦⎥⎤,E1−1=⎣⎢⎡10+4010001⎦⎥⎤
E1E1−1=⎣⎢⎡10−4010001⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎡10+4010001⎦⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎡100010001⎦⎥⎤=I
🔆 7. 이론 7 - Theorem 7
An n×n matrix A is invertible if and only if A is row equivalent to In,and in this case, any sequence of elementary row operations that reduces A to In also transforms In into A−1
- A가 [n × n] invertible 행렬이면 A는 In과 행 상등(row equivalent)함
- A를 In으로 감소시키는 행 연산(row operation)은 In을 A−1로 변환
A∼E1A∼E2(E1A)∼⋯∼Ep(Ep−1⋯E1A)=In
Ep⋯E1A=In
(Ep⋯E1)−1(Ep⋯E1)AA=(Ep⋯E1)−1In=(Ep⋯E1)−1
A−1=[(Ep⋯E1)−1]=Ep⋯E1
🔆 8. A−1를 찾는 알고리즘 - Algorithm for Finding A−1
- A가 [m × n]이고 invertible이면 항등 행렬(identity matrix)를 이용해서 A−1를 찾을 수 있음
ALGORITHM FOR FINDING A−1Row reduce the augmented matrix [AI].If A is row equivalent to I, then [AI] is row equivalent to [IA−1].A does not have an inverse.
A=⎣⎢⎡01410−3238⎦⎥⎤
[AI]Interchange=⎣⎢⎢⎡01410−3238A100010001I⎦⎥⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡10401−3328010100001⎦⎥⎤ReplacementReplacement(1행×−4,1행+3행=new3행)(2행×3,2행+3행=new3행)∼⎣⎢⎡10001−332−401010−4001⎦⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎡10001032201310−4001⎦⎥⎤Scaling(3행÷2)∼⎣⎢⎡100010321013/210−2001/2⎦⎥⎤Replacement(3행×−3,3행+1행=new1행)(3행×−2,3행+2행=new2행)∼⎣⎢⎢⎡100010001I−9/2−23/274−2−3/2−11/2A−1⎦⎥⎥⎤=[IA−1]
이 방법은 4 × 4부터 굉장히 복잡하여 손으로 구하는건 거의 불가능
📖 역행렬의 특징
🔆 1. 이론 8. 역행렬 이론 - Theorem 8. The Invertible Matrix Theorem
- A가 invertible이면 다음 조건을 다 만족하고, not invertible이면 다음 조건을 만족하지 않음
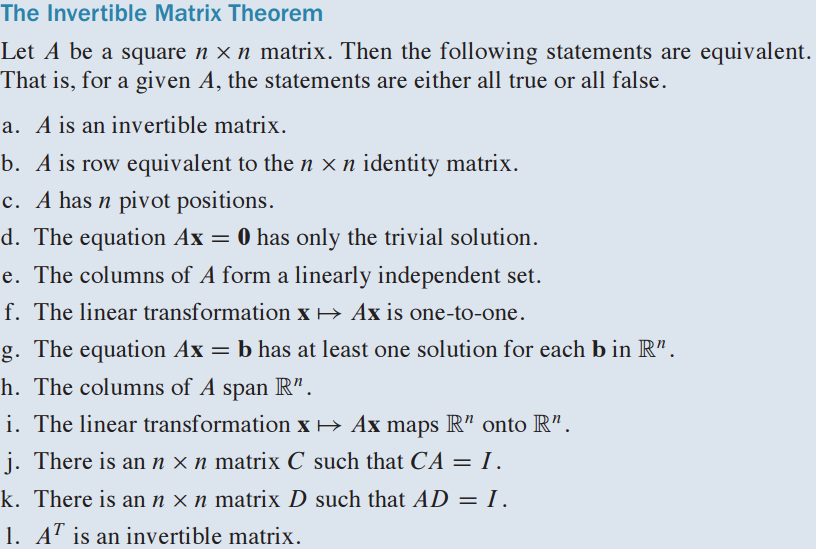
- Ax=0은 trivial solution만을 갖으므로 independent, n pivot position을 만족
- n개의 pivot position을 만족하므로 one-to-one도 성립
- A는 solution이 있으므로 A는 R공간에 span하고, onto도 성립
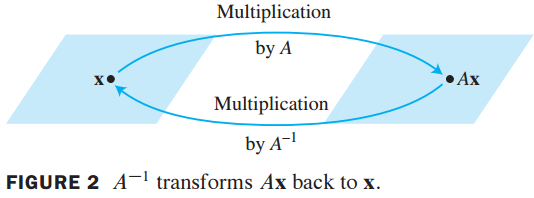
- linear Transformation이 invertible이라고 불릴 조건은 다음과 같음
A linear transformation T:Rn→Rn is said to be invertible if there exists a function S:Rn→Rn such that(1)S(T(x))=xfor all x in Rn(2)T(S(x))=xfor all x in Rn
- x의 image에 S 함수를 위하면 원래 x로 돌아옴
- S 함수가 존재하는 경우에 T는 invertible하다고 함
🔆 3. 이론 9 - Theorem 9
- 선형 변환(linear transformation)은 항상 표준 행렬(standard matrix)이 존재
- T가 invertible이면 A(standard matrix)도 invertible 함
- 또, 선형 변환(linear transformation) S함수는S(x)=A−1x로 주어짐
Let T:Rn→Rn be a linear transformation and let A be the standard matrix for T.Then T is invertible if and only if A is an invertible matrix.In that case, the linear transformation S given by S(x)=A−1x is the unique function satisfying equations (1) and (2) 

