❇️ 요약
- LU 분해(LU decomposition)
- LU 분해 공식
📖 LU 분해(LU decomposition)
🔆 1. 분해 - Factorization, decomposition
- 분해는 하나의 행렬을 2개 혹은 3개 이상의 행렬 곱으로 표현한 식을 의미
- A 행렬을 B와 C의 곱으로 표현했는데 이런 형태를 분해(factorization)이라고 함
🔆 2. LU 분해 - LU decomposition
Ax=b1,Ax=b2,⋯,Ax=bp
-
A의 역행렬을 이용
- A−1b1,A−1b2 모든 경우를 구해야 하므로 비효율적임
-
LU 분해⭐⭐⭐
- 행 줄임(row reduction)으로 A를 LU분해하여 방정식을 푸는 것이 효과적
A=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡1∗∗∗01∗∗001∗0001⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡■000∗■00∗∗00∗∗■0∗∗∗0⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤LUFIGURE 1An LU factorization
- L은 a unit triangular matrix(하삼각행렬)를 의미
- U는 echelon form(행사다리꼴)을 의미
- ❗주의할 점 : U는 reduced echelon form이 아님
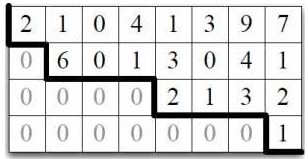
echelon form(행사다리꼴)이란?
⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡■000∗■00∗∗00∗∗■0∗∗∗0⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤
- 한 matrix의 대각선을 기준으로 위쪽에 0이 아닌 값들이 존재하고 그 아래는 모두 0이어서 값이 있는 곳들을 보면 사다리꼴 모양인 matrix
- ■표시된 부분은 0이 아닌 값이 열을 기준으로 처음 나오는 값
- 이 ■를 포함하는 열(column)을 leading entry
- * 또한 0이 아닌 값
특징
- row를 기준으로 모든 element가 0인 row는 모든 element가 0이 아닌 row보다 아래에 있어야 한다.
- 각각의 leading entry들은 위의 row의 leading entry보다 오른쪽에 위치해야 한다.
- 각각의 leading entry column은 ∎아래의 element는 0이어야 한다.
여기서 leading entry에서 column의 첫번째 값을 제외하고는 0이 되어야 함
그리고 첫번째 값이 1이 되어야 함. 그래야 우리가 해석하기가 쉬워짐
-
A를 분해해서 U로 변환할 때 row interchange, scaling 없이 replacement만을 이용해서 변환 해야함
-
L은 diagonal term이 모두 1이고 아래는 nonzero entry인 행렬임
-
nonzero entry에 zero가 들어가도 상관 없음
-
diagonal term이 모두 1이어야만 하는 이유 : 대각선이 1이 아니면 너무 다양하기 때문
🔆 3. LU 분해의 유용성
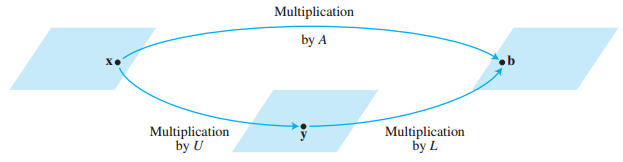
- A=LU로 분해하였을 때 Ax=b 방정식을 다음과 같이 표현 가능
A=LUAx=b
- Ux=y로 치환하여 대입 → Ly=b에서 y를 품
- Ux=y, U와 y를 알고있으므로 x를 풀 수 있음
LUx=bLy=b
- L과 U는 pivot을 사용해서 나머지 entry를 0으로 만들 수 있는 쉬운 형태로 이루어져 있기 때문에 빠르게 문제를 풀 수 있다.
🔆 4. LU 분해 예시 문제
[참고 - 선형대수 : 02 행렬 - 3 : 기타 특수 행렬 중 삼각행렬]
- A=LU→Ax=b→LUx=b→Ux=y(치환)→Ly=b→Ux=y→x의해를찾음
A=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡3−36−9−75−45−210−520−512⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡1−12−301−5800130001⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡3000−7−200−2−1−10221−1⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤=LU
Ax=b,where b=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡−95711⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤
Ux=yLUx⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡1−12−301−5800130001⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡3000−7−200−2−1−10221−1⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡x1x2x3x4⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤b=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡−95711⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤
- A와 b가 주어졌을 때 우선 Ly=b로 y를 구한다.
[Lb]=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎛⎣⎢⎡L⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡y1y2y3y4⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡−95711⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤⎠⎟⎟⎟⎞=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡1−12−301−5800130001−95711⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡1000010000100001−9−451⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤=[Iy]
y=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡−9−451⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤
- Ux=y에서 U와 y를 알고 있으므로 x를 구할 수 있다.
[Uy]=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎛⎣⎢⎡U⎦⎥⎤⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡x1x2x3x4⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡−9−451⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤⎠⎟⎟⎟⎞=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡3000−7−200−2−1−10221−1−9−451⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤∼⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡100001000010000134−6−1⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤
x=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎡34−6−1⎦⎥⎥⎥⎤
이처럼 L과 U를 알고 있으면 해를 구하기가 쉽다.
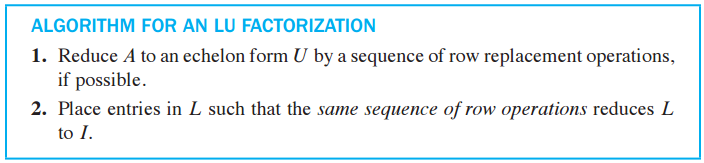
🔆 5. LU 구하는 방법 - LU decomposition Algorithm
- A가 row replacement만을 사용해서 사다리 꼴(echelon form) 형태로 변환될 수 있다고 가정
- U(echelon form)로 변환하기 위한 행 줄임(row operation) 기본 행렬(elementary matrix) E1,⋯,Ep가 존재
- 이 기본 행렬의 역행렬(inverse)이 L이 됨
- A가 m × n 행렬일 때 L과 U의 크기는 m × m, m × n이 되어야 함
Ep⋯E1A=UA=(Ep⋯E1)−1U=LUL=(Ep⋯E1)−1
[4633]=[1l2101][u110u12u22]
1⋅u11+0⋅01⋅u12+0⋅u22l21⋅u11+1⋅0l21⋅u12+1⋅u22=4=3=4=3l21u11u11u11=1.5=4=3=−1.5[4633]=[11.501][403−1.5]
🔆 6. 수와 관련된 메모 - Numerical Notes

- A−1로 해를 구했을 때 보다 LU 분해의 연산량이 1/3배 적음
- 또한 A가 sparse(대부분이 0으로 채워져있는 경우)하면 L과 U도 sparse 함
- 하지만 A−1는 dense(값이 많은 경우) 함
- 이 의미는 L과 U를 저장하는 memory와 A−1 값을 저장하는 memory의 차이가 큰 것을 의미
- 공학적인 문제를 풀 때 LU 분해는 속도와 메모리적 측면에서 큰 이점을 얻을 수 있음




