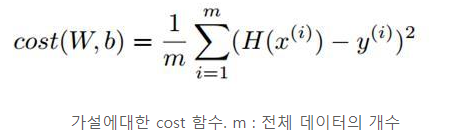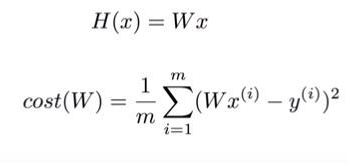
📊 Linear Regression
가장 기본이라고 할 수 있는 Linear Regression(선형 회귀분석)을 학습해보려 한다.
📚 위키백과
통계학에서, 선형 회귀(線型回歸, 영어: linear regression)는 종속 변수 y와 한 개 이상의 독립 변수 (또는 설명 변수) X와의 선형 상관 관계를 모델링하는 회귀분석 기법이다. 한 개의 설명 변수에 기반한 경우에는 단순 선형 회귀
- 간단하게 말하자면 주어진 데이터를 기반으로 모델을 생성하여 새로운 값이 들어왔을때 결과값을 예측하는 지도학습 예측 알고리즘.
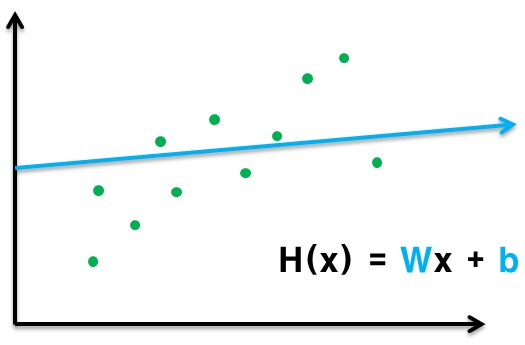
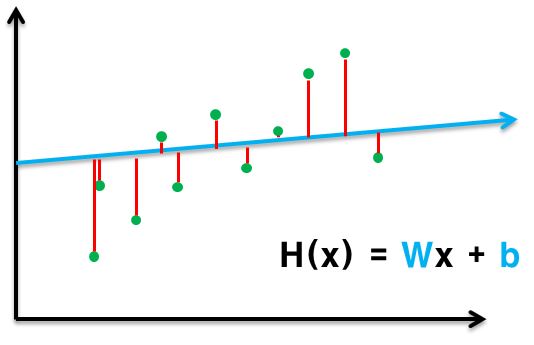
- "데이터를 반복적으로 관찰하면 어떤 패턴으로 회귀한다"는 것을 의미. 선형 회귀는 이 패턴이 직선의 모습을 하고 있는데 'y = wx + b'라는 1차 방정식으로 표현
🕵 그래서 무엇을 해야하는가?
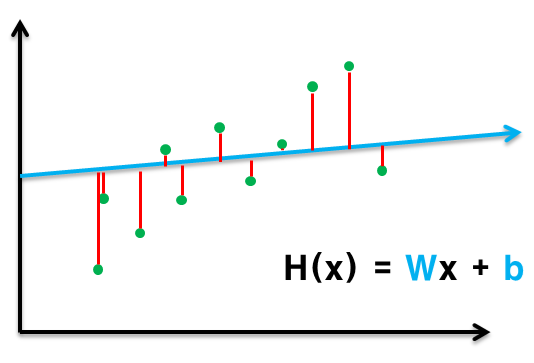
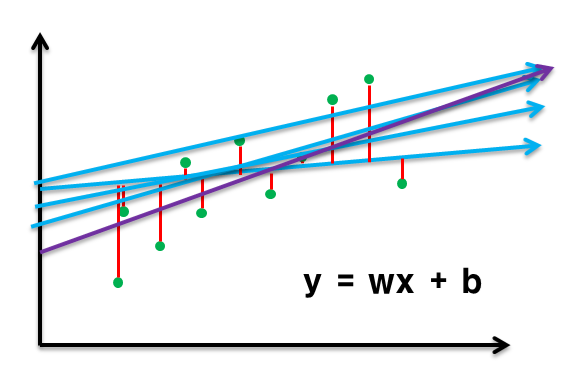
선을 바꿔가면서 최소의 손실 값을 가지는 선을 찾으면 된다.
제곱을 하여 절대값 구하고, (양수, 음수 차이 제거)
계산을 쉽게 해보기 위해 식을 간단하게 바꾼 뒤(B 제거)
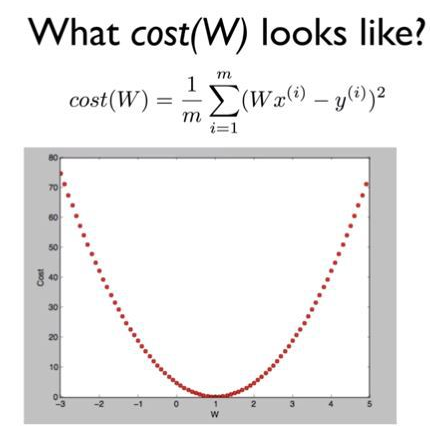
W에 2를 넣으면 4.67를 구할 수 있고, 이렇게 값을 쭉 넣다보면 밑에 그림처럼
이차함수를 얻을 수있다.
최종 목표
cost 최소 값 즉 0에 대한 W = 1를 구하는 것 !
🧐 무엇을 만들것인가?
나무의 높이를 예측해보자.
기본 공식 H(x) = Wx + b
- 나무를 심었다. (약 200cm)
- 20일 동안 100번 높이를 체크한다.
- 그때까지의 좌표를 가지고 학습을 시키고 가중치 값을 구한다. (w, b)
- w, b를 구했으니 60일 뒤에는 어느정도의 높이가 될 지 파악해본다.
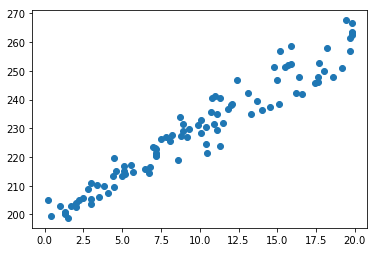

학습 결과 W = 3.11 b = 198.64
즉 H(x) = 3.11x + 198.64가 나왔고, x에 60(60일)을 대입하게 되면
3.11 * 60 + 198.64 = 385.24(cm)
나무의 60일 후의 높이는 385.24로 예측해볼 수 있다.
예제 소스
# 모듈 로드
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 데이터 시각화
plt.scatter(x, y, label="input data set")
# 선형 모델 클래스
class LinearModel:
def __call__(self, x):
return self.Weight * x + self.Bias
def __init__(self):
self.Weight = tf.Variable(0.)
self.Bias = tf.Variable(0.)
# 오차(손실) 구하기 함수
def loss(y, pred):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - pred))
# 학습 함수
def train(linear_model, x, y, lr):
with tf.GradientTape() as t:
current_loss = loss(y, linear_model(x))
lr_weight, lr_bias = t.gradient(current_loss, [linear_model.Weight, linear_model.Bias])
linear_model.Weight.assign_sub(lr * lr_weight)
linear_model.Bias.assign_sub(lr * lr_bias)
# 학습 진행
linear_model = LinearModel()
epochs = 10000
for epoch_count in range(epochs + 1):
real_loss = loss(y, linear_model(x))
train(linear_model, x, y, lr=0.003)
if epoch_count % 100 == 0:
print(f"{epoch_count}:: W:{linear_model.Weight.numpy()} b:{linear_model.Bias.numpy()} Loss: {real_loss.numpy()} ")출처 및 참조 :
https://www.yalco.kr/34_tensorflow/
https://doorbw.tistory.com/97