Machine Learning and Deep Learning
1.[ML&DL] 1. Statistical Learning

Statistical Learning? > `Predict target data using Observation or Given Data` $$ \textcolor{blue}{Sales} = f(TV, Radio, Newspaper) $$ $$\textcolor{blue}{Sales}$$ : `Target Variable, Response Variable...
2.[ML&DL] 2. Linear regression
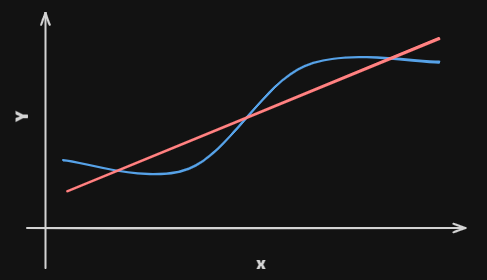
Linear regression is a simple approach to supervised learning. It assumes that the dependence of $Y$ on $X_1, X_2, \\cdots , X_p$ is linear.True regre
3.[ML&DL] 3. Classification

Classification Qualitative variables take values in an unordered set $C$, such as $$ \text{eye color}\in\{\text{{brown, blue, green}}\}\\ \text{email}
4.[ML&DL] 4. Resampling Methods
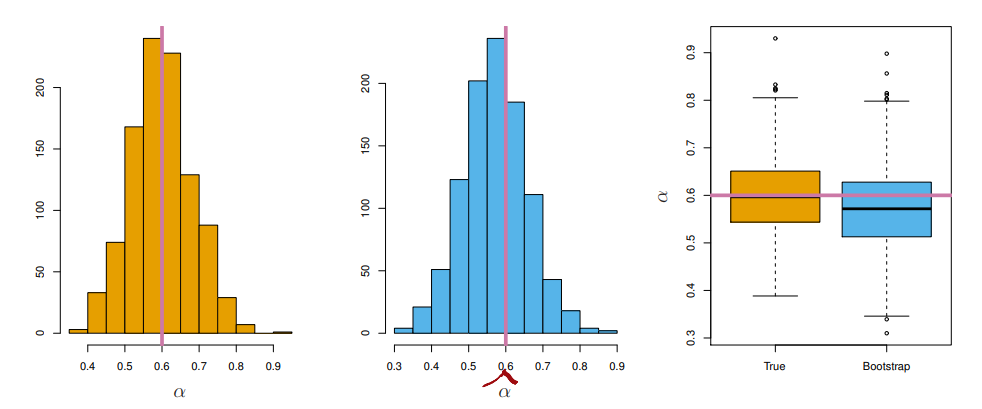
Cross-validation and the Bootstrap In the section we discuss two resampling methods Cross-validation Bootstrap These methods refit a model of inte
5.[ML&DL] 5. Moving Beyond Linearity
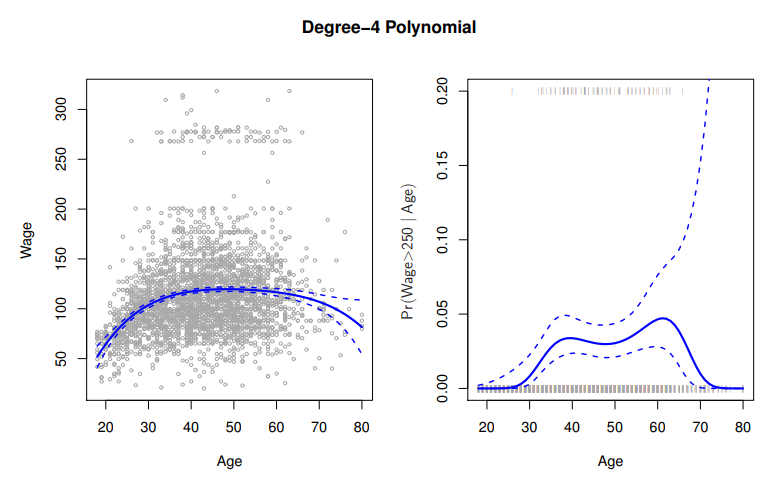
Often the linearity assumption is good enoughWhen its not...PolynomialsStep functionsSplinesLocal regressionGeneralized additive modelsOffer a lot of
6.[ML&DL] 6. Tree Based Methods
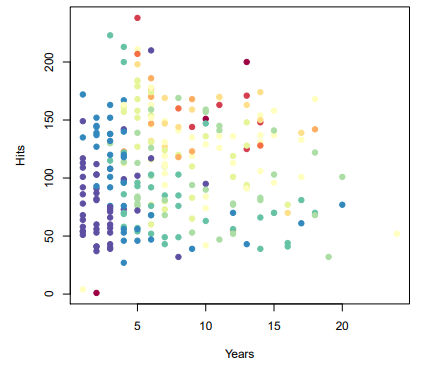
Here we describe tree-based methods for regression and classificationThese involve stratifying or segmenting the predictor space into a number of simp
7.[ML&DL] 7. Multiple Hypothesis Testing
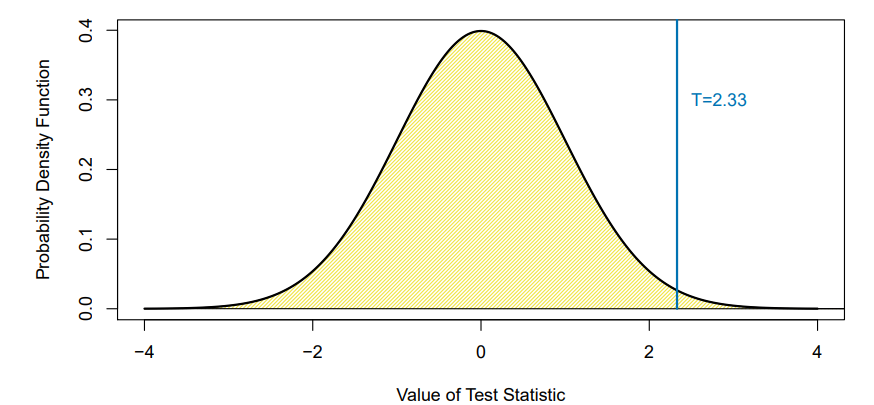
This session focuses on multiple hypothesis testingA single null hypothesis might look like$\\mathcal{H}\_0$ : the expected blood pressures of mice in
8.[ML&DL] 8. Support Vector Machines
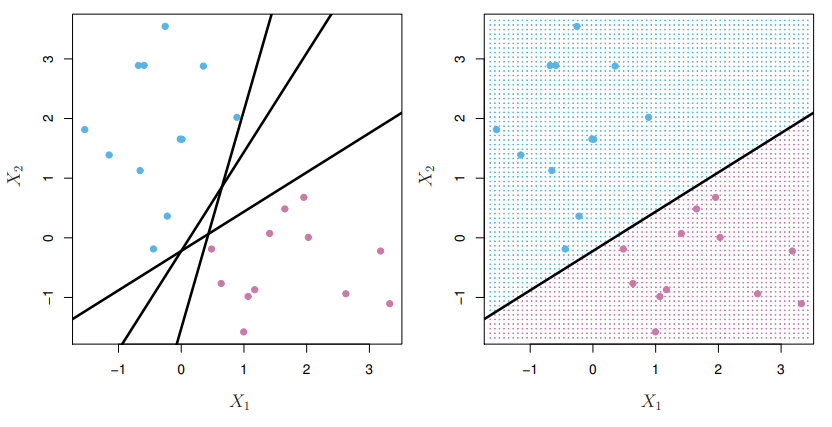
Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way :We try and find a plane that seperates the classes in feature spaceIf we cannot
9.[ML&DL] 9. Survival Analysis
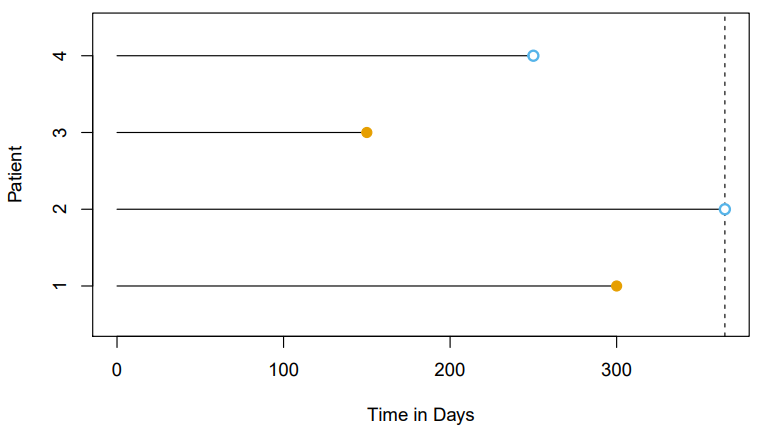
Survival analysis concerns a special kind of outcome variable : the time until an event occursFor example, suppose that we have conducted a five-year
10.[ML&DL] 10. Unsupervised Learning
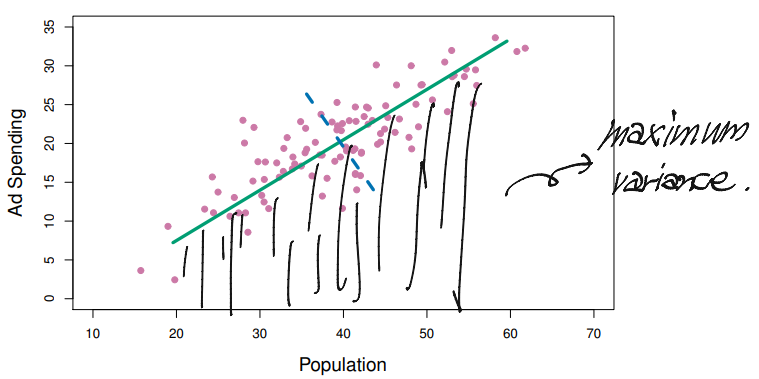
Most of this course focuses on supervised learning methods such as regression and classificationIn that setting we observe obth a set of features $X_1
11.[ML&DL] 11. Deep Learning
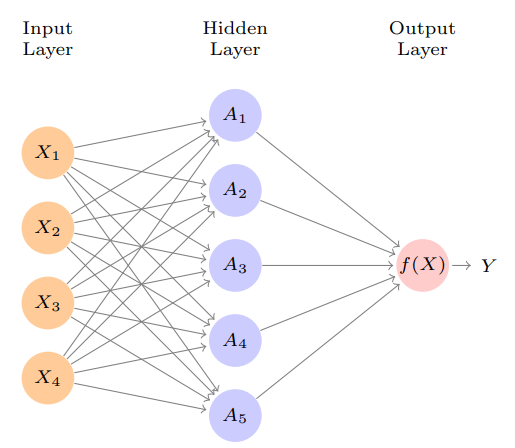
$$f(X)=\\beta0+\\sum^K{k=1}\\betakh_k(X)\\0.2cm=\\beta_0+\\sum^K{k=1}\\betak g(w{k0}+\\sum^p{j=1}w{kj}X_j)$$$Ak=h_k(X)=g(w{k0}+\\sum^p{j=1} w{kj}X_j)$